NIO--05--非阻塞网络通信 选择器(Selector)和 管道(Pipe)
Posted 高高for 循环
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了NIO--05--非阻塞网络通信 选择器(Selector)和 管道(Pipe)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
选择器(Selector)
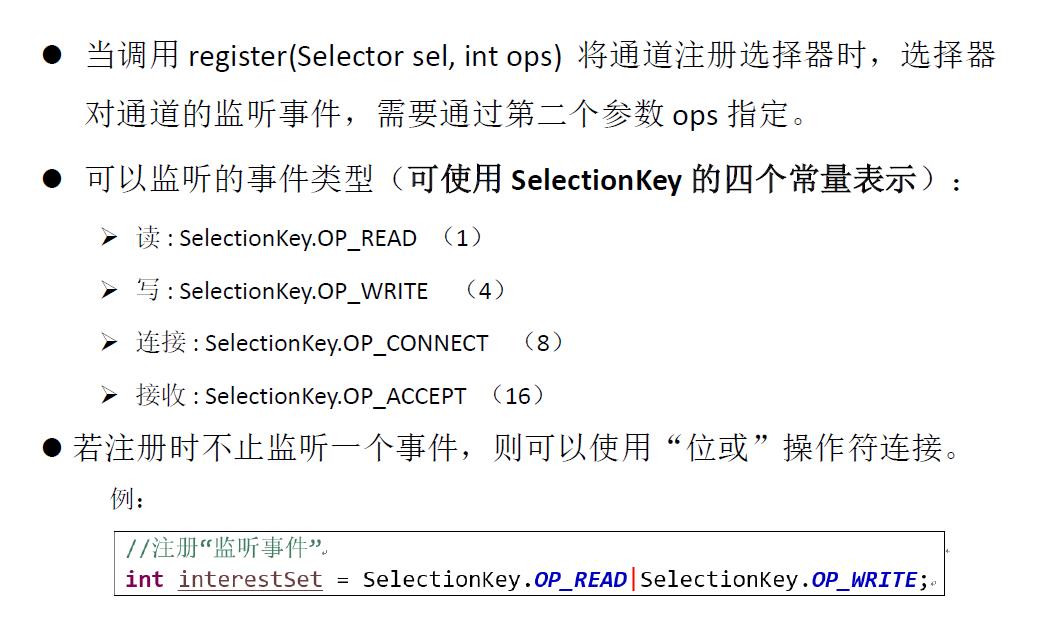
选择器是SelectableChannel对象的多路复用器,Selector可以同时监控多个SelectableChannel的IO状况,
即Selector可监控的对象必须式SelectChannel的子类,Selector是非阻塞IO的核心
选择器的使用方式
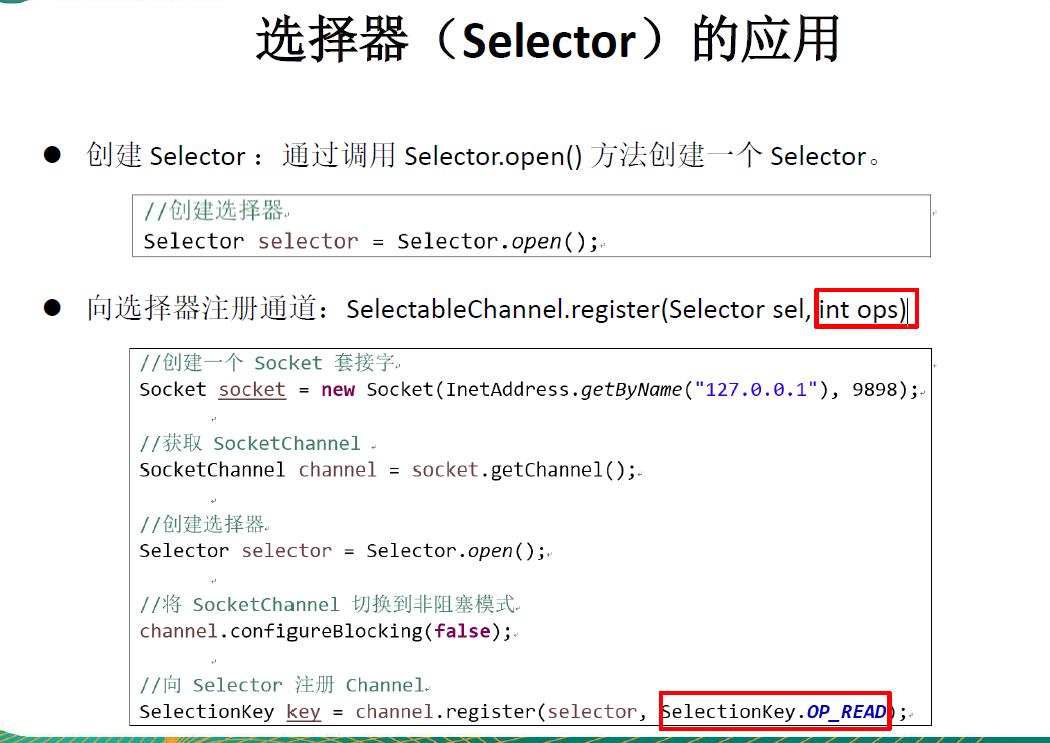
将通道注册到选择器上, 并且指定“监听接收事件”
SelectableChannel.register(Selector sel, int ops)
其中关于ops表示指定选择器所要监听的事件
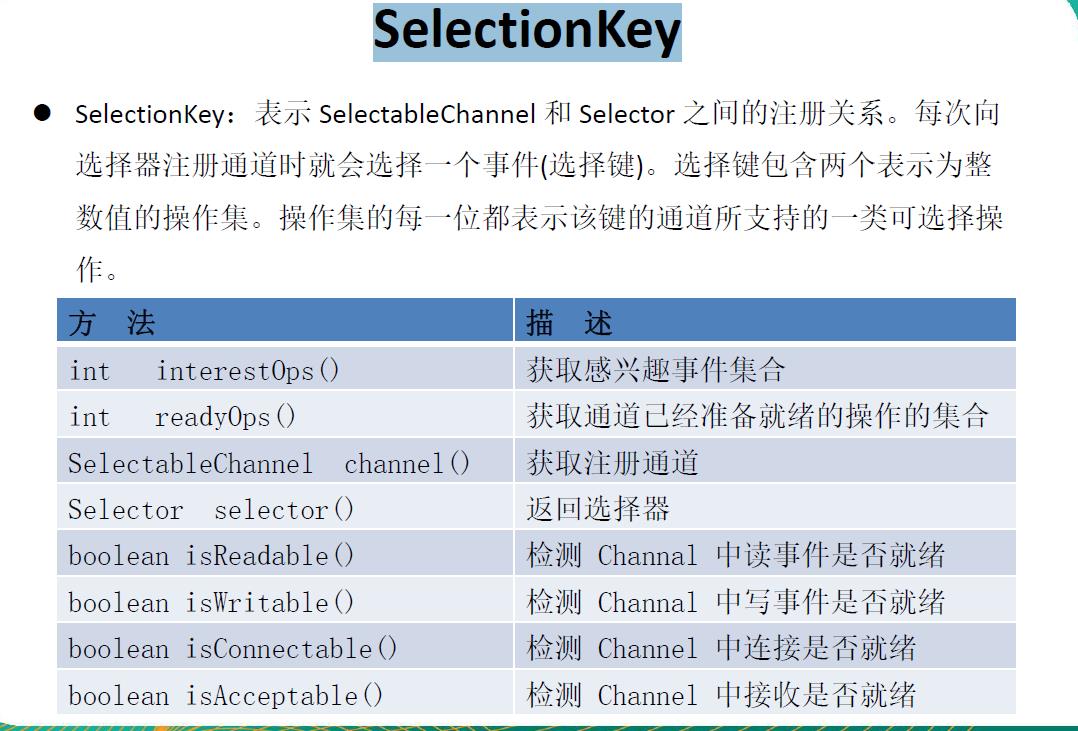
SelectionKey
表示SelectableChannel 和Selector 之间的注册关系
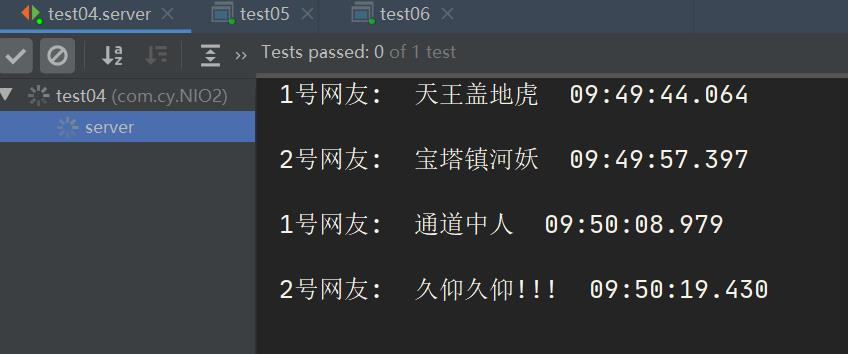
案例1 : 做一个聊天室
客户端 1:
注意: idea只有在main方法里面才能使用Scanner函数,Test里面不行
package com.cy.NIO2;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class test06 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1. 获取通道
SocketChannel sChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9899));
//2. 切换非阻塞模式
sChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//3. 分配指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//4. 发送数据给服务端
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
while(scan.hasNext()){
String str = scan.next();
buf.put(("1号网友: "+ str+" "+ LocalTime.now() +"\\n" ).getBytes());
buf.flip();
sChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear();
}
//5. 关闭通道
sChannel.close();
}
}
客户端 2:
package com.cy.NIO2;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class test05 {
//客户端
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1. 获取通道
SocketChannel sChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9899));
//2. 切换非阻塞模式
sChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//3. 分配指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//4. 发送数据给服务端
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
while(scan.hasNext()){
String str = scan.next();
buf.put(("2号网友: "+ str+" "+ LocalTime.now() +"\\n" ).getBytes());
buf.flip();
sChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear();
}
//5. 关闭通道
sChannel.close();
}
}
服务端:
package com.cy.NIO2;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class test01 {
//服务端
@Test
public void server() throws IOException {
//1. 获取通道
ServerSocketChannel ssChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//2. 切换非阻塞模式
ssChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//3. 绑定连接
ssChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9899));
//4. 获取选择器
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//5. 将通道注册到选择器上, 并且指定“监听接收事件”
ssChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
//6. 轮询式的获取选择器上已经“准备就绪”的事件
while(selector.select() > 0){
//7. 获取当前选择器中所有注册的“选择键(已就绪的监听事件)”
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
//8. 获取准备“就绪”的是事件
SelectionKey sk = it.next();
//9. 判断具体是什么事件准备就绪
if(sk.isAcceptable()){
//10. 若“接收就绪”,获取客户端连接
SocketChannel sChannel = ssChannel.accept();
//11. 切换非阻塞模式
sChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//12. 将该通道注册到选择器上
sChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}else if(sk.isReadable()){
//13. 获取当前选择器上“读就绪”状态的通道
SocketChannel sChannel = (SocketChannel) sk.channel();
//14. 读取数据
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int len = 0;
while((len = sChannel.read(buf)) > 0 ){
buf.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(), 0, len));
buf.clear();
}
}
//15. 取消选择键 SelectionKey
it.remove();
}
}
}
}
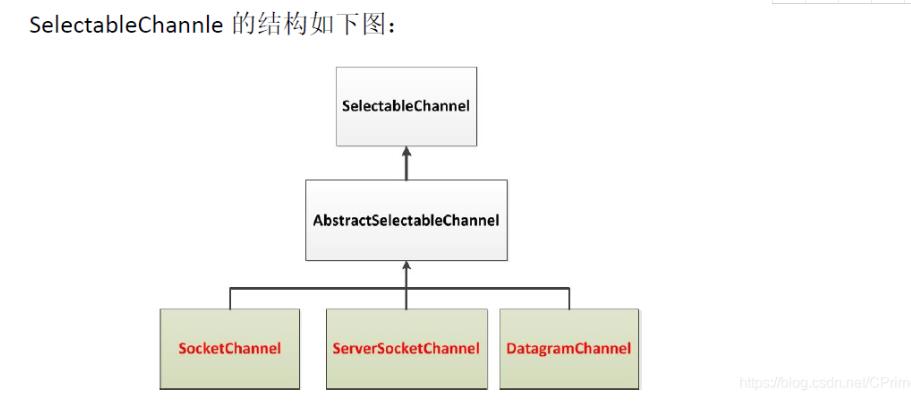
SocketChannel 和 DatagramChannel



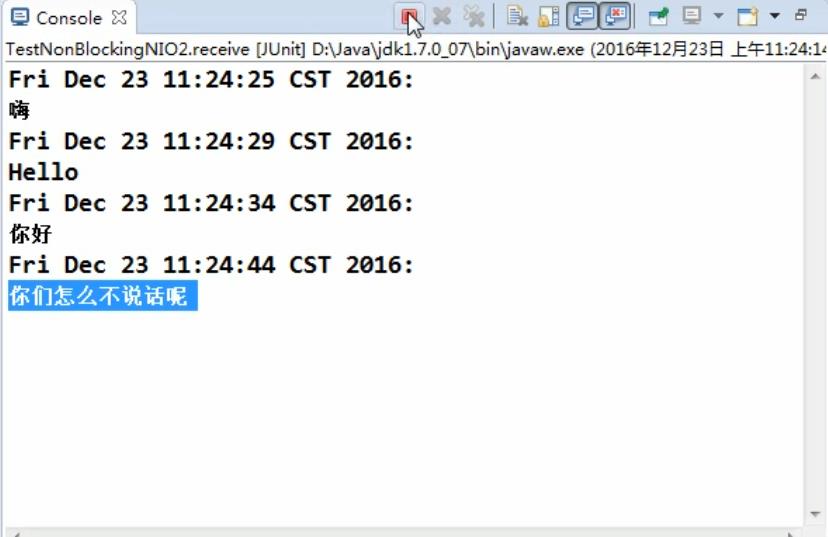
案例2 : UTP传输案例
DatagramChannel
package com.atguigu.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.DatagramChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Scanner;
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestNonBlockingNIO2 {
@Test
public void send() throws IOException{
DatagramChannel dc = DatagramChannel.open();
dc.configureBlocking(false);
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
while(scan.hasNext()){
String str = scan.next();
buf.put((new Date().toString() + ":\\n" + str).getBytes());
buf.flip();
dc.send(buf, new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9898));
buf.clear();
}
dc.close();
}
@Test
public void receive() throws IOException{
DatagramChannel dc = DatagramChannel.open();
dc.configureBlocking(false);
dc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9898));
Selector selector = Selector.open();
dc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
while(selector.select() > 0){
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
SelectionKey sk = it.next();
if(sk.isReadable()){
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
dc.receive(buf);
buf.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(), 0, buf.limit()));
buf.clear();
}
}
it.remove();
}
}
}
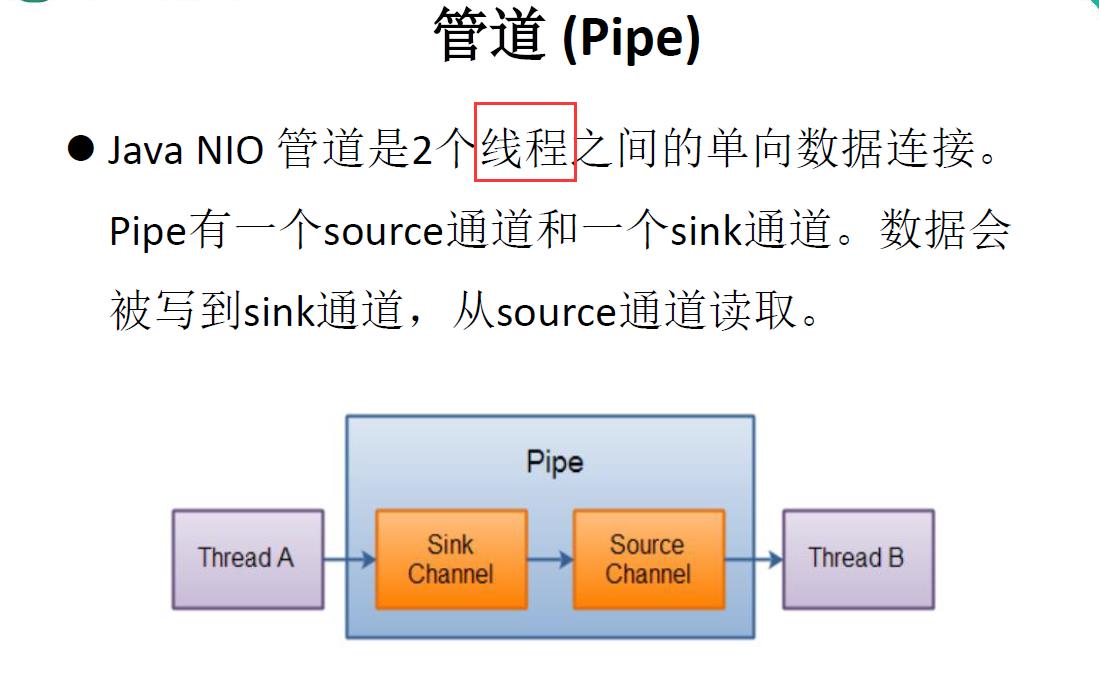
管道(Pipe)


案例:
package com.atguigu.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.Pipe;
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestPipe {
@Test
public void test1() throws IOException{
//1. 获取管道
Pipe pipe = Pipe.open();
//2. 将缓冲区中的数据写入管道
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
Pipe.SinkChannel sinkChannel = pipe.sink();
buf.put("通过单向管道发送数据".getBytes());
buf.flip();
sinkChannel.write(buf);
//3. 读取缓冲区中的数据
Pipe.SourceChannel sourceChannel = pipe.source();
buf.flip();
int len = sourceChannel.read(buf);
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(), 0, len));
sourceChannel.close();
sinkChannel.close();
}
}
以上是关于NIO--05--非阻塞网络通信 选择器(Selector)和 管道(Pipe)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章