超详细Pytorch 入门教程
Posted ZSYL
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了超详细Pytorch 入门教程相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Pytorch 入门教程(二)
Pytorch 入门教程(一)
学习目标:
- 知道张量和Pytorch中的张量
- 知道pytorch中如何创建张量
- 知道pytorch中tensor的常见方法
- 知道pytorch中tensor的数据类型
- 知道pytorch中如何实现tensor在cpu和cuda中转化
1. 张量Tensor
张量是一个统称,其中包含很多类型:
- 0阶张量:标量、常数,0-D Tensor
- 1阶张量:向量,1-D Tensor
- 2阶张量:矩阵,2-D Tensor
- 3阶张量
- …
- N阶张量
2. Pytorch中创建张量
-
使用python中的列表或者序列创建tensor
torch.tensor([[1., -1.], [1., -1.]]) tensor([[ 1.0000, -1.0000], [ 1.0000, -1.0000]]) -
使用numpy中的数组创建tensor
torch.tensor(np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])) tensor([[ 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6]]) -
使用torch的api创建tensor
-
torch.empty(3,4)创建3行4列的空的tensor,会用无用数据进行填充 -
torch.ones([3,4])创建3行4列的全为1的tensor -
torch.zeros([3,4])创建3行4列的全为0的tensor -
torch.rand([3,4])创建3行4列的随机值的tensor,随机值的区间是[0, 1)>>> torch.rand(2, 3) tensor([[ 0.8237, 0.5781, 0.6879], [ 0.3816, 0.7249, 0.0998]]) -
torch.randint(low=0,high=10,size=[3,4])创建3行4列的随机整数的tensor,随机值的区间是[low, high)>>> torch.randint(3, 10, (2, 2)) tensor([[4, 5], [6, 7]]) -
torch.randn([3,4])创建3行4列的随机数的tensor,随机值的分布式均值为0,方差为1
-
3. Pytorch中tensor的常用方法
-
获取tensor中的数据(当tensor中只有一个元素可用):
tensor.item()In [10]: a = torch.tensor(np.arange(1)) In [11]: a Out[11]: tensor([0]) In [12]: a.item() Out[12]: 0 -
转化为numpy数组
In [55]: z.numpy() Out[55]: array([[-2.5871205], [ 7.3690367], [-2.4918075]], dtype=float32) -
获取形状:
tensor.size()In [72]: x Out[72]: tensor([[ 1, 2], [ 3, 4], [ 5, 10]], dtype=torch.int32) In [73]: x.size() Out[73]: torch.Size([3, 2]) -
形状改变:
tensor.view((3,4))。类似numpy中的reshape,是一种浅拷贝,仅仅是形状发生改变In [76]: x.view(2,3) Out[76]: tensor([[ 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 10]], dtype=torch.int32) -
获取阶数:
tensor.dim()In [77]: x.dim() Out[77]: 2 -
获取最大值:
tensor.max()In [78]: x.max() Out[78]: tensor(10, dtype=torch.int32) -
转置:
tensor.t()In [79]: x.t() Out[79]: tensor([[ 1, 3, 5], [ 2, 4, 10]], dtype=torch.int32)
- 二维:
tensor.t() / tensor.transpose(0, 1) - 高维:
tensor.transpose(1, 2) / tensor.permute(0, 2, 1)
-
tensor[1,3]获取tensor中第一行第三列的值 -
tensor[1,3]=100对tensor中第一行第三列的位置进行赋值100 -
tensor的切片
In [101]: x
Out[101]:
tensor([[1.6437, 1.9439, 1.5393],
[1.3491, 1.9575, 1.0552],
[1.5106, 1.0123, 1.0961],
[1.4382, 1.5939, 1.5012],
[1.5267, 1.4858, 1.4007]])
In [102]: x[:,1]
Out[102]: tensor([1.9439, 1.9575, 1.0123, 1.5939, 1.4858])
4. tensor的数据类型
tensor中的数据类型非常多,常见类型如下:
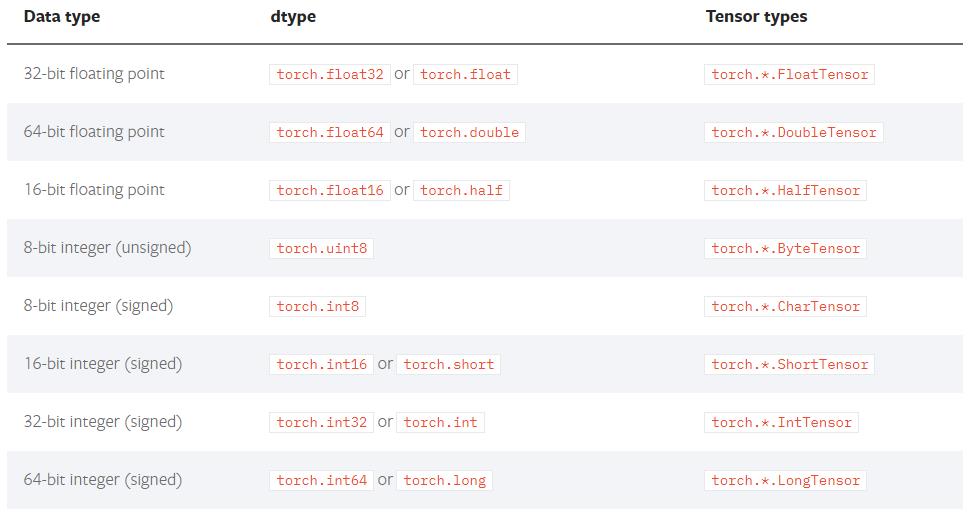
上图中的Tensor types表示这种type的tensor是其实例
-
获取tensor的数据类型:
tensor.dtypeIn [80]: x.dtype Out[80]: torch.int32 -
创建数据的时候指定类型
In [88]: torch.ones([2,3],dtype=torch.float32) Out[88]: tensor([[9.1167e+18, 0.0000e+00, 7.8796e+15], [8.3097e-43, 0.0000e+00, -0.0000e+00]]) -
类型的修改
In [17]: a Out[17]: tensor([1, 2], dtype=torch.int32) In [18]: a.type(torch.float) Out[18]: tensor([1., 2.]) In [19]: a.double() Out[19]: tensor([1., 2.], dtype=torch.float64)
5. tensor的其他操作
-
tensor和tensor相加
In [94]: x = x.new_ones(5, 3, dtype=torch.float) In [95]: y = torch.rand(5, 3) In [96]: x+y Out[96]: tensor([[1.6437, 1.9439, 1.5393], [1.3491, 1.9575, 1.0552], [1.5106, 1.0123, 1.0961], [1.4382, 1.5939, 1.5012], [1.5267, 1.4858, 1.4007]]) In [98]: torch.add(x,y) Out[98]: tensor([[1.6437, 1.9439, 1.5393], [1.3491, 1.9575, 1.0552], [1.5106, 1.0123, 1.0961], [1.4382, 1.5939, 1.5012], [1.5267, 1.4858, 1.4007]]) In [99]: x.add(y) Out[99]: tensor([[1.6437, 1.9439, 1.5393], [1.3491, 1.9575, 1.0552], [1.5106, 1.0123, 1.0961], [1.4382, 1.5939, 1.5012], [1.5267, 1.4858, 1.4007]]) In [100]: x.add_(y) #带下划线的方法会对x进行就地修改 Out[100]: tensor([[1.6437, 1.9439, 1.5393], [1.3491, 1.9575, 1.0552], [1.5106, 1.0123, 1.0961], [1.4382, 1.5939, 1.5012], [1.5267, 1.4858, 1.4007]]) In [101]: x #x发生改变 Out[101]: tensor([[1.6437, 1.9439, 1.5393], [1.3491, 1.9575, 1.0552], [1.5106, 1.0123, 1.0961], [1.4382, 1.5939, 1.5012], [1.5267, 1.4858, 1.4007]])注意:带下划线的方法(比如:
add_)会对tensor进行就地修改 -
tensor和数字操作
In [97]: x +10 Out[97]: tensor([[11., 11., 11.], [11., 11., 11.], [11., 11., 11.], [11., 11., 11.], [11., 11., 11.]]) -
CUDA中的tensor
CUDA(Compute Unified Device Architecture),是NVIDIA推出的运算平台。 CUDA™是一种由NVIDIA推出的通用并行计算架构,该架构使GPU能够解决复杂的计算问题。
torch.cuda这个模块增加了对CUDA tensor的支持,能够在cpu和gpu上使用相同的方法操作tensor通过
.to方法能够把一个tensor转移到另外一个设备(比如从CPU转到GPU)#device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") if torch.cuda.is_available(): device = torch.device("cuda") # cuda device对象 y = torch.ones_like(x, device=device) # 创建一个在cuda上的tensor x = x.to(device) # 使用方法把x转为cuda 的tensor z = x + y print(z) print(z.to("cpu", torch.double)) # .to方法也能够同时设置类型 >>tensor([1.9806], device='cuda:0') >>tensor([1.9806], dtype=torch.float64)
通过前面的学习,可以发现torch的各种操作几乎和numpy一样。
加油!
感谢!
努力!
以上是关于超详细Pytorch 入门教程的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
超详细的的PyTorch安装教程,成功率高,适合初学者,亲测可用。
基于PyTorch实现图片去模糊降噪,超详细,有代码,数据,可直接运行。