QCustomPlot绘图实现光标滑过曲线显示点的坐标
Posted shaderdx
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了QCustomPlot绘图实现光标滑过曲线显示点的坐标相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
有两种方法可实现这个效果:
1.通过关联QCustomPlot的mouseMove信号槽事件实现;
2.通过继承QCustomPlot类,重写mouseMove虚函数实现;
这个两个方法都是获取鼠标位置,然后计算出点的坐标值,利用QToolTip显示点坐标的方法。
方向弄清楚了,现在我们去实现出来,go……
一、信号槽方法
1、首先建立一个鼠标移动时间响应函数:
private slots:
void MyMouseMoveEvent(QMouseEvent *event);2、将槽函数MyMouseMoveEvent与QCustomPlot的mouseMove信号建立连接。
Plus,这里推荐基于qt5的信号槽连接,因为编译时,基于qt4的connect不会检查信号和槽的参数以及槽函数正确与否,而基于qt5的connect会有这一个检查过程(原来遇见过基于qt4的槽函数没有响应的情况)。
connect(m_pHistoryPlot, &QCustomPlot::mouseMove, this, &HistoryDataView::MyMouseMoveEvent);3、槽函数实现光标划过曲线显示点坐标功能。
代码有详细注释,这里就不详细讲解。
void HistoryDataView::MyMouseMoveEvent(QMouseEvent* event)
{
if (m_pHistoryPlot->graphCount() == 0)
{
return;
}
//获取鼠标坐标,相对父窗体坐标
int x_pos = event->pos().x();
int y_pos = event->pos().y();
//鼠标坐标转化为CustomPlot内部坐标
float x_val = m_pHistoryPlot->xAxis->pixelToCoord(x_pos);
float y_val = m_pHistoryPlot->yAxis->pixelToCoord(y_pos);
//通过坐标轴范围判断光标是否在点附近
float x_begin = m_pHistoryPlot->xAxis->range().lower;
float x_end = m_pHistoryPlot->xAxis->range().upper;
float y_begin = m_pHistoryPlot->yAxis->range().lower;
float y_end = m_pHistoryPlot->yAxis->range().upper;
float x_tolerate = (x_end - x_begin) / 40;//光标与最近点距离在此范围内,便显示该最近点的值
float y_tolerate = (y_end - y_begin) / 40;
//判断有没有超出坐标轴范围
if (x_val < x_begin || x_val > x_end)
{
return;
}
//通过x值查找离曲线最近的一个key值索引
int index = 0;
int index_left = m_pHistoryPlot->graph(0)->findBegin(x_val, true);//左边最近的一个key值索引
int index_right = m_pHistoryPlot->graph(0)->findEnd(x_val, true);//右边
float dif_left = fabs(m_pHistoryPlot->graph(0)->data()->at(index_left)->key - x_val);
float dif_right = fabs(m_pHistoryPlot->graph(0)->data()->at(index_right)->key - x_val);
index = ((dif_left < dif_right) ? index_left : index_right);
double x_posval = m_pHistoryPlot->graph(0)->data()->at(index)->key;//通过得到的索引获取key值
double y_posval = m_pHistoryPlot->graph(0)->data()->at(index)->value;//通过得到的索引获取value值
float dx = fabs(x_posval - x_val);
float dy = fabs(y_posval - y_val);
int graphIndex = 0;//curve index closest to the cursor
//通过遍历每条曲线在index处的value值,得到离光标点最近的value及对应曲线索引
for (int i = 0, n = m_pHistoryPlot->xAxis->graphs().count(); i < n; i++)
{
y_posval = fabs(m_pHistoryPlot->graph(i)->data()->at(index)->value - y_val);
if (y_posval < dy)
{
dy = y_posval;
graphIndex = i;
}
}
//判断光标点与最近点的距离是否在设定范围内
if (dy <= y_tolerate && dx <= x_tolerate)
{
y_posval = m_pHistoryPlot->graph(graphIndex)->data()->at(index)->value;
QString strToolTip = QString("CH%1 \\nx=%2\\ny=%3").arg(graphIndex + 1).arg(y_posval).arg(y_posval);
QToolTip::showText(cursor().pos(), strToolTip, m_pHistoryPlot);
}
}4、最终效果
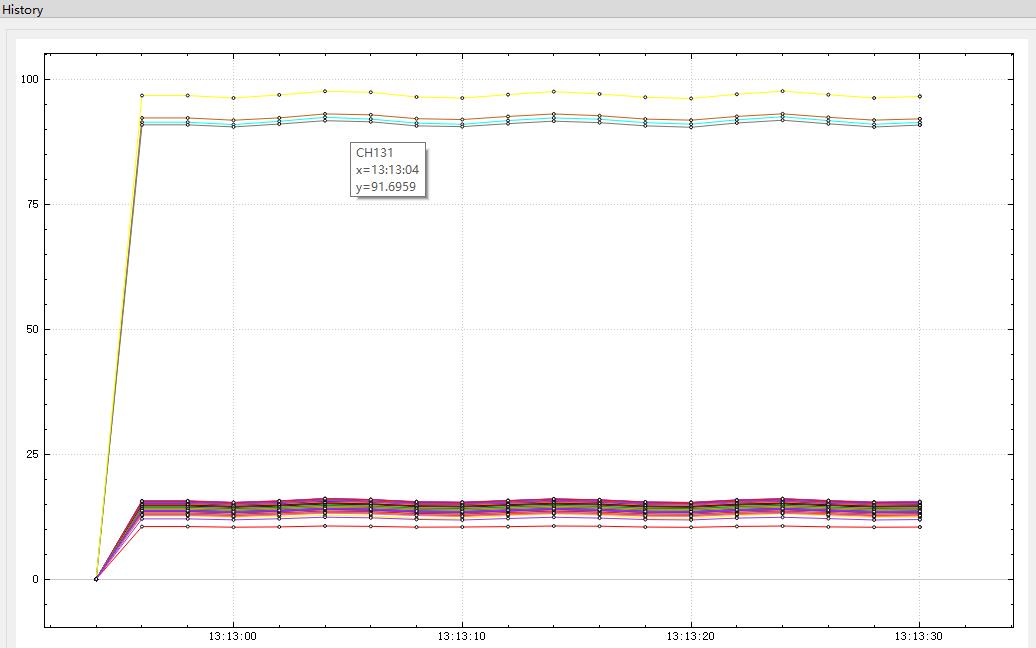
二、继承通过虚函数实现
1、继承QCustomPlot
class MyCustomPlot : public QCustomPlot
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
MyCustomPlot(QWidget *parent = 0);
protected:
virtual void mouseMoveEvent(QMouseEvent *event);
//……
}2、重写虚函数
void MyCustomPlot::mouseMoveEvent(QMouseEvent *event)
{
QCustomPlot::mouseMoveEvent(event);
if(!m_isShowTracer)
{
return;
}
//获取鼠标坐标,相对父窗体坐标
int x_pos = event->pos().x();
int y_pos = event->pos().y();
//鼠标坐标转化为CustomPlot内部坐标
float x_val = m_pHistoryPlot->xAxis->pixelToCoord(x_pos);
float y_val = m_pHistoryPlot->yAxis->pixelToCoord(y_pos);
//通过坐标轴范围判断光标是否在点附近
float x_begin = m_pHistoryPlot->xAxis->range().lower;
float x_end = m_pHistoryPlot->xAxis->range().upper;
float y_begin = m_pHistoryPlot->yAxis->range().lower;
float y_end = m_pHistoryPlot->yAxis->range().upper;
float x_tolerate = (x_end - x_begin) / 40;//光标与最近点距离在此范围内,便显示该最近点的值
float y_tolerate = (y_end - y_begin) / 40;
//判断有没有超出坐标轴范围
if (x_val < x_begin || x_val > x_end)
{
return;
}
//通过x值查找离曲线最近的一个key值索引
int index = 0;
int index_left = m_pHistoryPlot->graph(0)->findBegin(x_val, true);//左边最近的一个key值索引
int index_right = m_pHistoryPlot->graph(0)->findEnd(x_val, true);//右边
float dif_left = fabs(m_pHistoryPlot->graph(0)->data()->at(index_left)->key - x_val);
float dif_right = fabs(m_pHistoryPlot->graph(0)->data()->at(index_right)->key - x_val);
index = ((dif_left < dif_right) ? index_left : index_right);
double x_posval = m_pHistoryPlot->graph(0)->data()->at(index)->key;//通过得到的索引获取key值
double y_posval = m_pHistoryPlot->graph(0)->data()->at(index)->value;//通过得到的索引获取value值
float dx = fabs(x_posval - x_val);
float dy = fabs(y_posval - y_val);
int graphIndex = 0;//curve index closest to the cursor
//通过遍历每条曲线在index处的value值,得到离光标点最近的value及对应曲线索引
for (int i = 0, n = m_pHistoryPlot->xAxis->graphs().count(); i < n; i++)
{
y_posval = fabs(m_pHistoryPlot->graph(i)->data()->at(index)->value - y_val);
if (y_posval < dy)
{
dy = y_posval;
graphIndex = i;
}
}
//判断光标点与最近点的距离是否在设定范围内
if (dy <= y_tolerate && dx <= x_tolerate)
{
y_posval = m_pHistoryPlot->graph(graphIndex)->data()->at(index)->value;
//QString strToolTip = QString("CH%1:(%2, %3)").arg(graphIndex + 1).arg(x_val).arg(y_val);
int hor = x_posval / 3600;
int tmp = (int)x_posval % 3600;
int min = tmp / 60;
int sec = tmp % 60;
char arx[32] = { 0 };
sprintf(arx, "%02d:%02d:%02d", hor, min, sec);
QString strToolTip = QString("CH%1 \\nx=%2\\ny=%3").arg(graphIndex + 1).arg(arx).arg(y_posval);
QToolTip::showText(cursor().pos(), strToolTip, m_pHistoryPlot);
}
this->replot();//曲线重绘
}
QT5下,使用QCustomPlot显示折线图和曲线图,鼠标滑过折线曲线跟随鼠标显示此时鼠标指向的点的x轴数值和y轴数值。
以上是关于QCustomPlot绘图实现光标滑过曲线显示点的坐标的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章