编译原理 LL语法分析器的设计与实现
Posted Ice丨shine
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了编译原理 LL语法分析器的设计与实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
实验内容
针对SysY语言中简单算术表达式文法G[E]:
E→TE’
E’→ATE’|ε
T→FT’
T’→MFT’ |ε
F→(E) | i
A → + | -
M → * | /
求解相应的FIRST、FOLLOW集,构造预测分析表,并编写LL(1)语法分析程序,并给出测试句子的分析过程。
- 输入:是词法分析输出的二元组序列,即任意简单算术表达式经过专题1程序输出后得到的结果。【上述文法中i即对应词法分析的标识符, ±*/分别对应词法分析得到的运算符】
- 处理:基于分析表进行 LL(1)语法分析,判断其是否符合文法。
- 输出:串是否合法。
设计方法
给出语法分析表
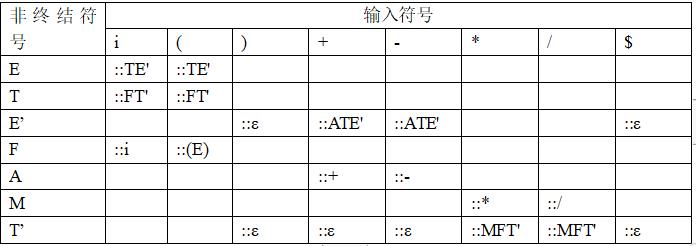
1.使用两个map储存该表,第一个表为Map<Character,Map>,储存左侧非终结符号和右侧输入符号对应的map,第二个map为Map<Character,String>,储存输入符号和应该转换为的字符串。
2.利用栈Deque来储存需要转换的符号,从E开始。每次开始遍历时先弹出栈顶符号,通过map的搜索找到对应的字符串,将字符串压入栈,如果不存在则跳过。并设置错误标记,如果有跳过则最后输出“不符合文法”。如果栈顶的符号和当前字符串符号相同,则输出匹配,遇到空值ε时,字符串往后一位,不把ε压入栈。
3.若栈或者字符串序列有一者率先到达底端,则直接报错。
函数定义
public static void Init()//初始化分析表
public static String txt2String(File file)//读入txt
public static void analyze(String s)//分析程序
程序
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Map;
public class LL1_2 {//LL(1)语法分析器的设计与实现
static Deque<Character> deque = new LinkedList<>();
static Map<Character,Map<Character,String>> mapcol = new HashMap<>();//找列
static String str="";
public static void Init(){//载入表格,X代表E',Y代表T',这里可以用语法糖简化书写
Map<Character,String> maprow1 = new HashMap<>();
maprow1.put('i',"TX");
maprow1.put('(',"TX");
mapcol.put('E',maprow1);
Map<Character,String> maprow2 = new HashMap<>();
maprow2.put('i',"FY");
maprow2.put('(',"FY");
mapcol.put('T',maprow2);
Map<Character,String> maprow3 = new HashMap<>();
maprow3.put(')',"ε");
maprow3.put('+',"ATX");
maprow3.put('-',"ATX");
maprow3.put('$',"ε");
mapcol.put('X',maprow3);
Map<Character,String> maprow4 = new HashMap<>();
maprow4.put('i',"i");
maprow4.put('(',"(E)");
mapcol.put('F',maprow4);
Map<Character,String> maprow5 = new HashMap<>();
maprow5.put('+',"+");
maprow5.put('-',"-");
mapcol.put('A',maprow5);
Map<Character,String> maprow6 = new HashMap<>();
maprow6.put('*',"*");
maprow6.put('/',"/");
mapcol.put('M',maprow6);
Map<Character,String> maprow7 = new HashMap<>();
maprow7.put(')',"ε");
maprow7.put('+',"ε");
maprow7.put('-',"ε");
maprow7.put('$',"ε");
maprow7.put('*',"MFY");
maprow7.put('/',"MFY");
mapcol.put('Y',maprow7);
// System.out.println(mapcol);
deque.push('$');
deque.push('E');//初始符号入栈
}
public static String txt2String(File file){
try{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));//构造一个BufferedReader类来读取文16
String s = null;
while((s = br.readLine())!=null){//使用readLine方法,一次读一行
str = str +s;
}
br.close();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return str;
}
public static void analyze(String s){
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
int length = s.length();
int index=0;
int flag = 0,flagk=0;
while(!deque.isEmpty()&&index<length){
Character pop = deque.pop();
if(pop=='$'&&index!=length-1) {
System.out.println("已到栈底,错误!");
break;
}else if(chars[index]=='$'&&!mapcol.containsKey(pop)&&pop!='$'){//判断是否非终结符
System.out.println("字符串到底,错误!");
break;
}
if(pop==chars[index]){
index++;
System.out.println("匹配"+pop);
continue;
}
Map map = mapcol.get(pop);//找到对应的行
if(map.containsKey(chars[index])) {//找到该符号在表中是否符合条件
Object o = map.get(chars[index]);
char[] chars1 = o.toString().toCharArray();
if(chars1[0]!='ε') {
for (int i = chars1.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
deque.push(chars1[i]);
}
}
System.out.println(deque);
}else{
System.out.println("错误,略过当前记号");
flag=1;
index++;
}
}
System.out.println("分析结束");
if(flag==1||flagk==1) System.out.println("不符合文法!");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("diguiin.txt");
File file2 = new File("diguiout.txt");
str = txt2String(file);
System.out.println(str);
Init();
analyze(str);
}
}
程序测试
输入:i*i+i$
输出:
[T, X, $]
[F, Y, X, $]
[i, Y, X, $]
匹配i
[M, F, Y, X, $]
[*, F, Y, X, $]
匹配*
[i, Y, X, $]
匹配i
[X, $]
[A, T, X, $]
[+, T, X, $]
匹配+
[F, Y, X, $]
[i, Y, X, $]
匹配i
[X, $]
[$]
匹配$
分析结束
输入:i*(i+i)$
输出:
[T, X, $]
[F, Y, X, $]
[i, Y, X, $]
匹配i
[M, F, Y, X, $]
[*, F, Y, X, $]
匹配*
[(, E, ), Y, X, $]
匹配(
[T, X, ), Y, X, $]
[F, Y, X, ), Y, X, $]
[i, Y, X, ), Y, X, $]
匹配i
[X, ), Y, X, $]
[A, T, X, ), Y, X, $]
[+, T, X, ), Y, X, $]
匹配+
[F, Y, X, ), Y, X, $]
[i, Y, X, ), Y, X, $]
匹配i
[X, ), Y, X, $]
[), Y, X, $]
匹配)
[X, $]
[$]
匹配$
分析结束
输入:i*i+i)$
输出:
[T, X, $]
[F, Y, X, $]
[i, Y, X, $]
匹配i
[M, F, Y, X, $]
[*, F, Y, X, $]
匹配*
[i, Y, X, $]
匹配i
[X, $]
[A, T, X, $]
[+, T, X, $]
匹配+
[F, Y, X, $]
[i, Y, X, $]
匹配i
[X, $]
[$]
已到栈底,错误!
分析结束
输入:i*i+ii$
输出:
[T, X, $]
[F, Y, X, $]
[i, Y, X, $]
匹配i
[M, F, Y, X, $]
[*, F, Y, X, $]
匹配*
[i, Y, X, $]
匹配i
[X, $]
[A, T, X, $]
[+, T, X, $]
匹配+
[F, Y, X, $]
[i, Y, X, $]
匹配i
错误,略过当前记号
[$]
匹配$
分析结束
不符合文法!
以上是关于编译原理 LL语法分析器的设计与实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章