MATLAB作业选登-无限弱化的图像识别拼接程序
Posted 迈特莱博
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了MATLAB作业选登-无限弱化的图像识别拼接程序相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
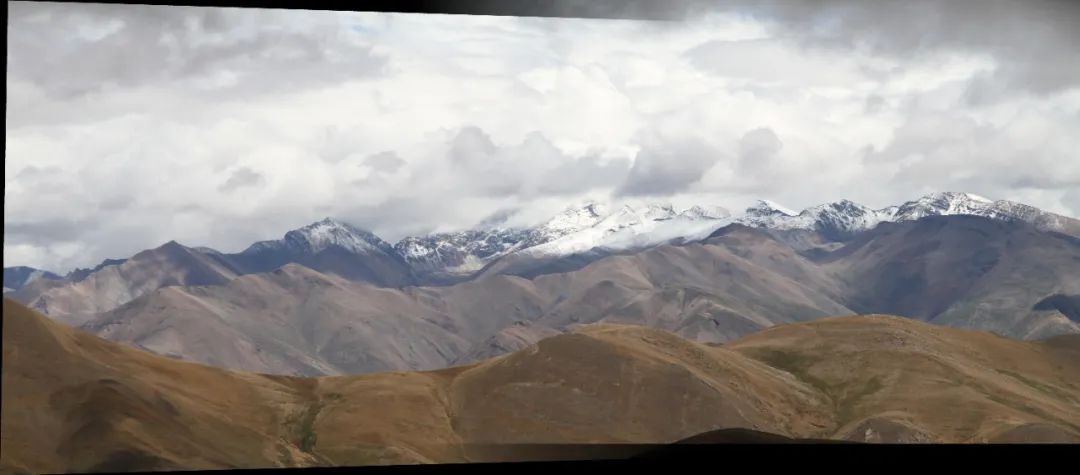

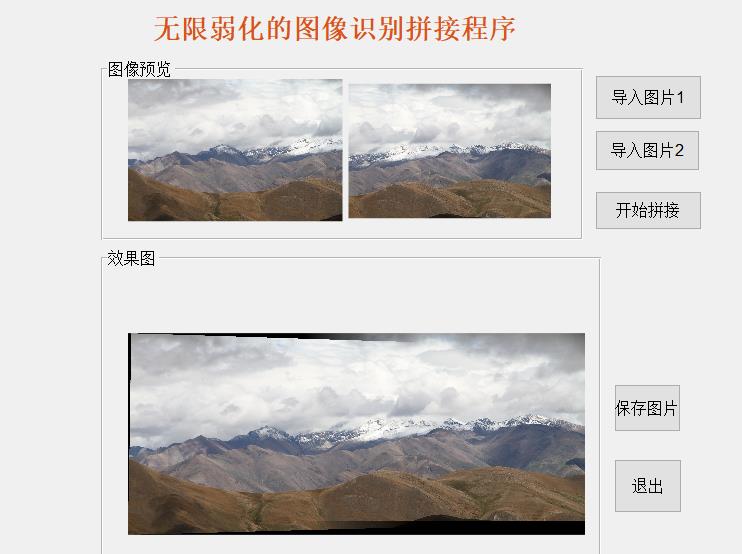

一、程序设计主界面(ImageProcess.fig)
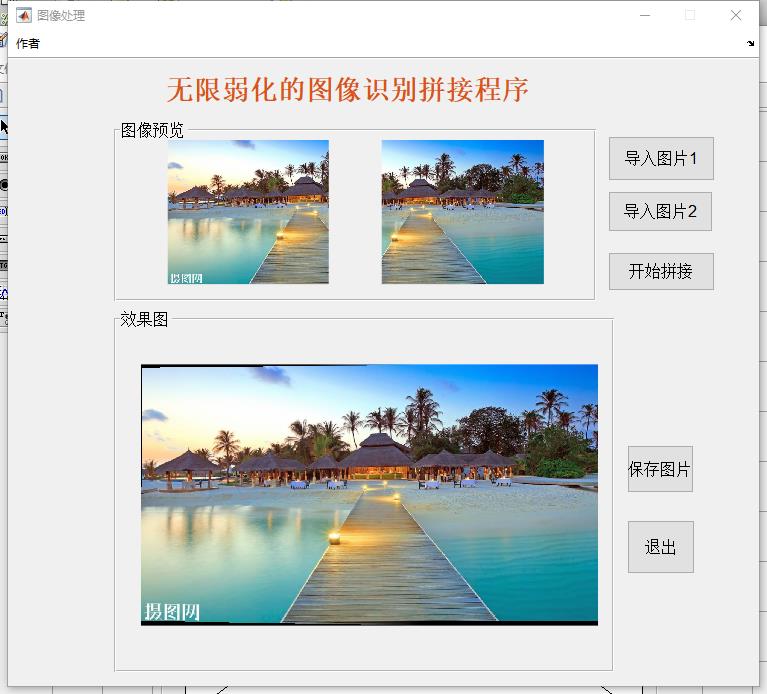
二、程序运行情况
三、程序代码(ImageProcess.m)
function varargout = image(varargin)
% IMAGE MATLAB code for image.fig
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @image_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @image_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
function image_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
handles.output = hObject;
guidata(hObject, handles);
setappdata(handles.figure_function,'newImage',0);
function varargout = image_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
varargout{1} = handles.output;
function m_image_open1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
[filename,pathname]=uigetfile(...
{'*.bmp;*.jpg;*.png;*.jpeg','Image Files(*.bmp,*.jpg,*.png,*.jpeg)';...
'*.*', 'All Files(*,*)'},...
'选择图片');
axes(handles.axes_image1);
fpath=[pathname filename];
global img_src1;
img_src1=imread(fpath);imshow(img_src1);
function m_image_open2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
[filename,pathname]=uigetfile(...
{'*.bmp;*.jpg;*.png;*.jpeg','Image Files(*.bmp,*.jpg,*.png,*.jpeg)';...
'*.*', 'All Files(*,*)'},...
'选择图片');
axes(handles.axes_image2);
fpath=[pathname filename];
global img_src2;
img_src2=imread(fpath);imshow(img_src2);
function image_process_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
global img_src1;
global img_src2;
[height_wrap, width_wrap,~] = size(img_src1);
[height_unwrap, width_unwrap,~] = size(img_src2);
gray_A = im2double(rgb2gray(img_src1));
gray_B = im2double(rgb2gray(img_src2));
[x_A, y_A, v_A] = harris(gray_A, 2, 0.0, 2);
[x_B, y_B, v_B] = harris(gray_B, 2, 0.0, 2);
ncorners = 500;
[x_A, y_A, ~] = ada_nonmax_suppression(x_A, y_A, v_A, ncorners);
[x_B, y_B, ~] = ada_nonmax_suppression(x_B, y_B, v_B, ncorners);
sigma = 7;
[des_A] = getFeatureDescriptor(gray_A, x_A, y_A, sigma);
[des_B] = getFeatureDescriptor(gray_B, x_B, y_B, sigma);
dist = dist2(des_A,des_B);
[ord_dist, index] = sort(dist, 2);
ratio = ord_dist(:,1)./ord_dist(:,2);
threshold = 0.5;
idx = ratio<threshold;
x_A = x_A(idx);
y_A = y_A(idx);
x_B = x_B(index(idx,1));
y_B = y_B(index(idx,1));
npoints = length(x_A);
matcher_A = [y_A, x_A, ones(npoints,1)]';
matcher_B = [y_B, x_B, ones(npoints,1)]';
[hh, ~] = ransacfithomography(matcher_B, matcher_A, npoints, 10);
[newH, newW, newX, newY, xB, yB] = getNewSize(hh, height_wrap, width_wrap, height_unwrap, width_unwrap);
[X,Y] = meshgrid(1:width_wrap,1:height_wrap);
[XX,YY] = meshgrid(newX:newX+newW-1, newY:newY+newH-1);
AA = ones(3,newH*newW);
AA(1,:) = reshape(XX,1,newH*newW);
AA(2,:) = reshape(YY,1,newH*newW);
AA = hh*AA;
XX = reshape(AA(1,:)./AA(3,:), newH, newW);
YY = reshape(AA(2,:)./AA(3,:), newH, newW);
newImage(:,:,1) = interp2(X, Y, double(img_src1(:,:,1)), XX, YY);
newImage(:,:,2) = interp2(X, Y, double(img_src1(:,:,2)), XX, YY);
newImage(:,:,3) = interp2(X, Y, double(img_src1(:,:,3)), XX, YY);
[newImage] = blend(newImage, img_src2, xB, yB);
axes(handles.axes_image3);
imshow(uint8(newImage));
setappdata(handles.figure_function,'newImage',newImage);
function save_image_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
[filename,pathname]=uiputfile({'*.bmp','BMP files';'*.jpg;','JPG files'},'选择路径');
if isequal(filename,0)||isequal(pathname,0)
return;
else
fpath=fullfile(pathname,filename);
end
newImage=getappdata(handles.figure_function,'newImage');
newImage=newImage/255;
imwrite(newImage,fpath);
function exit_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
close(handles.figure_function);
function author_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
function Untitled_3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
function Untitled_1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
h=helpdlg('16017520李青峰','关于作者');
四、其他子函数
1、ada_nonmax_suppression.m
function [newx, newy, newvalue] = ada_nonmax_suppression(xp, yp, value, n)
if(length(xp) < n)
newx = xp;
newy = yp;
newvalue = value;
return;
end
radius = zeros(n,1);
c = .9;
maxvalue = max(value)*c;
for i=1:length(xp)
if(value(i)>maxvalue)
radius(i) = 99999999;
continue;
else
dist = (xp-xp(i)).^2 + (yp-yp(i)).^2;
dist((value*c) < value(i)) = [];
radius(i) = sqrt(min(dist));
end
end
[~, index] = sort(radius,'descend');
index = index(1:n);
newx = xp(index);
newy = yp(index);
newvalue = value(index);
2、blend.m
function [newImage] = blend(warped_image, unwarped_image, x, y)
% MAKE MASKS FOR BOTH IMAGES
warped_image(isnan(warped_image))=0;
maskA = (warped_image(:,:,1)>0 |warped_image(:,:,2)>0 | warped_image(:,:,3)>0);
newImage = zeros(size(warped_image));
newImage(y:y+size(unwarped_image,1)-1, x: x+size(unwarped_image,2)-1,:) = unwarped_image;
mask = (newImage(:,:,1)>0 | newImage(:,:,2)>0 | newImage(:,:,3)>0);
mask = and(maskA, mask);
% GET THE OVERLAID REGION
[~,col] = find(mask);
left = min(col);
right = max(col);
mask = ones(size(mask));
if( x<2)
mask(:,left:right) = repmat(linspace(0,1,right-left+1),size(mask,1),1);
else
mask(:,left:right) = repmat(linspace(1,0,right-left+1),size(mask,1),1);
end
% BLEND EACH CHANNEL
warped_image(:,:,1) = warped_image(:,:,1).*mask;
warped_image(:,:,2) = warped_image(:,:,2).*mask;
warped_image(:,:,3) = warped_image(:,:,3).*mask;
% REVERSE THE ALPHA VALUE
if( x<2)
mask(:,left:right) = repmat(linspace(1,0,right-left+1),size(mask,1),1);
else
mask(:,left:right) = repmat(linspace(0,1,right-left+1),size(mask,1),1);
end
newImage(:,:,1) = newImage(:,:,1).*mask;
newImage(:,:,2) = newImage(:,:,2).*mask;
newImage(:,:,3) = newImage(:,:,3).*mask;
newImage(:,:,1) = warped_image(:,:,1) + newImage(:,:,1);
newImage(:,:,2) = warped_image(:,:,2) + newImage(:,:,2);
newImage(:,:,3) = warped_image(:,:,3) + newImage(:,:,3);
3、dist2.m
function n2 = dist2(x, c)
[ndata, dimx] = size(x);
[ncentres, dimc] = size(c);
if dimx ~= dimc
error('Data dimension does not match dimension of centres')
end
n2 = (ones(ncentres, 1) * sum((x.^2)', 1))' + ...
ones(ndata, 1) * sum((c.^2)',1) - ...
2.*(x*(c'));
% Rounding errors occasionally cause negative entries in n2
if any(any(n2<0))
n2(n2<0) = 0;
end
4、getFeatureDescriptor.m
function [descriptors] = getFeatureDescriptor(input_image, xp, yp, sigma)
% FIRST BLUR WITH GAUSSIAN KERNEL
g = fspecial('gaussian', 5, sigma);
blurred_image = imfilter(input_image, g, 'replicate','same');
% THEN TAKE A 40x40 PIXEL WINDOW AND DOWNSAMPLE TO 8x8 PATCH
npoints = length(xp);
descriptors = zeros(npoints,64);
for i = 1:npoints
%pA = imresize( blurred_image(xp(i)-20:xp(i)+19, yp(i)-20:yp(i)+19), .2);
patch = blurred_image(xp(i)-20:xp(i)+19, yp(i)-20:yp(i)+19);
patch = imresize(patch, .2);
descriptors(i,:) = reshape((patch - mean2(patch))./std2(patch), 1, 64);
end
5、getHomographyMatrix.m
function [hh] = getHomographyMatrix(point_ref, point_src, npoints)
% NUMBER OF POINT CORRESPONDENCES
x_ref = point_ref(1,:)';
y_ref = point_ref(2,:)';
x_src = point_src(1,:)';
y_src = point_src(2,:)';
% COEFFICIENTS ON THE RIGHT SIDE OF LINEAR EQUATIONS
A = zeros(npoints*2,8);
A(1:2:end,1:3) = [x_ref, y_ref, ones(npoints,1)];
A(2:2:end,4:6) = [x_ref, y_ref, ones(npoints,1)];
A(1:2:end,7:8) = [-x_ref.*x_src, -y_ref.*x_src];
A(2:2:end,7:8) = [-x_ref.*y_src, -y_ref.*y_src];
% COEFFICIENT ON THE LEFT SIDE OF LINEAR EQUATIONS
B = [x_src, y_src];
B = reshape(B',npoints*2,1);
% SOLVE LINEAR EQUATIONS
h = AB;
hh = [h(1),h(2),h(3);h(4),h(5),h(6);h(7),h(8),1];
6、getNewSize.m
function [newH, newW, x1, y1, x2, y2] = getNewSize(transform, h2, w2, h1, w1)
% CREATE MESH-GRID FOR THE WARPED IMAGE
[X,Y] = meshgrid(1:w2,1:h2);
AA = ones(3,h2*w2);
AA(1,:) = reshape(X,1,h2*w2);
AA(2,:) = reshape(Y,1,h2*w2);
% DETERMINE THE FOUR CORNER OF NEW IMAGE
newAA = transformAA;
new_left = fix(min([1,min(newAA(1,:)./newAA(3,:))]));
new_right = fix(max([w1,max(newAA(1,:)./newAA(3,:))]));
new_top = fix(min([1,min(newAA(2,:)./newAA(3,:))]));
new_bottom = fix(max([h1,max(newAA(2,:)./newAA(3,:))]));
newH = new_bottom - new_top + 1;
newW = new_right - new_left + 1;
x1 = new_left;
y1 = new_top;
x2 = 2 - new_left;
y2 = 2 - new_top;
7、harris.m
function [xp, yp, value] = harris(input_image, sigma,thd, r)
% CONVERT RGB IMAGE TO GRAY-SCALE, AND BLUR WITH G1 KERNEL
g1 = fspecial('gaussian', 7, 1);
gray_image = imfilter(input_image, g1);
% FILTER INPUT IMAGE WITH SOBEL KERNEL TO GET GRADIENT ON X AND Y
% ORIENTATION RESPECTIVELY
h = fspecial('sobel');
Ix = imfilter(gray_image,h,'replicate','same');
Iy = imfilter(gray_image,h','replicate','same');
% GENERATE GAUSSIAN FILTER OF SIZE 6*SIGMA (± 3SIGMA) AND OF MINIMUM SIZE 1x1
g = fspecial('gaussian',fix(6*sigma), sigma);
Ix2 = imfilter(Ix.^2, g, 'same').*(sigma^2);
Iy2 = imfilter(Iy.^2, g, 'same').*(sigma^2);
Ixy = imfilter(Ix.*Iy, g, 'same').*(sigma^2);
% HARRIS CORNER MEASURE
R = (Ix2.*Iy2 - Ixy.^2)./(Ix2 + Iy2 + eps);
% ANOTHER MEASUREMENT, USUALLY k IS BETWEEN 0.04 ~ 0.06
% response = (Ix2.*Iy2 - Ixy.^2) - k*(Ix2 + Iy2).^2;
% GET RID OF CORNERS WHICH IS CLOSE TO BORDER
R([1:20, end-20:end], :) = 0;
R(:,[1:20,end-20:end]) = 0;
% SUPRESS NON-MAX
d = 2*r+1;
localmax = ordfilt2(R,d^2,true(d));
R = R.*(and(R==localmax, R>thd));
% RETURN X AND Y COORDINATES
[xp,yp,value] = find(R);
8、ransacfithomography.m
function [hh, inliers] = ransacfithomography(ref_P, dst_P, npoints, threshold);
ninlier = 0;
fpoints = 8; %number of fitting points
for i=1:2000
rd = randi([1 npoints],1,fpoints);
pR = ref_P(:,rd);
pD = dst_P(:,rd);
h = getHomographyMatrix(pR,pD,fpoints);
rref_P = h*ref_P;
rref_P(1,:) = rref_P(1,:)./rref_P(3,:);
rref_P(2,:) = rref_P(2,:)./rref_P(3,:);
error = (rref_P(1,:) - dst_P(1,:)).^2 + (rref_P(2,:) - dst_P(2,:)).^2;
n = nnz(error<threshold);
if(n >= npoints*.95)
hh=h;
inliers = find(error<threshold);
pause();
break;
elseif(n>ninlier)
ninlier = n;
hh=h;
inliers = find(error<threshold);
end
end
文件目录如下:
以上是关于MATLAB作业选登-无限弱化的图像识别拼接程序的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
matlab图像如何用代码完成图像的分割、边缘检测和拼接的任务?