微服务分享--一致性HASH算法
Posted 程序员地铁时光
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了微服务分享--一致性HASH算法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
微服务往期文章
今日主题: 一致性HASH算法解析代码实现
今日内容: 上一篇文章中主要是对一致性HASH算法进行解析,这篇文章主要是对于一致性HASH原理的JAVA代码实现以及在微服务的负载均衡中的使用做出说明,原理文章链接《》
1.哈希算法的设计
为了能够让机器均衡的分布在各个服务器上,我们使用了MD5算法,主要是用来保证平衡性,即能够使其均衡的分布在整个hash环上,如果使用JDK自带的String类的hashCode方法无法保证平衡性。
import java.security.MessageDigest;import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;/*** @Author smile7up* @createDate 2019-09-08* @Description 一致性hash原理中,使用MD5方法作为均衡算法*/public class Md5HashFunction {private MessageDigest md5 = null;public long hash(String key) {if (md5 == null) {try {md5 = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {throw new IllegalStateException("no md5 algrithm found");}}md5.reset();md5.update(key.getBytes());byte[] bKey = md5.digest();//具体的哈希函数实现细节--每个字节 & 0xFF 再移位long result = ((long) (bKey[3] & 0xFF) << 24)| ((long) (bKey[2] & 0xFF) << 16| ((long) (bKey[1] & 0xFF) << 8) | (long) (bKey[0] & 0xFF));return result & 0xffffffffL;}}
1.不清楚hash算法的可能就会问了,其中25行为什么要与OXFF取与之后再移位呢?
答:为保证生成的Md5字符串为固定长度32
2.后续为什么还要做移位运算呢?主要是为了能够使得获取结果能够更加分散在0~2^32-1值空间之内,更加详细的Md5原理,可以查看以下文章《Md5原理》
有关Hash函数的相关知识,查看另一篇文章:《》
2.一致性hash算法的实现
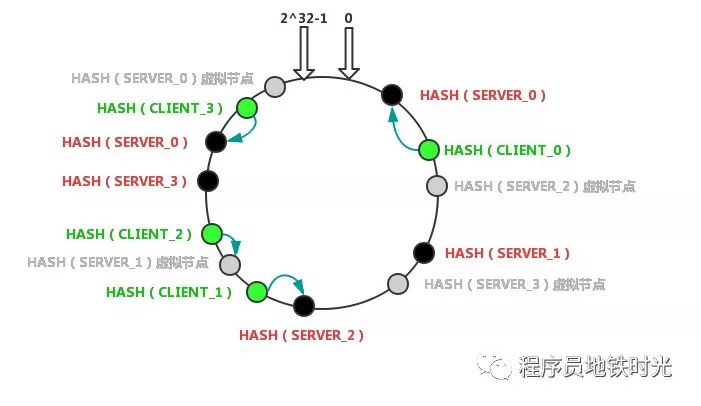
在上一篇文章中,我们讲解了一致性hash算法的原理,其中核心部分就是服务器节点;虚拟节点;客户端节点;服务器节点对一致性Hash环的映射关系;虚拟节点对一致性Hash环的映射关系;客户端节点对一致性Hash环的映射关系;
整体类图如下:
hashFunction: 此处实现相应的接口,即可实现根据不同的场景选择不同的Hash算法
serverReplicators:其中服务器节点和虚拟节点相同,我们只需要定义相应的虚拟节点复制因子,即每个服务器节点复制出多少个虚拟节点;
nodeHashCircle:每个节点对应的Hash环的映射关系,使用SortedMap进行存储,后续可以使用SortedMap中的tailMap方法获取节点的映射
/***tailMap(K fromKey) 方法用于返回此映射,其键大于或等于fromKey的部分*视图。返回的映射受此映射支持,因此改变返回映射反映在此映射中,反之亦然。**/public SortedMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey);
接下来对于每个类进行代码展示,每一部分的代码详解都有详细的注释
ServerNode.java
/*** @Author smile7up* @createDate 2019-09-08* @Description 节点信息的接口*/public interface ServerNode {/*** 根据不同的情况,选择自定义不同的Key** @return*/String getServerNodeKey();}
InstanceServerNode.java
/*** @Author smile7up* @createDate 2019-09-08* @Description 示例节点信息*/public class InstanceServerNode implements ServerNode {/*** 服务器节点名称*/private String serverName;/*** 服务器节点Ip*/private String serverIp;public String getServerName() {return serverName;}public void setServerName(String serverName) {this.serverName = serverName;}public String getServerIp() {return serverIp;}public void setServerIp(String serverIp) {this.serverIp = serverIp;}public String getServerNodeKey() {return serverIp;}}
IHashFunctionService.java
/*** @Author smile7up* @createDate 2019-09-08* @Description hash算法接口*/public interface IHashFunctionService {/*** 获取Hash值* @return*/long hash(String key);}
Md5HashFunctionServiceImpl
/*** @Author smile7up* @createDate 2019-09-08* @Description 使用MD5方法做实现类*/public class Md5HashFunctionServiceImpl implements IHashFunctionService {private MessageDigest md5 = null;public long hash(String key) {if (md5 == null) {try {md5 = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {throw new IllegalStateException("no md5 algrithm found");}}md5.reset();md5.update(key.getBytes());byte[] bKey = md5.digest();//具体的哈希函数实现细节--每个字节 & 0xFF 再移位long result = ((long) (bKey[3] & 0xFF) << 24)| ((long) (bKey[2] & 0xFF) << 16| ((long) (bKey[1] & 0xFF) << 8) | (long) (bKey[0] & 0xFF));return result & 0xffffffffL;}}
ConsistentHash.java
/*** @Author smile7up* @createDate 2019-09-08* @Description 一致性hash原理的实现类*/public class ConsistentHash<T extends ServerNode> {/*** hash算法接口*/private final IHashFunctionService hashFunction;/*** 节点的复制因子,实际节点个数 * serverReplicators = 虚拟节点个数*/private final int serverReplicators;/*** 存储虚拟节点的hash值到真实节点的映射*/private final SortedMap<Long, T> nodeHashCircle = new TreeMap<Long, T>();/*** 构造函数** @param hashFunction hash算法接口* @param serverReplicators 节点复制因子* @param serverNodes 服务节点列表*/public ConsistentHash(IHashFunctionService hashFunction, int serverReplicators,Collection<T> serverNodes) {this.hashFunction = hashFunction;this.serverReplicators = serverReplicators;for (T serverNode : serverNodes)add(serverNode);}/*** 添加一个新的节点** @param serverNode 节点信息*/public void add(T serverNode) {for (int i = 0; i < serverReplicators; i++)// 对于一个实际机器节点 node, 对应 serverReplicators 个虚拟节点/** 不同的虚拟节点(i不同)有不同的hash值,但都对应同一个实际机器node* 虚拟node一般是均衡分布在环上的,数据存储在顺时针方向的虚拟node上*/nodeHashCircle.put(hashFunction.hash(serverNode.getServerNodeKey() + i), serverNode);}/*** 删除旧的节点** @param serverNode 节点信息*/public void remove(T serverNode) {for (int i = 0; i < serverReplicators; i++)nodeHashCircle.remove(hashFunction.hash(serverNode.getServerNodeKey() + i));}/** 获得一个最近的顺时针节点,根据给定的key 取Hash* 然后再取得顺时针方向上最近的一个虚拟节点对应的实际节点* 再从实际节点中取得 数据*/public T get(Object key) {if (nodeHashCircle.isEmpty())return null;long hash = hashFunction.hash((String) key);// node 用String来表示,获得node在哈希环中的hashCodeif (!nodeHashCircle.containsKey(hash)) {//数据映射在两台虚拟机器所在环之间,就需要按顺时针方向寻找机器SortedMap<Long, T> tailMap = nodeHashCircle.tailMap(hash);//获取最邻近的一个节点hash = tailMap.isEmpty() ? nodeHashCircle.firstKey() : tailMap.firstKey();}return nodeHashCircle.get(hash);}public long getSize() {return nodeHashCircle.size();}}
附上均衡性检测的方法
/** 查看MD5算法生成的hashCode值---表示整个哈希环中各个虚拟节点位置*/public void testBalance() {Set<Long> sets = nodeHashCircle.keySet();//获得TreeMap中所有的KeySortedSet<Long> sortedSets = new TreeSet<Long>(sets);//将获得的Key集合排序for (Long hashCode : sortedSets) {System.out.println(hashCode);}System.out.println("----节点间距离为: ----");/** 查看用MD5算法生成的long hashCode 相邻两个hashCode的差值*/Iterator<Long> it = sortedSets.iterator();Iterator<Long> it2 = sortedSets.iterator();if (it2.hasNext()) {it2.next();}long keyPre, keyAfter;while (it.hasNext() && it2.hasNext()) {keyPre = it.next();keyAfter = it2.next();System.out.println(keyAfter - keyPre);}}
最后是测试类:
/*** @Author smile7up* @createDate 2019-09-08* @Description 一致性hash算法的检验类*/public class ConsistentHashTest {public static void main(String[] args) {List<InstanceServerNode> nodeList = new ArrayList<>();InstanceServerNode instanceServerNode1 = new InstanceServerNode();instanceServerNode1.setServerIp("192.168.1.110");instanceServerNode1.setServerName("节点A");InstanceServerNode instanceServerNode2 = new InstanceServerNode();instanceServerNode2.setServerIp("192.168.1.111");instanceServerNode2.setServerName("节点B");InstanceServerNode instanceServerNode3 = new InstanceServerNode();instanceServerNode3.setServerIp("192.168.1.112");instanceServerNode3.setServerName("节点C");InstanceServerNode instanceServerNode4 = new InstanceServerNode();instanceServerNode4.setServerIp("192.168.1.113");instanceServerNode4.setServerName("节点D");nodeList.add(instanceServerNode1);nodeList.add(instanceServerNode2);nodeList.add(instanceServerNode3);nodeList.add(instanceServerNode4);Md5HashFunctionServiceImpl md5HashFunctionService = new Md5HashFunctionServiceImpl();ConsistentHash<InstanceServerNode> consistentHash = new ConsistentHash<InstanceServerNode>(md5HashFunctionService, 5, nodeList);for(int i=0;i<10;i++){InstanceServerNode instanceClientToServer1 = consistentHash.get("客户端"+i);System.out.println("《示例客户端"+i+"》路由服务器IP为:"+instanceClientToServer1.getServerIp());}System.out.println("hash环大小" + consistentHash.getSize());System.out.println("每一个server节点位置为:");consistentHash.testBalance();}}
运行结果如下:
《示例客户端0》路由服务器IP为:192.168.1.111《示例客户端1》路由服务器IP为:192.168.1.110《示例客户端2》路由服务器IP为:192.168.1.110《示例客户端3》路由服务器IP为:192.168.1.113《示例客户端4》路由服务器IP为:192.168.1.110《示例客户端5》路由服务器IP为:192.168.1.113《示例客户端6》路由服务器IP为:192.168.1.110《示例客户端7》路由服务器IP为:192.168.1.110《示例客户端8》路由服务器IP为:192.168.1.112《示例客户端9》路由服务器IP为:192.168.1.112hash环大小20每一个server节点位置为:539519409541648460554276368847166835978640042111030575812049455581369132475221211820423677164542578927039261843824026767703292908662684320993112233119185893318825325359532144238204717934210862366----节点见距离为: ----2129051126279082928904671314732071316657169463980016418691784298572915559825021121058539511201583320892318923553012684381019874676906736276496117225150351390390573
总结:在此示例中,对于Hash算法以及server端进行了封装,后续大家可以对于客户端、一致性hash算法的主实现类进行封装,提出add,remove,get方法,并运用到实际的项目中;大家可以查看注册中心的文章《》第3节,对于注册中心的服务端类(注册中心的客户端)进行了分析说明,结合该类可以自行写出微服务的负载均衡算法
以上是关于微服务分享--一致性HASH算法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章