C++哈希表/散列表
Posted 桃陉
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C++哈希表/散列表相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一.基本介绍
哈希表,也叫做散列表,是一种根据键(Key) 而直接访问在内存存储位置的数据结构。
它有一个关于计算键值的函数,将所需查询数据经过转换映射到表中的一个位置。这个映射函数叫做散列函数,这个存放记录的数组叫做散列表。
下面我们讲讲怎么建立这种数据结构:
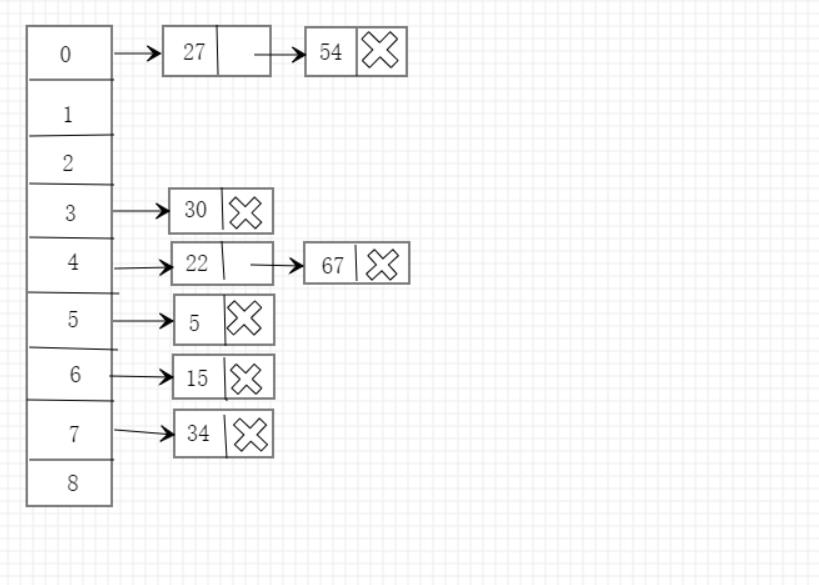
∙ \\bullet ∙ 首先我们确定散列表的大小(规模),这里我们取大小为9,所以就要建立一个大小为9的数组。
∙
\\bullet
∙ 下面给出一些我们需要存储的数据:5、15、67、34、22、27、30、54,我们先将其进行排序得到:5、15、22、27、30、34、54、67
∙ \\bullet ∙ 我们确定映射规则为取模(最简单的映射规则),从小到大依次对9进行取模,取得的模为多少就链接在对应下标的位置后面。
∙
\\bullet
∙ 得到结果如下:
实现思路:
∙ \\bullet ∙ 经过上面的分析,我们现在需要建立三个类,一个是节点类,一个是链表类,一个是哈希表类。
∙ \\bullet ∙ 节点类包括val值和next指针、链表类包括头结点Head、哈希表类包括哈希表规模size和链表数组arr。
∙ \\bullet ∙ 我们会实现哈希表的增删查改等基本操作。
∙ \\bullet ∙ 先将增删查改操作在链表类中实现,之后就使用哈希表类选择对应的链表执行这些操作。
二.代码实现
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
//节点类
class node
{
public:
int value;
node* next;
node(node* nextval=NULL)
{
this->next=nextval;
}
node(int val,node* nextval=NULL)
{
value=val;
next=nextval;
}
};
//链表类
class Link
{
private:
node* Head=new node(0);
public:
//增加节点
void add(node* Node)
{
if(Head==NULL)
{
cout<<"The list is empty!"<<endl;
return ;
}
node* temp=Head;
while(1)
{
if(temp->next==NULL)
{
break;
}
temp=temp->next;
}
temp->next=Node;
}
//打印链表
void list()
{
if(Head==NULL)
{
cout<<"The list is empty!"<<endl;
return ;
}
node* temp=Head;
while(temp)
{
cout<<temp->value<<" ";
temp=temp->next;
}
cout<<endl;
}
//寻找节点
node* find(int val)
{
if(Head==NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
node* temp=Head->next;
while(temp)
{
if(temp->value==val)
{
return temp;
}
temp=temp->next;
}
return NULL;
}
//删除并返回节点
node* del(int val)
{
if(Head==NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
node* temp=Head;
while(temp->next)
{
if(temp->next->value==val)
{
break;
}
}
node* ans=temp->next;
temp->next=temp->next->next;
return ans;
}
node* getHead()
{
return this->Head;
}
};
//哈希表类
class HashTable
{
private:
//链表数组
Link* arr;
int size;
//映射函数
int hashFunc(int val)
{
return val%size;
}
public:
HashTable(int Size)
{
size=Size;
arr = new Link[size];
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)
{
arr[i] = Link();
arr[i].getHead()->value=i;
}
}
void add(node* Node)
{
int index = hashFunc(Node->value);
arr[index].add(Node);
}
//打印哈希表
void print()
{
//一条一条链表进行打印
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)
{
arr[i].list();
}
}
//查找节点
node* find(int val)
{
int index=val%size;
if(index<0 || index>size)
{
cout<<"val = "<<val<<" is not fit!"<<endl;
return NULL;
}
node* temp=arr[index].find(val);
if(temp==NULL)
{
cout<<"In "<<index<<" Link, "<<val<<" is not exist!"<<endl;
return NULL;
}else
{
cout<<"In "<<index<<" Link, "<<val<<" is exist!"<<endl;
}
return temp;
}
//删除节点
node* del(int val)
{
int index=val%size;
if(index<0 || index>size)
{
cout<<"val = "<<val<<" is not fit!"<<endl;
return NULL;
}
node* temp=arr[index].del(val);
if(temp==NULL)
{
cout<<"In "<<index<<" Link, "<<val<<" is not successfully delete!"<<endl;
return NULL;
}else
{
cout<<"In "<<index<<" Link, "<<val<<" is successfully delete!"<<endl;
}
return temp;
}
};
int main()
{
HashTable ht=HashTable(9);
// ht.print();
ht.add(new node(5));
ht.add(new node(15));
ht.add(new node(22));
ht.add(new node(27));
ht.add(new node(30));
ht.add(new node(34));
ht.add(new node(54));
ht.add(new node(67));
ht.print();
ht.find(67);
ht.del(27);
ht.print();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
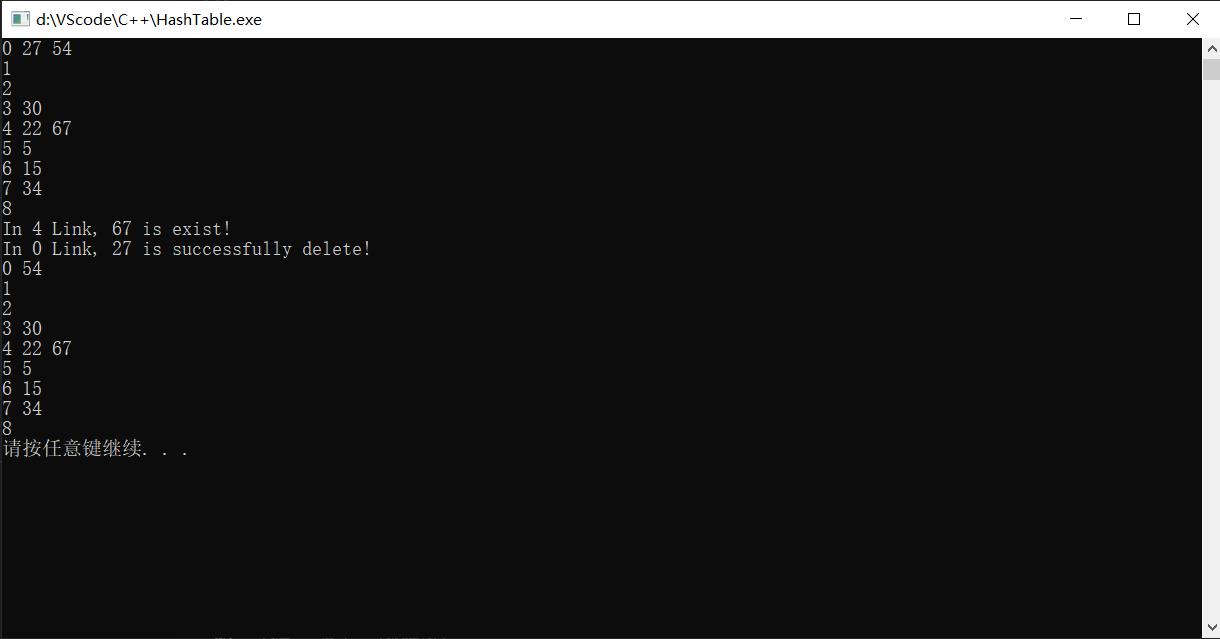
三.结果展示
以上是关于C++哈希表/散列表的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章