C++ 文件读写
Posted 我是小白呀
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C++ 文件读写相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
概述
所谓 “文件”, 一般指存储在外部介质上的数据的集合.
一批数据是以文件的形式存放在外部介质上的. 操作系统是以文件的单位对数据进行管理.

文件分类
按存储介质:
- 磁盘文件
- 光盘文件
- U 盘文件
按用途:
- 程序文件 (program file)
- 数据文件 (data file)
按文件中数据的组织形式
- ASCII 文件: 以 ASCII 表示的文件 (如 .txt, .cpp)
- 二进制文件: 用二进制形式表示的文件 (如 .o, .exe)
文件流
文件流
- 输出文件流是从内存流向外存文件的数据
- 输入文件流是从外存文件流向内存的数据
- 每一个文件流都有一个内存缓冲区与之对应
文件流 vs. 文件的:
- 文件流本身不是文件, 是以文件为输入输出对象的流
- 要对磁盘文件输入输出, 必须通过文件流来实现
- 文件操作需要流对象, cout, cin 是已定义的流对象
流对象
在 C++ I/O 类库中专门用于文件操作的类:
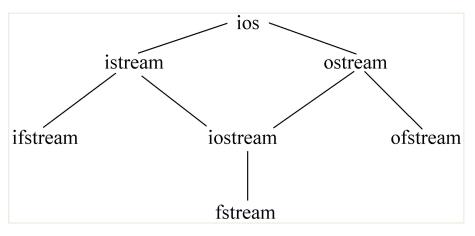
要对文件输入输出, 必须定义一个文件流类的对象. C++ 是通过流对象进行输入输出的:
- 在用标准设备为对象的输入输出中, cin, cout 是流对象
- 文件操作也是要定义对象, 例如: ofstream outfile
打开文件
打开文件是指在文件读写之前必要的准备工作. 打开分拣为流对象和指定磁盘文件建立关联, 以便使文件流流向指定的磁盘文件, 指定文件的工作方式.

打开文件有两种不同方法, 调用 open 函数和调用文件流构造函数.
open 函数
调用文件流的成员函数 open, 如:
ofstream outfile; // 定义输出文件流类对象
outfile.open(″f1.dat″,ios::out);
构造函数
在定义文件流对象是调用文件流类的构造函数:
istream infile(″c:\\\\new\\\\f1.dat″, ios::in);
打开文件的方式
| 方式 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ios::in | 供读, 文件不存在时, 打开失败 |
| ios::out | 供写, 文件不存在则创建, 若文件已存在, 则清空内容 |
| ios::ate | 文件打开时, 指针在文件最后. 可改变指针位置, 常和 in, out 联合使用 |
| ios::app | 供写, 文件不存在则创建, 若文件已存在, 则在原文内容后添加写入新的内容 |
| ios::trunc | 在读写前先将文件长度截断为 0 |
| ios::nocreate | 文件不存在时产生错误, 常和 in 或 app 联合使用 |
| ios::noreplace | 文件存在时产生错误, 常和 out 联合使用 |
| ios::binary | 二进制格式文件 |
如果打开操作失败, open 函数的返回值为 0. 如果是调用构造函数的方式打开文件的, 则流对象的值为 0.
关闭文件
在对已打开的磁盘文件的续写操作完成后, 应该关闭该文件. 例如:
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a[10];
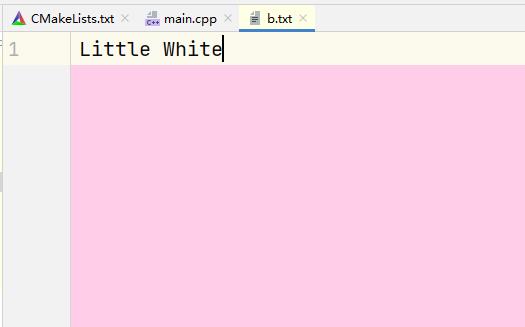
ofstream outfile("b.txt"); // 打开文件
outfile << "Little White"; // 输出
outfile.close(); // 关闭磁盘文件
return 0;
}
输出结果:
ASCII 文件操作
ASCII 文件, 即字符文件. 文件中的每一个字节均以 ASCII 代码的形式存放, 即一个字节存放一个字符.
程序可以从 ASCII 文件中读取若干个字符, 也可以向它输出一些字符.
对 ASCII 文件的读写操作的方法:
- 用流插入运算符
<<和流提取运算符>>输入输出标准类型的数据 - 用文件流的 put, get, getline 等成员函数进行字符串的输入输出
写入文件
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a[10];
// 打开文件
ofstream outfile("a.txt", ios::out);
if(!outfile){
cerr << "open error!" << endl;
exit(1); // 退出
}
// 操作文件
cout << "enter 10 integer numbers:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) { // 输入10次
cin >> a[i];
outfile << a[i] << " ";
}
// 关闭文件
cout << "The numbers have been writen to file." << endl;
outfile.close();
return 0;
}
读取文件
从文件读取整数, 并输出数中最大的数已经序列号.
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a[10], max, index;
// 打开文件
ifstream infile("a.txt", ios::in);
if(!infile){
cerr << "open error!" << endl;
exit(1); // 退出
}
// 操作文件
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) { // 输入10次
infile >> a[i];
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 关闭文件
cout << "The numbers have been read." << endl;
// 取最大
max = a[0]; // 初始化为第一个
index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
if(a[i] > max){
max = a[i];
index = i;
}
}
cout << "max= " << max << endl;
cout << "index= " << index << endl;
return 0;
}
输出结果:
1 3 5 4 6 8 4 2 1 2
The numbers have been read.
max= 8
index= 5
读写文件
从键盘读入一行字符, 把其中的小写字母字符依次存放在文件中. 再从文件中读出, 将其中的小写字母改为大写字母, 重新读入.
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
void get();
void set();
using namespace std;
int main() {
set();
get();
return 0;
}
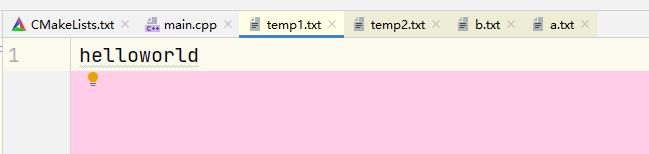
void set() {
ofstream outfile("temp1.txt");
if(!outfile) {
cerr << "open temp1 error" << endl;
exit(1);
}
char c[80];
cin.getline(c,80);
for(int i=0; c[i]!=0; i++)
if(c[i]>='a' && c[i]<='z')
outfile.put(c[i]);
outfile.close();
}
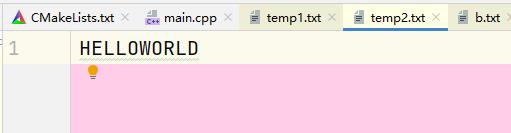
void get() {
char ch;
ifstream infile("temp1.txt", ios::in);
if(!infile) {
cerr << "open temp1 error" << endl;
exit(1);
}
ofstream outfile("temp2.txt");
if(!outfile) {
cerr << "open temp2 error" << endl;
exit(1);
}
while(infile.get(ch)){
outfile.put(ch - 32);
}
outfile.close();
infile.close();
}
输出结果:
以上是关于C++ 文件读写的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
我的Android进阶之旅NDK开发之在C++代码中使用Android Log打印日志,打印出C++的函数耗时以及代码片段耗时详情