MySQL 原理分析之 Trace 分析 order by 的索引原理
Posted Howinfun
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了MySQL 原理分析之 Trace 分析 order by 的索引原理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、背景
昨天早上,交流群有一位同学提出了一个问题。看下图:
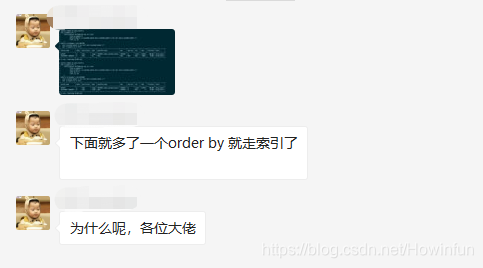
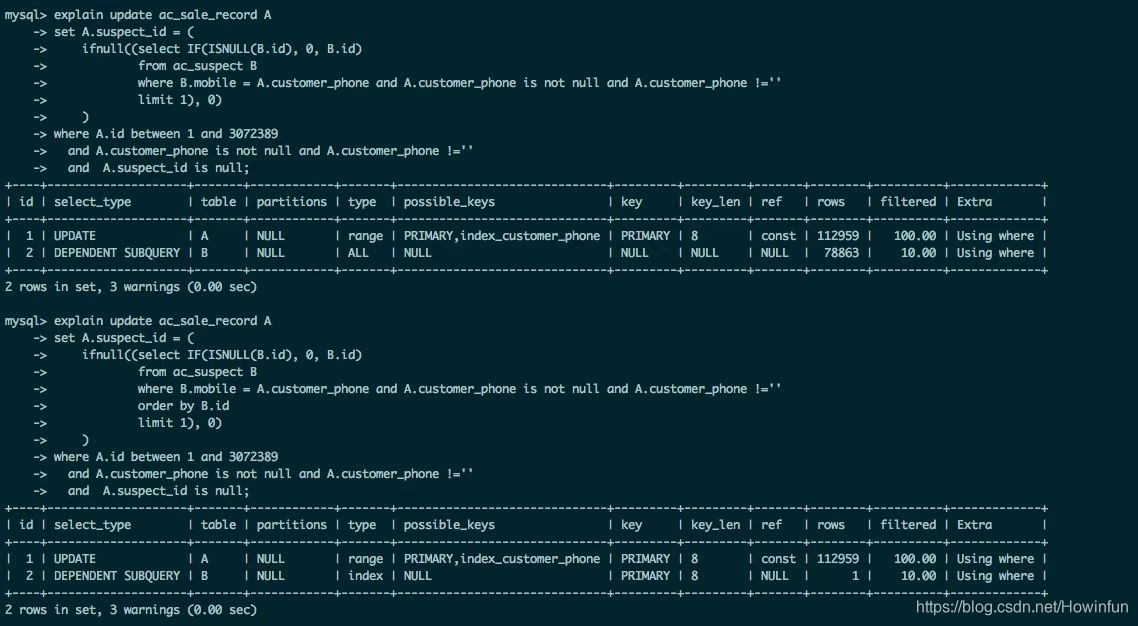
我不是大佬,而且当时我自己的想法也只是猜测,所以并没有回复那位同学,只是接下来自己做了一个测试验证一下。
他只简单了说了一句话,就是同样的sql,一个没加 order by 就全表扫描,一个加了 order by 就走索引了。
我们可以仔细点看一下他提供的图(主要分析子查询即可,就是关于表 B 的查询,因为只有表 B 的查询前后不一致),我们可以先得出两个前提:
1、首先可以肯定的是,where 条件中的 mobile 字段是没有索引的。因为没有 order by 时,是全表扫描,如果 mobile 字段有索引,查询优化器必定会使用 mobile 字段的索引。
2、其实重点不但在 order by,更重要的是在于 order by 后面跟着的字段是 表B 的主键 id。之所以判断 id 为主键,是因为 explain 执行计划里看到使用了 PRIMARY 索引,即主键索引。
二、数据准备和场景重现
创建表 user:
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`phone` varchar(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=100007 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;准备数据:
看了一下截图,数据量应该在10万左右,我们也准备10万数据,尽量做到一致。
delimiter ;
CREATE DEFINER=`root`@`localhost` PROCEDURE `iniData`()
begin
declare i int;
set i=1;
while(i<=100000)do
insert into user(name,age,phone) values('测试', i, 15627230000+i);
set i=i+1;
end while;
end;;
delimiter ;
call iniData();执行 SQL ,查看执行计划:
explain select * from user where phone = '15627231000' limit 1;
explain select * from user where phone = '15627231000' order by id limit 1;执行结果:
id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra
1 SIMPLE user (Null) ALL (Null) (Null) (Null) (Null) 99927 10 Using where
id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra
1 SIMPLE user (Null) index (Null) PRIMARY 4 1 10 Using where我们可以看到,执行计划和那位同学的基本一致,都是第一条 SQL 全表扫描,第二条 SQL 是走了主键索引。
三、猜想和猜测着总结
只要加 order by 就走索引?
根据上面的执行计划来看,明显这位同学的表达是不对的,更重要的是因为 order by 后跟着的字段是主键 id,所以才走了索引,走了主键索引。
我们可以试试用 age 字段来排序,这时候肯定是没有走索引的,因为我们压根没有为 age 字段没有建立索引。
explain select * from user where phone = '15627231000' order by age limit 1;id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra
1 SIMPLE user (Null) ALL (Null) (Null) (Null) (Null) 99927 10 Using where; Using filesort分析:
首先,我们看到 type 是 ALL,就是全表扫描,而且我们还留意到:Extra的值多了 using filesort,表明 mysql 有文件排序的操作。
我们可以拿 order by age 和 order by id 的执行计划来对比一下。
1、explain 的 tepe 字段:
首先,type 不一样,一个是 index,表明利用了索引树;一个是 ALL,表明是全表扫描。
2、explain 的 Extra 字段:
第二,也是最重点的,它其实可以说明为何利用了主键索引。就是 Extra 字段。
先说明一下正常的排序,Extra 都会有 Using filesort 来表明使用了文件排序。
而明显 order by id 是没有这个,这是因为,索引树本来就是一个带有顺序的数据结构,大家不了解的可以去看看 B+Tree 的介绍。查询优化器正是利用了索引的顺序性,使得 SQL 的执行计划走主键索引树来去掉原本需要的排序。
之前的大白话 MySQL 学习总结中也提到过查询优化器。SQL 的执行计划能有很多,并且结果是一样的,但是为了提高性能,MySQL 的查询优化器组件会为 SQL 制定一套最优的执行计划。
阶段总结:
查询优化器帮我们制定的最优计划是:充分利用主键索引的顺序性,避免了全表扫描后还是需要排序操作。
当然了,我们不能自己只是根据现象做判断,下面将利用 Trace 来查看优化器追踪的信息,进一步的验证我们的总结是没问题的。
四、通过 Trace 分析来验证
开启和查看 Trace
-- 开启优化器跟踪
set session optimizer_trace='enabled=on';
select * from user where phone = '15627231000' order by id limit 1;
-- 查看优化器追踪
select * from information_schema.optimizer_trace;下面我们只看 TRACE 就行了。
{
"steps": [
{
"join_preparation": {
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
{
"expanded_query": "/* select#1 */ select `user`.`id` AS `id`,`user`.`name` AS `name`,`user`.`age` AS `age`,`user`.`phone` AS `phone` from `user` where (`user`.`phone` = '15627231000') order by `user`.`id` limit 1"
}
]
}
},
{
"join_optimization": { // 优化工作的主要阶段
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
// .... 省略很多步骤
{
"reconsidering_access_paths_for_index_ordering": { // 重新考虑索引排序的访问路径
"clause": "ORDER BY",
"index_order_summary": {
"table": "`user`",
"index_provides_order": true,
"order_direction": "asc",
"index": "PRIMARY", // 排序的字段为主键 id,有主键索引
"plan_changed": true, // 改变执行计划
"access_type": "index"
}
}
},
{
"refine_plan": [
{
"table": "`user`"
}
]
}
]
}
},
{
"join_explain": {
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
]
}
}
]
}好了,在最后的那里,我们看到了查询优化器帮我们使用了主键索引。
所以,我们上面的猜想是正确的,因为 where 条件后的 phone 字段没有加上索引,所以到 order by id 时,查询优化器发现可以利用主键索引所以来避免排序,所以最后就使用了主键索引。
那么,按照上面的说法,如果 phone 字段加上了索引,那么最后应该就是走 phone 的索引而不是主键索引了。而且,SQL 调优有那么一条建议:建议经常在 where 条件后出现的字段加上索引来提高查询性能。
下面我们来继续验证一下我们的猜想。
五、关于 where 条件字段索引和 order by 字段索引的选择
1、给字段 phone 增加索引:
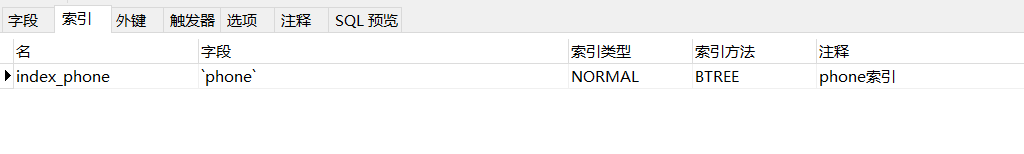
2、执行 SQL :
explain select * from user where phone = '15627231000' order by id limit 1;3、结果:
我们可以看到,最后查询优化器判断 phone索引 比 主键索引 更能提高性能,所以使用了 phone 的索引。
id select_type table partitions type possible_keys key key_len ref rows filtered Extra
1 SIMPLE user (Null) index index_phone index_phone 36 1 100 Using index condition4、Trace进一步验证:
最后,我们可以看到,查询优化器否定了使用主键索引,不改变之前的执行计划。
-- 开启优化器跟踪
set session optimizer_trace='enabled=on';
select * from user where phone = '15627231000' order by id limit 1;
-- 查看优化器追踪
select * from information_schema.optimizer_trace;Trace 分析:
{
"steps": [
{
"join_preparation": {
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
{
"expanded_query": "/* select#1 */ select `user`.`id` AS `id`,`user`.`name` AS `name`,`user`.`age` AS `age`,`user`.`phone` AS `phone` from `user` where (`user`.`phone` = '15627231000') order by `user`.`id` limit 1"
}
]
}
},
{
"join_optimization": {
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
// .... 省略很多步骤
{
"considered_execution_plans": [
{
"plan_prefix": [
],
"table": "`user`",
"best_access_path": {
"considered_access_paths": [
{
"access_type": "ref",
"index": "index_phone",
"rows": 1,
"cost": 1.2,
"chosen": true
},
{
"access_type": "range",
"range_details": {
"used_index": "index_phone" // 使用 phone 的索引
},
"chosen": false,
"cause": "heuristic_index_cheaper"
}
]
},
"condition_filtering_pct": 100,
"rows_for_plan": 1,
"cost_for_plan": 1.2,
"chosen": true
}
]
},
{
"attaching_conditions_to_tables": {
"original_condition": "(`user`.`phone` = '15627231000')",
"attached_conditions_computation": [
],
"attached_conditions_summary": [
{
"table": "`user`",
"attached": null
}
]
}
},
{
"clause_processing": {
"clause": "ORDER BY",
"original_clause": "`user`.`id`",
"items": [
{
"item": "`user`.`id`"
}
],
"resulting_clause_is_simple": true,
"resulting_clause": "`user`.`id`"
}
},
{
"added_back_ref_condition": "((`user`.`phone` <=> '15627231000'))"
},
{
"reconsidering_access_paths_for_index_ordering": { // 重新考虑索引排序的访问路径
"clause": "ORDER BY",
"index_order_summary": {
"table": "`user`",
"index_provides_order": true,
"order_direction": "asc",
"index": "index_phone",
"plan_changed": false // 不改变执行计划
}
}
},
{
"refine_plan": [
{
"table": "`user`",
"pushed_index_condition": "(`user`.`phone` <=> '15627231000')",
"table_condition_attached": null
}
]
}
]
}
},
{
"join_explain": {
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
]
}
}
]
}六、最后总结
到这里,分析就结束了,我们可以得出一个结论,当然了,只是基于上面的实验所得:
1、SQL 带有 order by :
order by 后面的字段有索引:
where 条件后面的所有字段都没索引,则使用 order by 后面的字段的索引。
where 条件后面有字段带有索引,则使用 where 条件对应的字段的索引。
order by 后面的字段没有索引:
- where 条件后面的所有字段都没索引,则全表扫描。
- where 条件后面有字段带有索引,则使用 where 条件后面的字段的索引。
2、SQL 不带 order by:
where 条件后面的所有字段都没索引,则全表扫描。
where 条件后面只要有字段带索引,则使用该字段对应的索引。
最后我们也可以得出一个绝对的结论:查询优化器是真的好使,哈哈哈!
七、题外话
其实上面的实验需要大家对 MySQL 的索引原理有一定的了解,但是不用特别深。
如果大家感兴趣的话,可以关注一下我现在写的 【大白话系列】MySQL 学习总结 这一系列的文章,我会将自己学习 MySQL 后的学习总结分享在这里。
以上是关于MySQL 原理分析之 Trace 分析 order by 的索引原理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章