再探“高并发利器”epoll:看了一下源码
Posted 看,未来
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了再探“高并发利器”epoll:看了一下源码相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
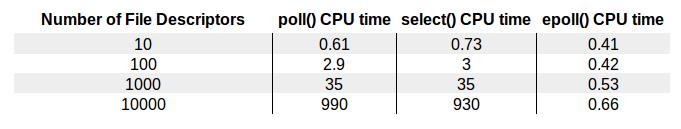
先看个图,懂得都懂。
咳咳,这篇很严肃哦!!!
面试的时候遇到过这样一个问题:epoll和select的区别。
当然,我知道这时候能挖到哪里就挖到哪里。然后我就说了epoll和select底层的区别,以及边缘触发、多路I/O等。
一直觉得回答的还不错。
从来没有想过,面试官们也没有问过:如果让你设计一个epoll模型,你会怎么设计?
有,有一个面试官说过类似的话:不要老是想着用轮子,要学会造。
虽然造出来也不一定有人用,但是能而不用,和不能、没有,是两回事。
造不出来,就多学习成功案例吧,希望有一天被问到这种问题的时候,不至于语塞。
基本数据结构
先看一下 epoll 中使用的数据结构, eventpoll、epitem 和 eppoll_entry。
eventpoll
在调用epoll_create之后内核创建的一个句柄,表示了一个epoll实例。
这部分数据将会被保存在epoll_create创建的匿名文件file的private_data字段中。
/*
* This structure is stored inside the "private_data" member of the file
* structure and represents the main data structure for the eventpoll
* interface.
其实吧,挺不想翻译的
*/
struct eventpoll {
/* Protect the access to this structure */
spinlock_t lock;
/*
* This mutex is used to ensure that files are not removed
* while epoll is using them. This is held during the event
* collection loop, the file cleanup path, the epoll file exit
* code and the ctl operations.
此互斥锁用于确保在epoll使用文件时不会删除这些文件。
在事件收集循环、文件清理路径、epoll文件退出代码和ctl操作期间发挥作用。
*/
struct mutex mtx;
/* Wait queue used by sys_epoll_wait() */
// 这个队列里存放的是执行 epoll_wait 从而等待的进程队列
wait_queue_head_t wq;
/* Wait queue used by file->poll() */
// 这个队列里存放的是该 eventloop 作为 poll 对象的一个实例,加入到等待的队列
// 这是因为 eventpoll 本身也是一个 file, 所以也会有 poll 操作
wait_queue_head_t poll_wait;
/* List of ready file descriptors */
// 这里存放的是事件就绪的 fd 列表,链表的每个元素是下面的 epitem
struct list_head rdllist;
/* RB tree root used to store monitored fd structs */
// 这是用来快速查找 fd 的红黑树
struct rb_root_cached rbr;
/*
* This is a single linked list that chains all the "struct epitem" that
* happened while transferring ready events to userspace w/out
* holding ->lock.
每当我们调用 epoll_ctl 增加一个 fd 时,内核就会为我们创建出一个 epitem 实例,并且把这个实例作为红黑树的一个子节点,
增加到 eventpoll 结构体中的红黑树中,对应的字段是 rbr。
这之后,查找每一个 fd 上是否有事件发生都是通过红黑树上的 epitem 来操作。
*/
struct epitem *ovflist;
/* wakeup_source used when ep_scan_ready_list is running */
struct wakeup_source *ws;
/* The user that created the eventpoll descriptor */
struct user_struct *user;
// 这是 eventloop 对应的匿名文件,充分体现了 Linux 下一切皆文件的思想
struct file *file;
/* used to optimize loop detection check */
int visited;
struct list_head visited_list_link;
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_RX_BUSY_POLL
/* used to track busy poll napi_id */
unsigned int napi_id;
#endif
};
epitem
/*
* Each file descriptor added to the eventpoll interface will
* have an entry of this type linked to the "rbr" RB tree.
* 每次当一个 fd 关联到一个 epoll 实例,就会有一个 eppoll_entry 产生。。
* Avoid increasing the size of this struct, there can be many thousands
* of these on a server and we do not want this to take another cache line.
* 一个服务器上可能有成千上万个这样的结构
*/
struct epitem {
union {
/* RB tree node links this structure to the eventpoll RB tree */
struct rb_node rbn;
/* Used to free the struct epitem */
struct rcu_head rcu;
};
/* List header used to link this structure to the eventpoll ready list */
// 将这个 epitem 连接到 eventpoll 里面的 rdllist 的 list 指针
struct list_head rdllink;
/*
* Works together "struct eventpoll"->ovflist in keeping the
* single linked chain of items.
*/
struct epitem *next;
/* The file descriptor information this item refers to */
//epoll 监听的 fd
struct epoll_filefd ffd;
/* Number of active wait queue attached to poll operations */
// 一个文件可以被多个 epoll 实例所监听,这里就记录了当前文件被监听的次数
int nwait;
/* List containing poll wait queues */
struct list_head pwqlist;
/* The "container" of this item */
// 当前 epollitem 所属的 eventpoll
struct eventpoll *ep;
/* List header used to link this item to the "struct file" items list */
struct list_head fllink;
/* wakeup_source used when EPOLLWAKEUP is set */
struct wakeup_source __rcu *ws;
/* The structure that describe the interested events and the source fd */
struct epoll_event event;
};
eppoll_entry
/* Wait structure used by the poll hooks */
struct eppoll_entry {
/* List header used to link this structure to the "struct epitem" */
struct list_head llink;
/* The "base" pointer is set to the container "struct epitem" */
struct epitem *base;
/*
* Wait queue item that will be linked to the target file wait
* queue head.
*/
wait_queue_entry_t wait;
/* The wait queue head that linked the "wait" wait queue item */
wait_queue_head_t *whead;
};
epoll_create
首先,epoll_create 会对传入的 flags 参数做简单的验证。
/* Check the EPOLL_* constant for consistency. */
BUILD_BUG_ON(EPOLL_CLOEXEC != O_CLOEXEC);
if (flags & ~EPOLL_CLOEXEC)
return -EINVAL;
/*
内核申请分配 eventpoll 需要的内存空间:
/* Create the internal data structure ("struct eventpoll").*/
error = ep_alloc(&ep);
if (error < 0)
return error;
在接下来,epoll_create 为 epoll 实例分配了匿名文件和文件描述字。
这里还有一个特别需要注意的地方,在调用 anon_inode_get_file 的时候,epoll_create 将 eventpoll 作为匿名文件 file 的 private_data 保存了起来,这样,在之后通过 epoll 实例的文件描述字来查找时,就可以快速地定位到 eventpoll 对象了。
最后,这个文件描述字作为 epoll 的文件句柄,被返回给 epoll_create 的调用者。
/*
* Creates all the items needed to setup an eventpoll file. That is,
* a file structure and a free file descriptor.
*/
fd = get_unused_fd_flags(O_RDWR | (flags & O_CLOEXEC));
if (fd < 0) {
error = fd;
goto out_free_ep;
}
file = anon_inode_getfile("[eventpoll]", &eventpoll_fops, ep,
O_RDWR | (flags & O_CLOEXEC));
if (IS_ERR(file)) {
error = PTR_ERR(file);
goto out_free_fd;
}
ep->file = file;
fd_install(fd, file);
return fd;
epoll_ctl
epoll_ctl 函数通过 epoll 实例句柄来获得对应的匿名文件:
// 获得 epoll 实例对应的匿名文件
f = fdget(epfd);
if (!f.file)
goto error_return;
接下来,获得添加的套接字对应的文件,即待处理的目标文件。
/* Get the "struct file *" for the target file */
// 获得真正的文件,如监听套接字、读写套接字
tf = fdget(fd);
if (!tf.file)
goto error_fput;
再接下来,进行了一系列的数据验证,以保证用户传入的参数是合法的,比如 epfd 真的是一个 epoll 实例句柄,而不是一个普通文件描述符。
/* The target file descriptor must support poll */
// 如果不支持 poll,那么该文件描述字是无效的
error = -EPERM;
if (!tf.file->f_op->poll)
goto error_tgt_fput;
...
红黑树查找
接下来 epoll_ctl 通过目标文件和对应描述字,在红黑树中查找是否存在该套接字,这也是 epoll 为什么高效的地方。红黑树(RB-tree)是一种常见的数据结构,这里 eventpoll 通过红黑树跟踪了当前监听的所有文件描述字,而这棵树的根就保存在 eventpoll 数据结构中。
/* RB tree root used to store monitored fd structs */
struct rb_root_cached rbr;
对于每个被监听的文件描述字,都有一个对应的 epitem 与之对应,epitem 作为红黑树中的节点就保存在红黑树中。
/*
* Try to lookup the file inside our RB tree, Since we grabbed "mtx"
* above, we can be sure to be able to use the item looked up by
* ep_find() till we release the mutex.
*/
epi = ep_find(ep, tf.file, fd);
红黑树是一棵二叉树,作为二叉树上的节点,epitem 必须提供比较能力,以便可以按大小顺序构建出一棵有序的二叉树。其排序能力是依靠 epoll_filefd 结构体来完成的,epoll_filefd 可以简单理解为需要监听的文件描述字,它对应到二叉树上的节点。
可以看到这个还是比较好理解的,按照文件的地址大小排序。如果两个相同,就按照文件文件描述字来排序。
struct epoll_filefd {
struct file *file; // pointer to the target file struct corresponding to the fd
int fd; // target file descriptor number
} __packed;
/* Compare RB tree keys */
static inline int ep_cmp_ffd(struct epoll_filefd *p1,
struct epoll_filefd *p2)
{
return (p1->file > p2->file ? +1:
(p1->file < p2->file ? -1 : p1->fd - p2->fd));
}
在进行完红黑树查找之后,如果发现是一个 ADD 操作,并且在树中没有找到对应的二叉树节点,就会调用 ep_insert 进行二叉树节点的增加。
case EPOLL_CTL_ADD:
if (!epi) {
epds.events |= POLLERR | POLLHUP;
error = ep_insert(ep, &epds, tf.file, fd, full_check);
} else
error = -EEXIST;
if (full_check)
clear_tfile_check_list();
break;
总结
epoll 维护了一棵红黑树来跟踪所有待检测的文件描述字,黑红树的使用减少了内核和用户空间大量的数据拷贝和内存分配,大大提高了性能。
同时,epoll 维护了一个链表来记录就绪事件,内核在每个文件有事件发生时将自己登记到这个就绪事件列表中,通过内核自身的文件 file-eventpoll 之间的回调和唤醒机制,减少了对内核描述字的遍历,大大加速了事件通知和检测的效率,这也为 level-triggered 和 edge-triggered 的实现带来了便利。
以上是关于再探“高并发利器”epoll:看了一下源码的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章