恋上数据结构与算法第一季笔记——二叉搜索树
Posted Johnny*
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了恋上数据结构与算法第一季笔记——二叉搜索树相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
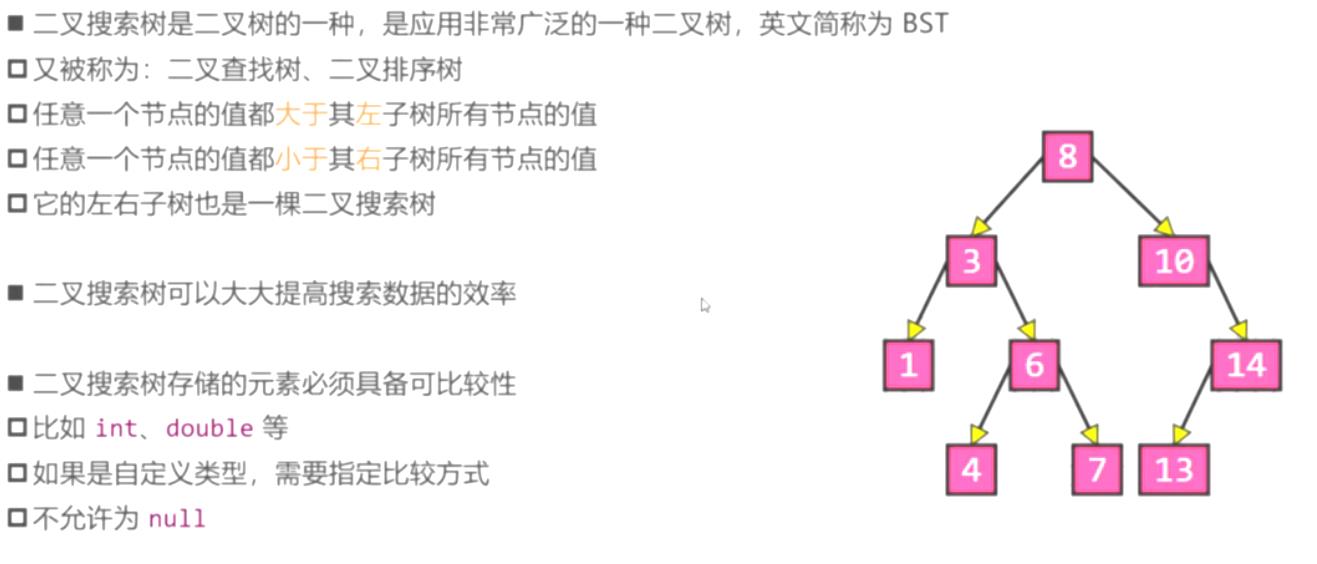
二叉搜索树
二叉搜索树的接口实现
BinarySearchTree
BinarySearchTree 属性与构造方法
//元素数量
private int size;
//二叉搜索树根节点
private Node root;
//比较器:由外部定义比较规则,并将比较器传进来使用
private Comparator comparator;
//带比较器的构造方法
public BinarySearchTree(Comparator comparator){
this.comparator = comparator;
}
//不带比较器则默认使用comparable的比较方法
public BinarySearchTree(){
this(null);
}
//内部类
private static class Node<E>{
private Node<E> parent;
private Node<E> left;
private Node<E> right;
private E element;
public Node(Node<E> parent, E element){
this.parent = parent;
this.element = element;
}
}
这里若外部构造BinarySearchTree时使用不传入比较器,则使用Comparable的比较方法,这样比较规则是由内部定义的,除非进入Comparable接口修改比较规则,否则是无法按自定义比较的。
若想自定义比较,则用户可在外部定义比较规则,再使用使用带比较器的构造方法将构造器传进来。
size()
/**
* 元素数量
* @return
*/
public int size(){
return size;
}
isEmpty()
/**
* 二叉搜索树是否为空
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
add()
public void add( E element){
//二叉树树不允许节点为空 插入前先判断
elementNotNullChck(element);
//添加第一个节点
if( root == null){
root = new Node<>(null, element);
size ++;
return ;
}
int cmp = 0;
Node<E> node = root;
Node<E> parent = root; //记录待插入节点的父节点位置
//找到待插入节点的父节点
while( node != null){//非叶子节点的下层
parent = node;
cmp = compare( element , node.element);
/**
* 待插入节点元素 与当前节点元素值比较:
* 1.小于则进入左子树
* 2.大于则进入右子树
* 3.等于则直接返回
*/
if( cmp < 0 ) node = node.left;
else if( cmp > 0) node = node.right;
else return;
}
Node newNode = new Node<>(parent, element);
if( cmp < 0) parent.left = newNode;
else parent.right = newNode;
//最后不要忘记了: 节点数目++
size ++;
}
private void elementNotNullChck(E element){
if( element == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("element must not be null");
}
public int compare(E e1, E e2){
if( this.comparator == null)
return ((Comparable)e1).compareTo(e2);
else
return this.comparator.compare(e1, e2);
}
Main类测试
匿名内部类
Comparator是一个接口,本身是不能new的,实际上是有一个匿名类实现的了该接口然后再new。
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//匿名内部类
BinarySearchTree<Person> bst1 = new BinarySearchTree<>(new Comparator<Person>() {
@Override
public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {
return o1.getAge() - o2.getAge();
}
});
}
}
作用于上面等效不过,上面代码较为紧凑,不用声明类PesonComparator 实现Comparator接口
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Main {
static class PesonComparator implements Comparator<Person> {
@Override
public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {
return o1.getAge() - o2.getAge();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinarySearchTree<Person> bst = new BinarySearchTree<>( new PesonComparator()) ;
bst.add( new Person(52));
bst.add( new Person(25));
}
}
以上是关于恋上数据结构与算法第一季笔记——二叉搜索树的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
学习数据结构笔记(12) --- [平衡二叉搜索树(AVLTREE)]