顺序表的基本实现
Posted 雨轩(小宇)
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了顺序表的基本实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1、头文件
-
我这里主要说的是动态的顺序表,当然静态顺序表的操作基本上是一样的,只是静态顺序表无法进行增容,数量是控制了的,会造成空间的浪费。
-
静态顺序表
#pragma once //防止头文件包含
#include<stdio.h>
#define MaxSize 100
typedef int SLDataType;
//利用typedef给int重命名为SLDataType,为以后改变数据类型提供方便
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDataType arr[MaxSize];
size_t size;//size_t -> unsigned int
}SeqList;
- 动态顺序表
#pragma once //防止头文件包含
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>//动态内存函数的头文件
#include<assert.h>//assert的头文件,用于检查
typedef int SLDataType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDataType* a;//创建为指针,可以动态的增加空间
size_t size;//当前数据量
size_t Capacity;//总容量
}SeqList;
2、初始化
- 初始化指针a=NULL,当前数据量size=0,总容量Capacity=0
void SeqListInit(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);//断言检查,程序出错,则报中断在显示端,指向哪里出错
ps->a = NULL;
ps->Capacity = 0;
ps->size = 0;
}
3、销毁
- 若指针ps->a不为null,则释放,在置空
void SeqListDestory(SeqList* ps)
{
if (ps->a)
{
free(ps->a);//防止内存泄漏
ps->a = NULL;//避免成为野指针
}
ps->Capacity = 0;//置0
ps->size = 0;//置0
}
4、打印
- 循环遍历,输出顺序表
- 时间复杂度:o(n)
void SeqListPrint(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
for (size_t i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);
}
printf("\\n");
}
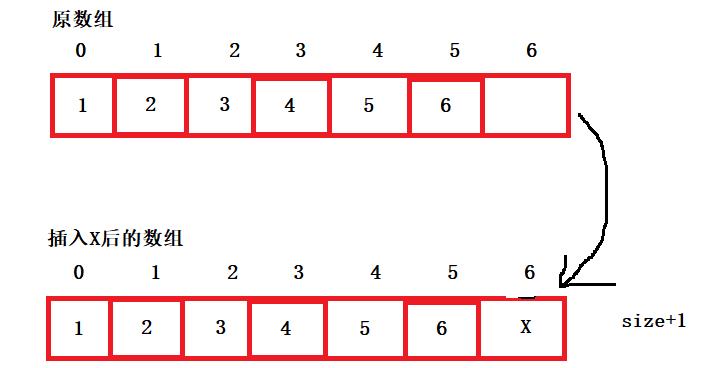
5、尾插
- 首先检查顺序表是否满了,满了就增容,再在数据的末尾插入值即可,size+1
- 时间复杂度:o(1)
void SeqListPushBack(SeqList* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
SeqListCheckCapacity(ps);//检查size是否等于Capacity,等于就扩容
ps->a[ps->size] = x;
ps->size++;
}
6、尾删
- 将size-1即可,就访问不到最后一个元素了
- 时间复杂度:o(1)
void SeqListPopBack(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->size--;
}
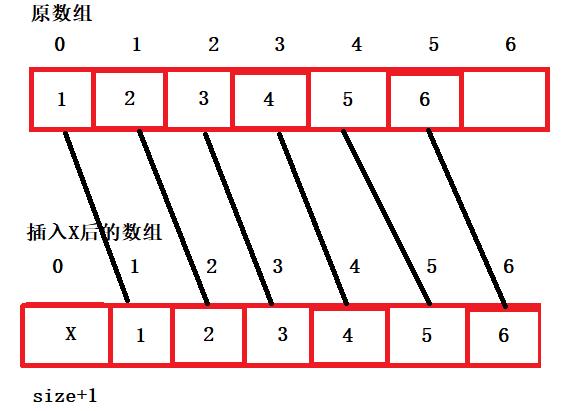
7、头插
- 头插跟尾插一样需要检查顺序表是否满员,满则增容,在将所有的元素往后挪一位,腾出0位置给x,size+1
- 时间复杂度:o(n)
void SeqListPushFront(SeqList* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
SeqListCheckCapacity(ps);//检查size是否等于Capacity,等于就扩容
size_t end = ps->size;
while (end > 0)
{
ps->a[end] = ps->a[end - 1];
--end;
}
ps->a[0] = x;
ps->size++;
}
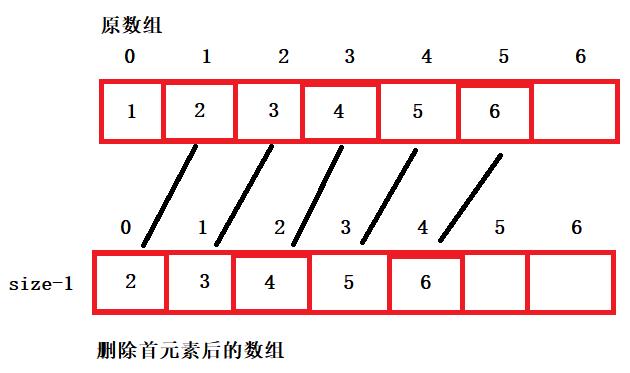
8、头删
- 删除首元素,需要将后面的元素往前挪一位,然后size-1
- 时间复杂度:o(n)
void SeqListPopFront(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
size_t begin = 1;
while (begin < ps->size)
{
ps->a[begin-1] = ps->a[begin];
++begin;
}
ps->size--;
}
9、查找
- 按照元素x在顺序表中查找,遍历查找即可,找到返回在顺序表中的位置,没找到返回 -1
- 最差时间复杂度:o(n)
- 最好时间复杂度:o(1)
- 平均时间复杂度:o(n/2)
- 时间复杂度:o(n)
int SeqListFind(SeqList* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
size_t begin = 0;
while (begin < ps->size)
{
if (ps->a[begin] == x)
return begin;
begin++;
}
return -1;
}
10、插入
- 按照pos的值在顺序表中插入值x,需要检查pos是否在顺序表的长度+1的范围内,在找到pos这个位置,将原来的数据往后移动一位,pos位置插入值x
- 最差时间复杂度:o(n)
- 最好时间复杂度:o(1)
- 平均时间复杂度:o(n/2)
- 时间复杂度:o(n)
void SeqListInsert(SeqList* ps, size_t pos, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos <= ps->size && pos >= 0);
SeqListCheckCapacity(ps);
size_t end = ps->size;
while (end > pos)
{
ps->a[end] = ps->a[end - 1];
--end;
}
ps->a[pos] = x;
ps->size++;
}
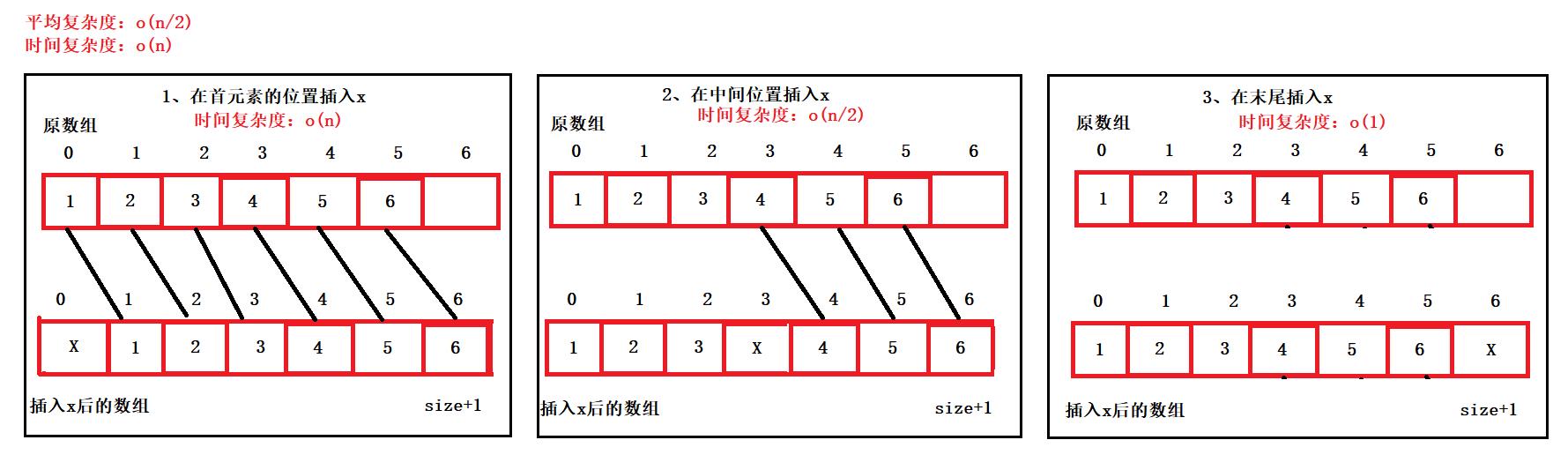
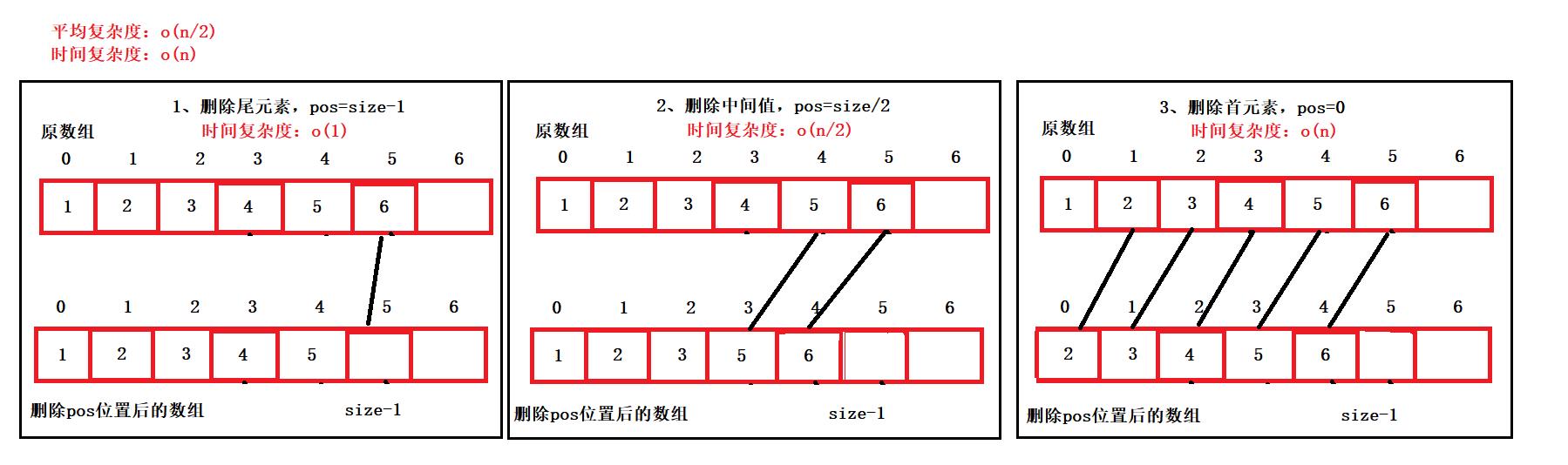
11、删除
- 按照pos的值在顺序表中查找,首先检查pos的值是否在顺序表长度范围内,在则将pos位置后的数据往前移动一位,将pos位置的值进行删除
- 最差时间复杂度:o(n)
- 最好时间复杂度:o(1)
- 平均时间复杂度:o(n/2)
- 时间复杂度:o(n)
void SeqListErase(SeqList* ps, size_t pos)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos < ps->size && pos >= 0);
size_t begin = pos;
while (begin < ps->size - 1)
{
ps->a[begin] = ps->a[begin + 1];
++begin;
}
ps->size--;
}
12、检查容量
- 检查容量的,如果size增加到与Capacity相等了,此时说明顺序表满了,得扩容增加大小,此时就调用此函数将Capacity的数值进行增加
void SeqListCheckCapacity(SeqList* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->size == ps->Capacity)
{
size_t newCapacity = ps->Capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->Capacity * 2;
SLDataType*ps1 = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newCapacity * sizeof(SLDataType));//利用realloc函数重新开辟一块空间进行扩容
if (ps1==NULL)//检查是否开辟失败
{
perror("realloc");
return;
}
ps->a = ps1;//新空间赋给a
ps->Capacity = newCapacity;//赋值给Capacity,进行扩容
}
}

完整代码链接:
https://gitee.com/deng_yuniubi/data-structure
https://github.com/yuxuanniu6/Data-Struct
以上是关于顺序表的基本实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章