计算字符串最后一个单词的长度,单词以空格隔开。
LeetCode刷题
Posted 心默默言
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了LeetCode刷题相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.字符串最后一个单词的长度
输入描述:
一行字符串,非空,长度小于5000。
输出描述:
整数N,最后一个单词的长度。
输入
hello world
输出
5
import java.util.Scanner; /** * 计算字符串最后一个单词的长度,单词以空格隔开。 * */ public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); while (scanner.hasNext()) { String s = scanner.nextLine(); String[] words = s.split(" "); System.out.println(words[words.length-1].length()); } } }

2.计算字符个数
写出一个程序,接受一个由字母和数字组成的字符串,和一个字符,然后输出输入字符串中含有该字符的个数。不区分大小写。
输入描述:
第一行输入一个有字母和数字以及空格组成的字符串,第二行输入一个字符。
输出描述:
输出输入字符串中含有该字符的个数。
输入
ABCDEF A
输出
1
import java.util.Scanner; /** * 接受一个由字母和数字组成的字符串,和一个字符,然后输出输入字符串中含有该字符的个数。不区分大小写。 * */ public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); String s = input.next().toUpperCase(); char c = input.next().toUpperCase().charAt(0); int count = getNum(s, c); System.out.println(count); } /*public static int getNum(String s, char c) { char[] arr = s.toCharArray(); int count = 0; for (char i : arr) { if (i == c) count++; } return count; }*/ public static int getNum(String s, char c) { int count = 0; for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { if (c == s.charAt(i)) count++; } return count; } }
3.去重和排序
对一组数据完成去重与排序的工作,注意第一个数字为数据的个数。
import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Set; import java.util.TreeSet; /** * 对一组数据完成去重与排序的工作 * */ public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); while (input.hasNext()) { int num = input.nextInt(); Set<Integer> set = new TreeSet<>(); for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) { set.add(input.nextInt()); } for (Integer i : set) { System.out.print(i + " "); } System.out.println(); } } }

4.字符串分割与补零
•连续输入字符串,请按长度为8拆分每个字符串后输出到新的字符串数组;
•长度不是8整数倍的字符串请在后面补数字0,空字符串不处理。
输入描述:
连续输入字符串(输入2次,每个字符串长度小于100)
输出描述:
输出到长度为8的新字符串数组
输入
abc 123456789
输出
abc00000 12345678 90000000
import java.util.Scanner; /** * •连续输入字符串,请按长度为8拆分每个字符串后输出到新的字符串数组; * •长度不是8整数倍的字符串请在后面补数字0,空字符串不处理。 */ public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); while (input.hasNextLine()) { String s = input.nextLine(); splitString(s); System.out.println(); } } public static void splitString(String s) { while (s.length() >= 8) { System.out.print(s.substring(0, 8)+" "); s = s.substring(8); } if (s.length() < 8 && s.length() > 0) { s = s + "0000000"; System.out.print(s.substring(0, 8)); } } }

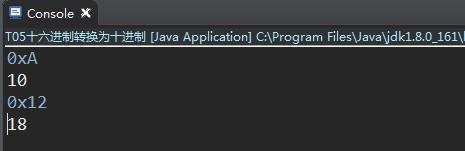
5.十六进制转换为十进制
写出一个程序,接受一个十六进制的数,输出该数值的十进制表示。(多组同时输入 )
输入描述:
输入一个十六进制的数值字符串。
输出描述:
输出该数值的十进制字符串。
输入
0xA
输出
10
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); while (input.hasNext()) { String s = input.nextLine(); /* char[] arr = s.toCharArray(); int result = 0; int index = 0; for (int i = arr.length - 1; i > 1; i--) { int num = conversion(arr[i]); result += num * Math.pow(16, index++); } System.out.println(result);*/ System.out.println(conversion(s.substring(2))); } input.close(); }public static int conversion(String s) { int n = 0; int count = 0; int temp = 0; char ch; while (count < s.length()) { ch = s.charAt(s.length() - count - 1); if (ch >= \'0\' && ch <= \'9\') { temp = ch - \'0\'; } else if (ch >= \'A\' && ch <= \'Z\') { temp = ch - \'A\' + 10; } else if (ch >= \'a\' && ch <= \'z\') { temp = ch - \'a\' + 10; } else { break; } n += temp * Math.pow(16, count); count++; } return n; } }
6.质数因子
功能:输入一个正整数,按照从小到大的顺序输出它的所有质因子(如180的质因子为2 2 3 3 5 )
输入描述:
输入一个long型整数
输出描述:
按照从小到大的顺序输出它的所有质数的因子,以空格隔开。最后一个数后面也要有空格。
输入
180
输出
2 2 3 3 5
import java.util.Scanner; /** * 功能:输入一个正整数,按照从小到大的顺序输出它的所有质数的因子(如180的质数因子为2 2 3 3 5 )最后一个数后面也要有空格 */ public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); Long number = input.nextLong(); if (number < 2) { input.close(); return; } isPrimeFactors(number); input.close(); } public static void isPrimeFactors(Long number) { while (number != 1) { for (int i = 2; i <= number; i++) { if (number % i == 0) { number = number / i; System.out.print(i + " "); break; } } } } }

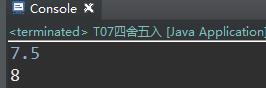
7.四舍五入
写出一个程序,接受一个正浮点数值,输出该数值的近似整数值。如果小数点后数值大于等于5,向上取整;小于5,则向下取整。
输入描述:
输入一个正浮点数值
输出描述:
输出该数值的近似整数值
输入
5.5
输出
6
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); double number = input.nextDouble(); int res = round(number); System.out.println(res); input.close(); } public static int round(double number) { int res = (int) number; return (number - res) >= 0.5 ? res + 1 : res; } }
8.对表索引相同的记录进行合并
数据表记录包含表索引和数值(int范围的整数),请对表索引相同的记录进行合并,即将相同索引的数值进行求和运算,输出按照key值升序进行输出。
输入描述:
先输入键值对的个数
然后输入成对的index和value值,以空格隔开
输出描述:
输出合并后的键值对(多行)
输入
4 0 1 0 2 1 2 3 4
输出
0 3 1 2 3 4
import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.TreeMap; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int num = Integer.parseInt(input.nextLine()); TreeMap<Integer, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>(); for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) { String s = input.nextLine(); getResult(s, map); } for (Integer key : map.keySet()) { System.out.println(key + " " + map.get(key)); } } public static void getResult(String s, TreeMap<Integer, Integer> map) { String[] arr = s.split(" "); int key = Integer.parseInt(arr[0]); int value = Integer.parseInt(arr[1]); if (map.containsKey(key)) { value += map.get(key); map.put(key, value); } else { map.put(key, value); } } }

9.提取不重复的整数
输入一个int型整数,按照从右向左的阅读顺序,返回一个不含重复数字的新的整数。
输入描述:
输入一个int型整数
输出描述:
按照从右向左的阅读顺序,返回一个不含重复数字的新的整数
输入
9876673
输出
37689
import java.util.LinkedHashSet; import java.util.Scanner; public class T09提取不重复的整数 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); String s = input.nextLine(); LinkedHashSet<Character> set = new LinkedHashSet<>(); for (int i = s.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { char ch = s.charAt(i); set.add(ch); } for (Character ch : set) { System.out.print(ch); } input.close(); } }

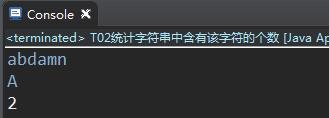
10.统计字符个数
编写一个函数,计算字符串中含有的不同字符的个数。字符在ACSII码范围内(0~127),换行表示结束符,不算在字符里。不在范围内的不作统计。
输入描述:
输入N个字符,字符在ACSII码范围内。
输出描述:
输出范围在(0~127)字符的个数。
输入
abc
输出
3
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); String s = input.nextLine(); int count = 0; int[] arr = new int[128]; for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { if (arr[s.charAt(i)] == 0) { arr[s.charAt(i)]++; } } for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { if (arr[i] != 0) { count++; } } System.out.println(count); } }
11.按照字典的顺序排列字符串
给定n个字符串,请对n个字符串按照字典序排列。
输入描述:
输入第一行为一个正整数n(1≤n≤1000),下面n行为n个字符串(字符串长度≤100),字符串中只含有大小写字母。
输出描述:
数据输出n行,输出结果为按照字典序排列的字符串。
输入
9 cap to cat card two too up boat boot
输出
boat boot cap card cat to too two up
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int num = Integer.parseInt(input.nextLine()); ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) { String s = input.nextLine(); list.add(s); } Collections.sort(list); for (String s : list) { System.out.println(s); } input.close(); } }
12.密码验证合格程序
密码要求:
1.长度超过8位
2.包括大小写字母.数字.其它符号,以上四种至少三种
3.不能有相同长度超2的子串重复
说明:长度超过2的子串
输入描述:
一组或多组长度超过2的子符串。每组占一行
输出描述:
如果符合要求输出:OK,否则输出NG
输入
021Abc9000 021Abc9Abc1 021ABC9000 021$bc9000
输出
OK NG NG OK
import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.regex.Pattern; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); while (input.hasNext()) { String str = input.nextLine(); String res = isPassword(str); System.out.println(res); } } public static String isPassword(String str) { //1.判断长度 if (str == null || str.length() < 9) { return "NG"; } int count = 0; //2.判断是否含有三种以上字符 /*Pattern p1 = Pattern.compile("[a-z]"); Matcher m1 = p1.matcher(str); if (m1.find()) count++; Pattern p2 = Pattern.compile("[A-Z]"); Matcher m2 = p2.matcher(str); if (m2.find()) count++; Pattern p3 = Pattern.compile("[0-9]"); Matcher m3 = p3.matcher(str); if (m3.find()) count++; Pattern p4 = Pattern.compile("[^a-zA-Z0-9]"); Matcher m4 = p4.matcher(str); if (m4.find()) count++;*/ if (Pattern.matches(".*[a-z]+.*", str)) //+表达式至少出现1次,相当于 {1,} count++; if (Pattern.matches(".*[A-Z]+.*", str)) //*表达式至少出现0次,表达式不出现或出现任意次,相当于 {0,} count++; if (Pattern.matches(".*[0-9]+.*", str)) //.小数点可以匹配任意一个字符(除了换行符) count++; if (Pattern.matches(".*[^a-zA-Z0-9]+.*", str)) count++; if (count < 3) { return "NG"; } else { return isHasSubString(str); } } private static String isHasSubString(String str) { for (int i = 0; i < str.length() - 3; i++) { String str1 = str.substring(i, i + 3); String str2 = str.substring(i + 3); if (str2.contains(str1)) return "NG"; } return "OK"; } }
13.密码转换
大家都知道手机上的字母: 1--1, abc--2, def--3, ghi--4, jkl--5, mno--6, pqrs--7, tuv--8 wxyz--9, 0--0,就这么简单,渊子把密码中出现的小写字母都变成对应的数字,数字和其他的符号都不做变换,
声明:密码中没有空格,而密码中出现的大写字母则变成小写之后往后移一位,如:X,先变成小写,再往后移一位,不就是y了嘛,简单吧。记住,z往后移是a哦。
输入描述:
输入包括多个测试数据。输入是一个明文,密码长度不超过100个字符,输入直到文件结尾
输出描述:
输出渊子真正的密文
输入
YUANzhi1987
输出
zvbo9441987
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); while (input.hasNext()) { String str = input.nextLine(); char[] arr = str.toCharArray(); for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { char num = arr[i]; if (num >= \'0\' && num <= \'9\') { continue; } else if ("abc".contains(num + "")) { arr[i] = \'2\'; } else if ("def".contains(num + "")) { arr[i] = \'3\'; } else if ("ghi".contains(num + "")) { arr[i] = \'4\'; } else if ("jkl".contains(num + "")) { arr[i] = \'5\'; } else if ("mno".contains(num + "")) { arr[i] = \'6\'; } else if ("pqrs".contains(num + "")) { arr[i] = \'7\'; } else if ("tuv".contains(num + "")) { arr[i] = \'8\'; } else if ("wxyz".contains(num + "")) { arr[i] = \'9\'; } else if (num>=\'A\' && num<=\'Y\') { arr[i] = (char) (num + 33); } else if (num ==\'Z\') { arr[i] = \'a\'; } else{ System.out.println("your password is error!"); return; } } for (char c : arr) { System.out.print(c); } } } }
14.删除出现次数最少的字符
输入描述:
字符串只包含小写英文字母, 不考虑非法输入,输入的字符串长度小于等于20个字节。
输出描述:
删除字符串中出现次数最少的字符后的字符串。
输入
abcdd
输出
dd
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Map.Entry; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.TreeMap; public class Main { /*public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); while (input.hasNext()) { String s = input.nextLine(); Map<Character, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>(); for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { char key = s.charAt(i); if (map.containsKey(key)) { map.put(key, map.get(key) + 1); } else { map.put(key, 1); } } List<Map.Entry<Character, Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>(map.entrySet()); Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Map.Entry<Character, Integer>>() { @Override public int compare(Entry<Character, Integer> o1, Entry<Character, Integer> o2) { return o1.getValue() - o2.getValue(); } }); String newS = s.replace(list.get(0).getKey() + "", ""); for (int i = 1; i < list.size(); i++) { if (list.get(0).getValue() == list.get(i).getValue()) { newS = newS.replace(list.get(i).getKey() + "", ""); }else { break; } } System.out.println(newS); } input.close(); }*/ public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); while (input.hasNext()) { String str = input.nextLine(); int[] count = new int[26]; char[] chs = str.toCharArray(); int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE; for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) { count[chs[i] - \'a\']++; min = min > count[chs[i] - \'a\'] ? count[chs[i] - \'a\'] : min; } for (int i = 0; i < count.length; i++) { if (count[i] == min) { str = str.replaceAll(String.valueOf((char) (i + \'a\')), ""); } } System.out.println(str); } input.close(); } }
15.蛇形矩阵
蛇形矩阵是由1开始的自然数依次排列成的一个矩阵上三角形。
样例输入
5
样例输出
1 3 6 10 15
2 5 9 14
4 8 13
7 12
11
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); while (input.hasNext()) { int N = Integer.parseInt(input.nextLine()); int[][] m = new int[N][N]; m[0][0] = 1; //核心思想,后一项与前一项的关系 System.out.print(m[0][0] + " "); for (int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) { m[i + 1][0] = m[i][0] + i + 1; for (int j = 0; j < N - 1 - i; j++) { m[i][j + 1] = m[i][j] + j + i + 2; System.out.print(m[i][j + 1] + " "); } System.out.print("\\n" + m[i + 1][0] + " "); } System.out.println(); //注意在每个测试用例后添加换行 } input.close(); } }
16.顺时针打印矩阵
package nowcode; /** * 顺时针打印矩阵 * 输入一个矩阵,按照从外向里以顺时针的顺序依次打印出每一个数字, * 例如,如果输入如下4 X 4矩阵: * 1 2 3 4 * 5 6 7 8 * 9 10 11 12 * 13 14 15 16 * 则依次打印出数字1,2,3,4,8,12,16,15,14,13,9,5,6,7,11,10. */ public class T22printMatrixInCircle { public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] m = { { 1, 2, 3, 4 }, { 5, 6, 7, 8 }, { 9, 10, 11, 12 }, { 13, 14, 15, 16 } }; int rows = m.length; int cols = m[0].length; int start = 0; while (cols > 2 * start && rows > 2 * start) { pringMatrixInCircle(m, rows, cols, start); start++; } } public static void pringMatrixInCircle(int[][] m, int rows, int cols, int start) { //1.从左到右打印 for (int j = start; j < cols - start; j++) { System.out.print(m[start][j] + " "); } //2.从上到下 for (int i = start + 1; i < rows - start; i++) { System.out.print(m[i][cols - start - 1] + " "); } //3.从右到左 for (int j = cols - start - 2; j >= start; j--) { System.out.print(m[rows - start - 1][j] + " "); } //4.从下到上 for (int i = rows - start - 2; i > start; i--) { System.out.print(m[i][start] + " "); } } }
17.字符串加密
package nowcode; import java.util.LinkedHashSet; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Set; /** * 有一种技巧可以对数据进行加密,它使用一个单词作为它的密匙。下面是它的工作原理:首先,选择一个单词作为密匙,如TRAILBLAZERS。如果单词中包含有重复的字母,只保留第1个,其余几个丢弃。现在,修改过的那个单词属于字母表的下面,如下所示: A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z T R A I L B Z E S C D F G H J K M N O P Q U V W X Y 上面其他用字母表中剩余的字母填充完整。在对信息进行加密时,信息中的每个字母被固定于顶上那行,并用下面那行的对应字母一一取代原文的字母(字母字符的大小写状态应该保留)。因此,使用这个密匙,Attack AT DAWN(黎明时攻击)就会被加密为Tpptad TP ITVH。 通过指定的密匙和明文得到密文。 输入描述: 先输入key和要加密的字符串 输出描述: 返回加密后的字符串 示例1 输入 nihao ni 输出 le */ public class T23字符串加密 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); String s1 = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"; while (input.hasNext()) { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(s1); String str = input.nextLine(); String data = input.nextLine(); String disStr = getDistinctString(str); // System.out.println(disStr); String key = completion(sb, disStr); // System.out.println(key); String result = getPlainText(key, data); System.out.println(result); } } /** * 字符串去重 */ public static String getDistinctString(String s) { Set<Character> set = new LinkedHashSet<>(); for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { set.add(s.charAt(i)); } String res = ""; for (Character ch : set) { res += ch; } return res; } /** * 字符串补齐 * @param sb:标准字符串 * @param str:去重之后的字符串 * @return */ public static String completion(StringBuffer sb, String str) { //int index = 0; for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) { char ch = str.charAt(i); sb.deleteCharAt(sb.indexOf(ch + "")); //sb.insert(index++, ch); } return str + sb.toString(); } /** * 得到明文 * @param key:密钥 * @param data:加密的数据 * @return