Elasticsearch基本操作
Posted ITLepeng
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Elasticsearch基本操作相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.使用kibana对索引库操作
①创建索引库
PUT /lepeng
②查看索引库
GET /lepeng
③删除索引库
DELETE /lepeng
2.使用kibana对类型及映射操作
有了
索引库,等于有了数据库中的database。接下来就需要创建数据库中的表。创建数据库表需要设置字段约束,索引库也一样,在创建索引库的类型时,需要知道这个类型下有哪些字段,每个字段有哪些约束信息,这就叫做字段映射(mapping)
①Elasticsearch支持的数据类型:
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/mapping-types.html
-
String类型,又分两种:
- text:可分词,不可参与聚合
- keyword:不可分词,数据会作为完整字段进行匹配,可以参与聚合
-
Numerical:数值类型,分两类
- 基本数据类型:long、interger、short、byte、double、float、half_float
- 浮点数的高精度类型:scaled_float
- 需要指定一个精度因子,比如10或100。elasticsearch会把真实值乘以这个因子后存储,取出时再还原。
-
Date:日期类型
elasticsearch可以对日期格式化为字符串存储,但是建议我们存储为毫秒值,存储为long,节省空间。
-
Array:数组类型
- 进行匹配时,任意一个元素满足,都认为满足
- 排序时,如果升序则用数组中的最小值来排序,如果降序则用数组中的最大值来排序
-
Object:对象
{
name:"Jack",
age:21,
girl:{
name: "Rose",
age:21
}
}
如果存储到索引库的是对象类型,例如上面的girl,会把girl编程两个字段:girl.name和girl.age
②创建字段映射
index的默认值就是true,也就是说你不进行任何配置,所有字段都会被索引。
但是有些字段是我们不希望被索引的,比如商品的图片信息,就需要手动设置index为false。
#ik_max_word 将文本做最细粒度的拆分
#ik_smart 会做最粗粒度的拆分
PUT /lepeng/_mapping/
{
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"images": {
"type": "keyword",
"index": "false"
},
"price": {
"type": "float"
}
}
}
③一次创建索引库和类型
settings 就是索引库设置,其中可以定义索引库的各种属性,可以不设置,都走默认。
put /lepengA
{
"settings":{
"索引库属性名":"索引库属性值"
},
"mappings":{
"properties":{
"字段名":{
"映射属性名":"映射属性值"
}
}
}
}
例如:
PUT /lepeng1
{
"settings": {},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
可以查看lepeng1索引库:
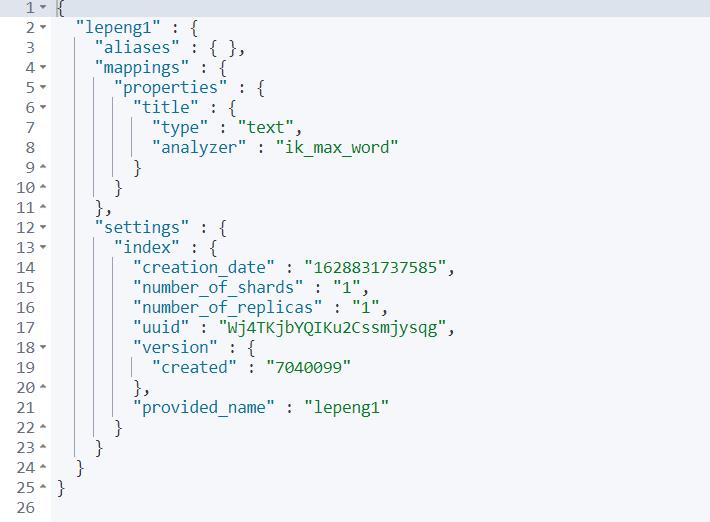
3.使用kibana对文档操作
对比于数据库,就是添加表中数据
①新增文档
POST /索引库名/_doc
{
"key":"value"
}
POST /lepeng/_doc
{
"title": "xiaomi",
"images": "images/1.jpg",
"price": 265.00
}
新增文档的时候会对这个数据生成一个随机的id
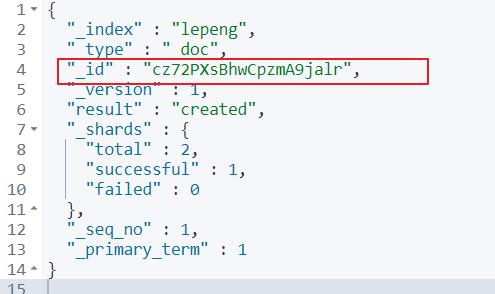
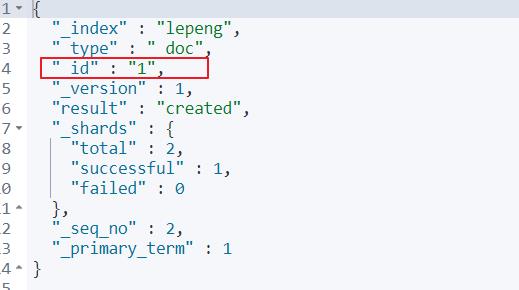
当然也可以自己指定一个id添加
POST /lepeng/_doc/1
{
"title": "redmi",
"images": "images/2.jpg",
"price": 670.00,
"stock": 20
}
②查看指定文档
GET /heima/_doc/id值
GET /lepeng/_doc/1
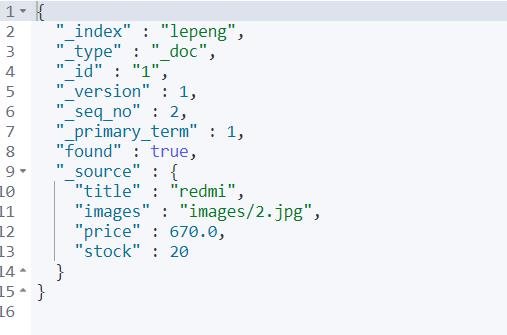
③更改文档
POST /lepeng/_doc/1
{
"title": "redmi",
"images": "images/2.jpg",
"price": 770.00
}
如果指定id不存在,就是添加,如果指定id存在就是更改
id不存在情况:
id存在时
④删除文档
DELETE /索引库名/_doc/id值
4.智能判断
①新增文档 添加索引库未被配置字段
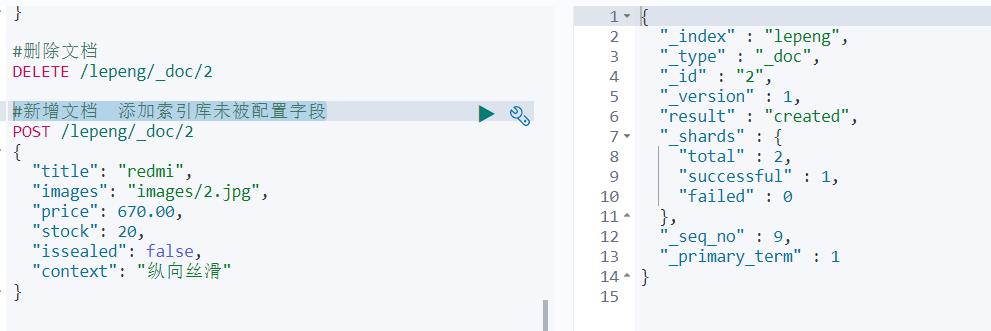
可见创建成功,然后看一下映射字段
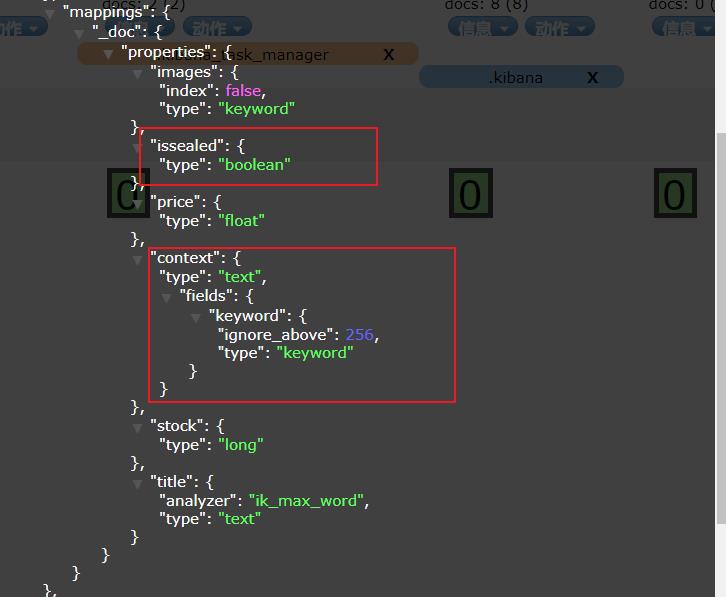
可以发现issealed被智能判断为Boolean类型,但是仔context是String类型数据,ES无法智能判断,它就会存入两种映射类型。例如:
- context:text类型
- context.keyword:keyword类型
出现这种情况的原因是,智能映射底层是根据一个指定的模板规则映射的,映射规则如下:
| JSON 类型 | Elasticsearch 类型 |
|---|---|
null | 不添加 |
true or false | boolean |
| floating point number | float |
| integer | long |
| string | text , 附带一个 keyword 子域 |
这种智能映射,底层原理是动态模板映射,如果我们想修改这种智能映射的规则,其实只要修改动态模板即可!
②修改智能映射模板的语法
"dynamic_templates": [
{
"my_template_name": {
... match conditions ...
"mapping": { ... }
}
},
...
]
说明:
-
my_template_name:自定义模板名称
-
match conditions:匹配条件,凡是符合条件的未定义字段,都会按照这个规则来映射
-
mapping:映射规则,匹配成功后的映射规则
示例:
PUT /lepeng2
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text"
},
"images": {
"type": "keyword",
"index": false
},
"price": {
"type": "float"
}
},
"dynamic_templates": [
{
"my_strings": {
"match_mapping_type": "string",
"mapping": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
]
}
}
然后再存入数据:
POST /lepeng2/_doc/1
{
"title": "redmi",
"images": "images/2.jpg",
"price": 670.00,
"stock": 20,
"issealed": false,
"context": "纵向丝滑"
}
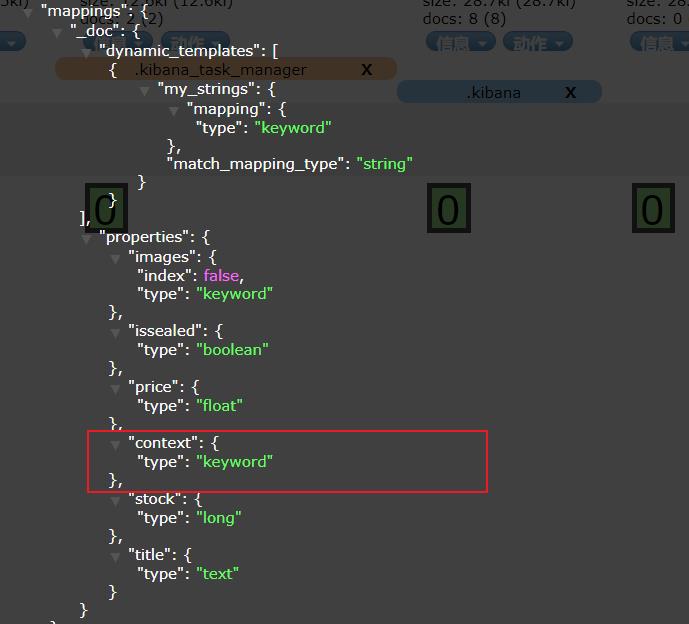
可以看到context被映射成了keyword,而非之前的text和keyword并存,说明我们的动态模板生效了!
5.基本查询
准备数据:
# 创建产品索引库,然后对title进行ik分词
PUT /product
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"images": {
"type": "keyword",
"index": "false"
},
"price": {
"type": "float"
}
}
}
}
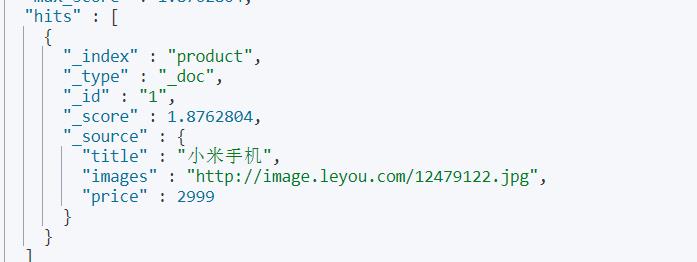
# 插入数据
POST product/_doc/1
{
"title": "小米手机",
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 2999
}
POST product/_doc/2
{
"title": "华为手机",
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 3999
}
POST product/_doc/3
{
"title": "苹果手机",
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 4999
}
POST product/_doc/4
{
"title": "小米笔记本",
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 5999
}
POST product/_doc/5
{
"title": "联想笔记本",
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 9000
}
POST product/_doc/6
{
"title": "apple",
"images": "http://image.leyou.com/12479122.jpg",
"price": 9000
}
①查询所有
GET /product/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {
}
}
}
②匹配查询
GET product/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "小米手机"
}
}
}
因为title采用了text类型,查询时会对搜索关键词进行分词,分为小米和手机,然后使用两个词分别做检索,最后将结果取并集

某些情况下,我们需要取分词检索结果的交集,此时使用"operator":"and"选项实现
GET product/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": {
"query": "小米手机", "operator": "and"
}
}
}
}
③词条匹配
term查询被用于精确值匹配,这些精确值可能是数字、时间、布尔或者那些未分词的字符串
GET product/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"price": {
"value": "2999"
}
}
}
}
④范围查询
range查询找出那些落在指定区间内的数字或者时间
range查询允许以下字符:
| 操作符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| gt | 大于 |
| gte | 大于等于 |
| lt | 小于 |
| lte | 小于等于 |
GET product/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"price": {
"gte": 2999,
"lt": 4999
}
}
}
}

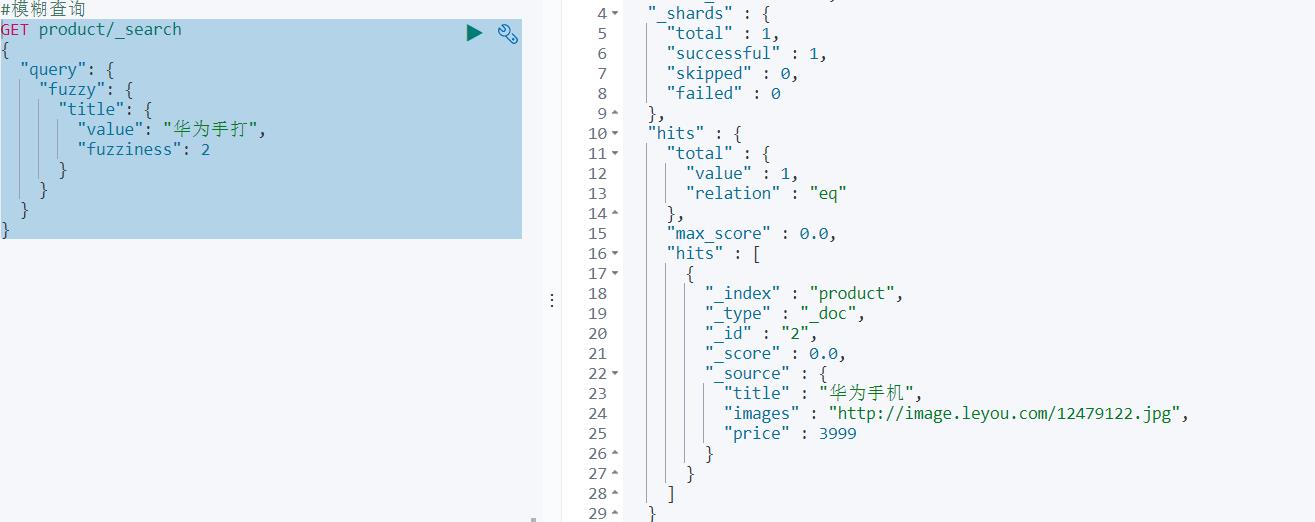
⑤模糊查询
fuzzy查询是term查询的模糊等价。它允许用户搜索词条与实际词条的拼写出现偏差
fuzziness表示偏差距离,如果为0,就成了词条匹配
GET product/_search
{
"query": {
"fuzzy": {
"title": {
"value": "华为手打",
"fuzziness": 2
}
}
}
}
⑥布尔组合(bool)
ool
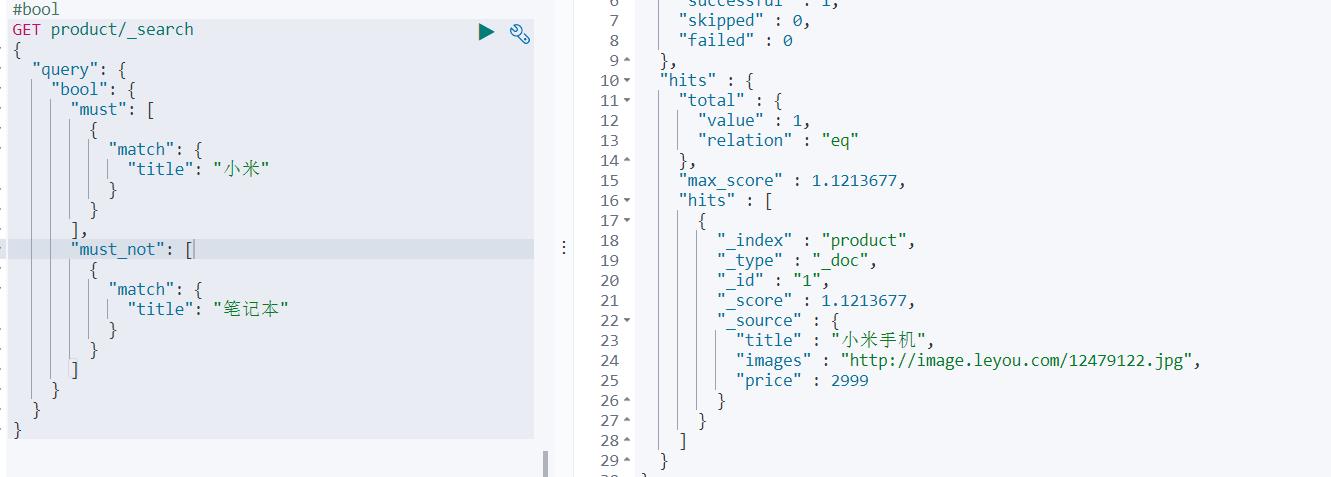
把各种其它查询通过must(与)、must_not(非)、should`(或)的方式进行组合
GET product/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"title": "小米"
}
}
],
"must_not": [
{
"match": {
"title": "笔记本"
}
}
]
}
}
}
⑦结果过滤
直接指定返回字段
指定要返回的字段,过滤掉非指定字段
GET product/_search
{
"_source": {
"includes": ["title","price"]
},
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
指定包含和排除
通过includes来指定想要显示的字段,通过excludes来指定不想要显示的字段,二者可选一个使用
GET product/_search
{
"_source": {
"excludes": "images"
},
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
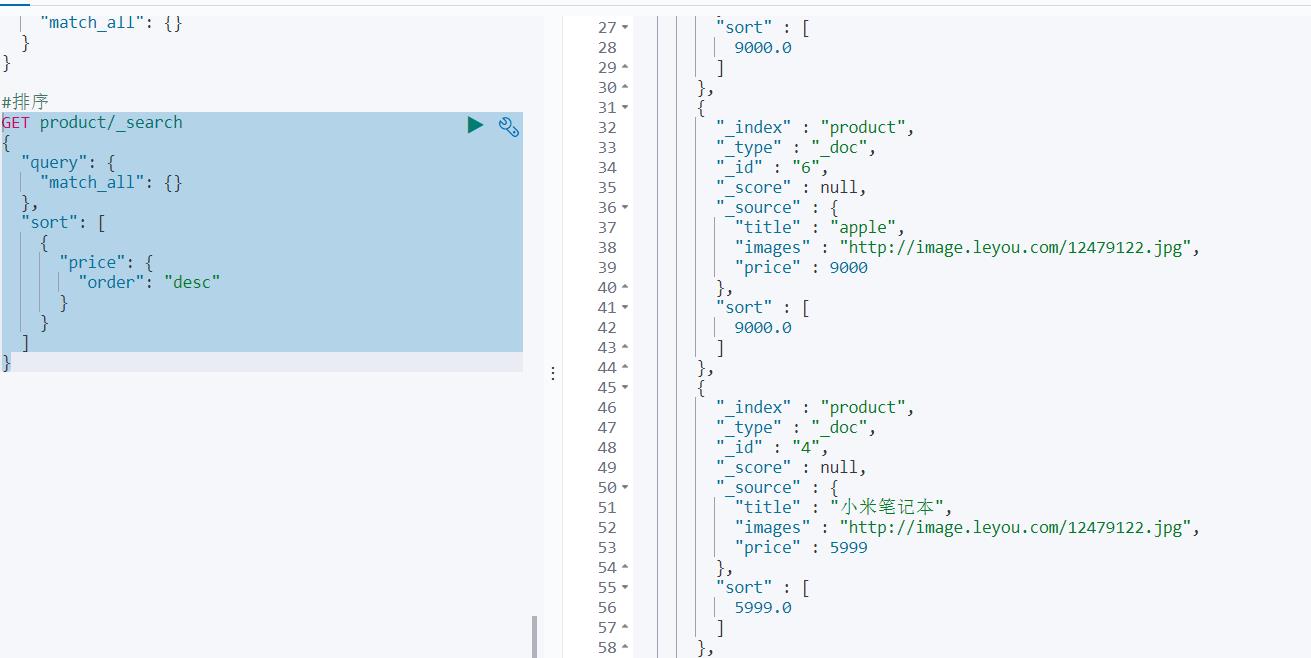
⑧排序
单字段排序
sort可以让我们按照不同的字段进行排序,并且通过order指定排序的方式
GET product/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"sort": [
{
"price": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
]
}
多字段排序
假定我们想要结合使用 price和 _score(得分) 进行查询,并且匹配的结果首先按照相关性得分排序,然后按照价格排序
GET product/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"sort": [
{
"_score": {
"order": "desc"
}
},
{
"price": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
]
}
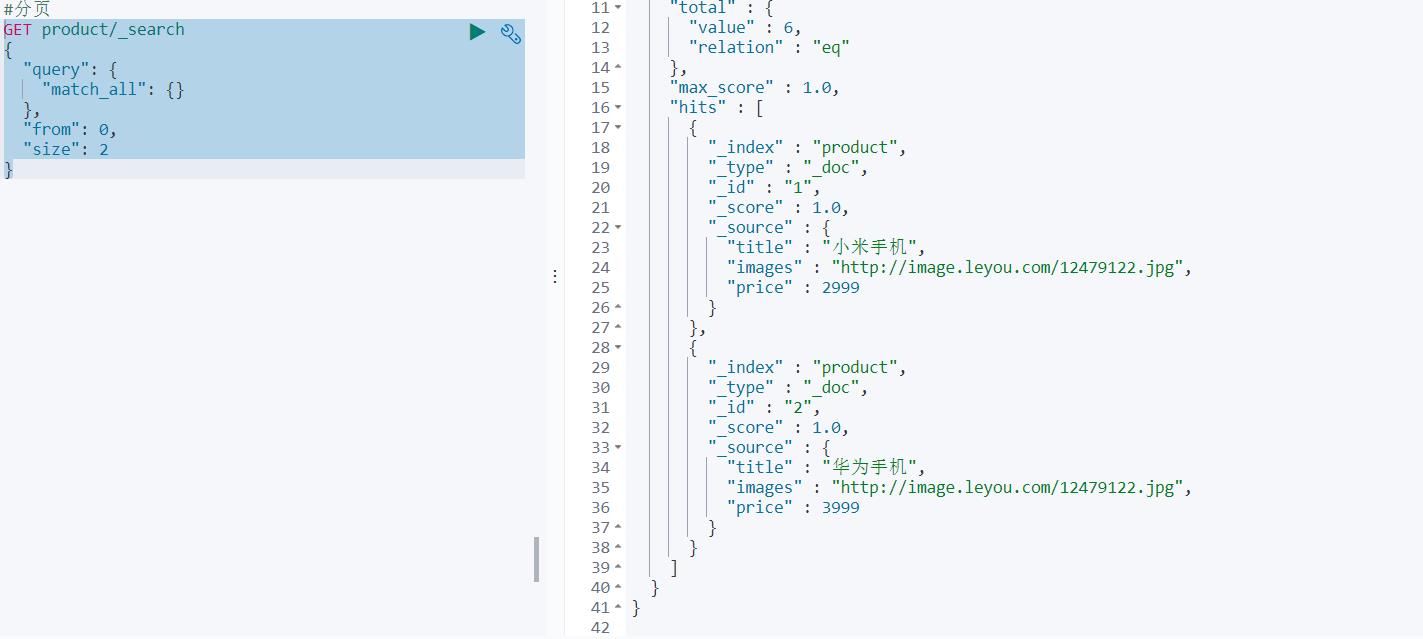
⑨分页
分页
elasticsearch的分页与mysql数据库非常相似,都是指定两个值
- from:开始位置
- size:每页大小
GET product/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"from": 0,
"size": 2
}
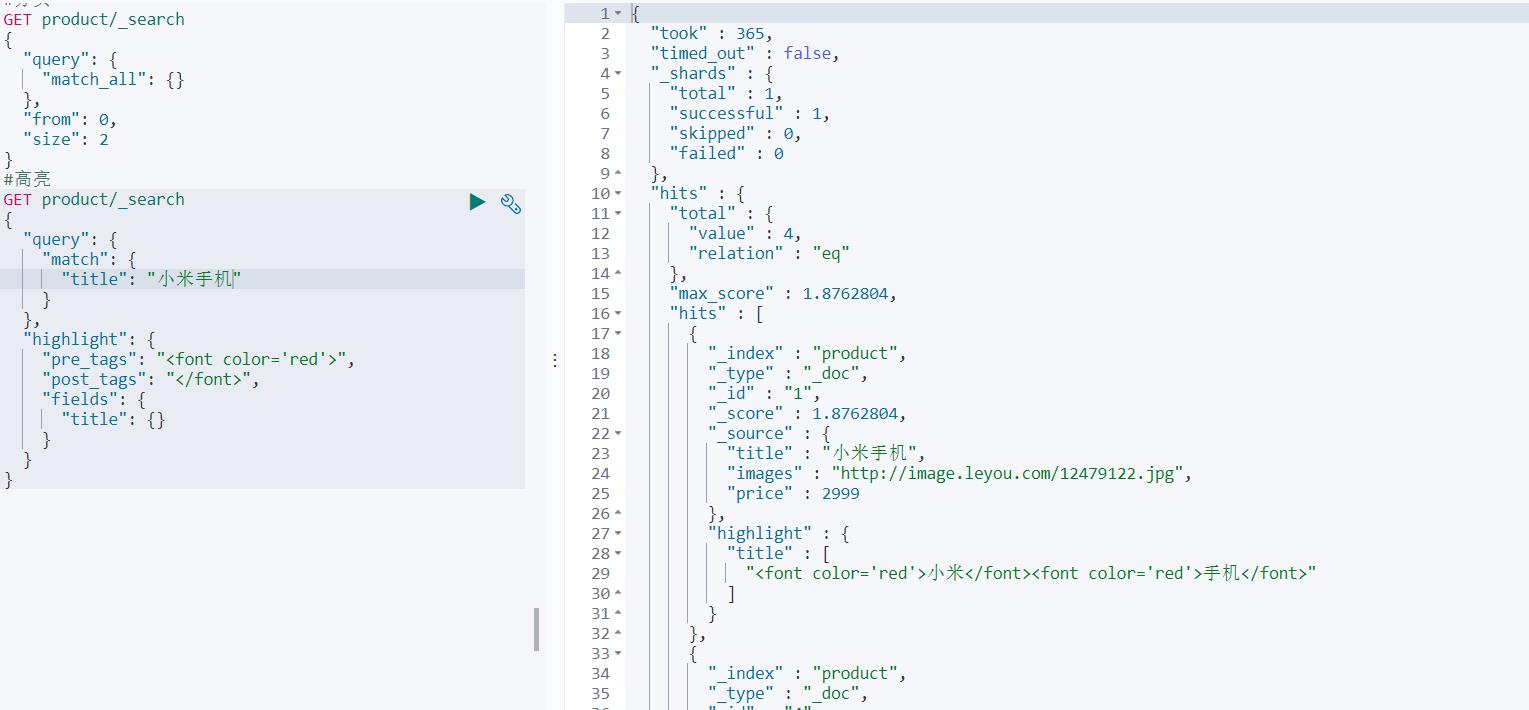
⑩高亮
在使用match查询的同时,加上一个highlight属性:
- pre_tags:前置标签
- post_tags:后置标签
- fields:需要高亮的字段
- title:这里声明title字段需要高亮,后面可以为这个字段设置特有配置,也可以空
GET product/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "小米手机"
}
},
"highlight": {
"pre_tags": "<font color='red'>",
"post_tags": "</font>",
"fields": {
"title": {}
}
}
}
6.分组聚合查询
基本概念
在我们的mysql有这么两类函数:
- 分组函数: group by
- 聚合函数: sum、avg、max、min
使用它们可以轻松实现对数据的统计分析,其实在ES中也存在类似的用法,只不过名字略有差异,称为桶和度量
桶(bucket)
桶的作用,是按照某种方式对数据进行分组,每一组数据在ES中称为一个桶,ES中提供的划分桶的方式有很多:
- Date Histogram Aggregation:根据日期阶梯分组,例如给定阶梯为周,会自动每周分为一组
- Histogram Aggregation:根据数值阶梯分组,与日期类似,需要知道分组的间隔(interval)
- Terms Aggregation:根据词条内容分组,词条内容完全匹配的为一组
- Range Aggregation:数值和日期的范围分组,指定开始和结束,然后按段分组
- ……
度量(metrics)
分组完成以后,我们一般会对组中的数据进行聚合运算,例如求平均值、最大、最小、求和等,这些在ES中称为度量
比较常用的一些度量聚合方式:
- Avg Aggregation:求平均值
- Max Aggregation:求最大值
- Min Aggregation:求最小值
- Percentiles Aggregation:求百分比
- Stats Aggregation:同时返回avg、max、min、sum、count等
- Sum Aggregation:求和
- Top hits Aggregation:求前几
- Value Count Aggregation:求总数
- ……
测试数据
# 在ES中,需要进行聚合、排序、过滤的字段其处理方式比较特殊,因此不能被分词,必须使用keyword或数值类型。
PUT /car
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"color": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"make": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
# 导入数据
POST /car/_bulk
{ "index": {}}
{ "price" : 10000, "color" : "红", "make" : "本田", "sold" : "2014-10-28" }
{ "index": {}}
{ "price" : 20000, "color" : "红", "make" : "本田", "sold" : "2014-11-05" }
{ "index": {}}
{ "price" : 30000, "color" : "绿", "make" : "福特", "sold" : "2014-05-18" }
{ "index": {}}
{ "price" : 15000, "color" : "蓝", "make" : "丰田", "sold" : "2014-07-02" }
{ "index": {}}
{ "price" : 12000, "color" : "绿", "make" : "丰田", "sold" : "2014-08-19" }
{ "index": {}}
{ "price" : 20000, "color" : "红", "make" : "本田", "sold" : "2014-11-05" }
{ "index": {}}
{ "price" : 80000, "color" : "红", "make" : "宝马", "sold" : "2014-01-01" }
{ "index": {}}
{ "price" : 25000, "color" : "蓝", "make" : "福特", "sold" : "2014-02-12" }
聚合为桶
汽车的颜色color来划分桶,按照颜色分桶,最好是使用TermAggregation类型,按照颜色的名称来分桶
GET car/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"aggs_color": {
"terms": {
"field": "color"
}
}
}
}
- aggs:声明这是一个聚合查询,是aggregations的缩写
- aggs_color:给这次聚合起一个名字,可任意指定。
- terms:聚合的类型,这里选择terms,是根据词条内容(这里是颜色)划分
- field:划分桶时依赖的字段

桶内度量
每种颜色汽车的平均价格是多少?
我们需要告诉ES使用哪个字段,使用何种度量方式进行运算,这些信息要嵌套在桶内,度量的运算会基于桶内的文档进行
GET car/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"aggs_color": {
"terms": {
"field": "color",
"size": 10
},
"aggs": {
"price_avg": {
"avg": {
"field": "price"
}
}
}
}
}
以上是关于Elasticsearch基本操作的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
使用标准库Ruby将数据标记到Elasticsearch批量中