源码分析:Spring是如何跟JDK动态代理结合
Posted Jeff.S
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了源码分析:Spring是如何跟JDK动态代理结合相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
从jdk代理的demo说起
首先看下基于JDK的动态代理是怎么实现的,先来一个简单的demo。
package com.jeff.study.proxy;
public interface PersonService {
void save(String user) throws Exception;
}
package com.jeff.study.proxy;
public class PersonServiceImpl implements PersonService {
private String user = null;
public PersonServiceImpl() {
}
public PersonServiceImpl(String user) {
this.user = user;
}
public final void save(String personid) throws Exception {
if (user != null) {
System.out.println("============" + personid);
} else {
System.out.println("------------" + personid);
}
}
public String getUser() {
return user;
}
}
package com.jeff.study.proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
public class JDKProxyFactory implements InvocationHandler {
private Object targetObject;
//根据目标对象生成代理对象
public Object createProxyInstance(Object targetObject) {
this.targetObject = targetObject;
Object proxyObj = Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.targetObject.getClass().getClassLoader(),
this.targetObject.getClass().getInterfaces(), this);
return proxyObj;
}
/**
* 当生成的代理对象调用相应的业务方法时,就会回调这个方法,
* 并根据目标对象的user是否为空判断是否执行目标对象的业务方法。
*/
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {//环绕通知
PersonServiceImpl bean = (PersonServiceImpl) this.targetObject;
Object result = null;
if (bean.getUser() != null) {
try {
//......Advice--->前置通知
System.out.println("before advice......");
result = method.invoke(targetObject, args);
System.out.println("after advice......");
//......AfterAdvice--->后置通知
} catch (Exception e) {
//......ExceptionAdvice--->例外通知
System.out.println("ExceptionAdvice......");
} finally {
//......finallyAdvice--->最后通知
System.out.println("finally Advice......");
}
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
JDKProxyFactory factory = new JDKProxyFactory();
Object proxyObj = factory.createProxyInstance(new PersonServiceImpl("zs"));
((PersonService) proxyObj).save("888");
}
}
可以看出基于JDK的动态代理是需要代理目标对象是实现了接口的,实际上JDK代理类就是代理接口基础上的一个代理实现类。
private Object targetObject;
//根据目标对象生成代理对象
public Object createProxyInstance(Object targetObject) {
this.targetObject = targetObject;
Object proxyObj = Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.targetObject.getClass().getClassLoader(),
this.targetObject.getClass().getInterfaces(), this);
return proxyObj;
}
在我们的demo中JDKProxyFactory实现了InvocationHandler接口,这个接口中只有一个方法就是invoke方法。用来执行目标对象的目标方法,执行的方式是反射。这个invoke方法在代理对象执行目标方法时触发调用。
SpringAOP中的JDK动态代理
接下来,让我们看下SpringAOP里的jdk动态代理:
org.springframework.aop.framework.JdkDynamicAopProxy
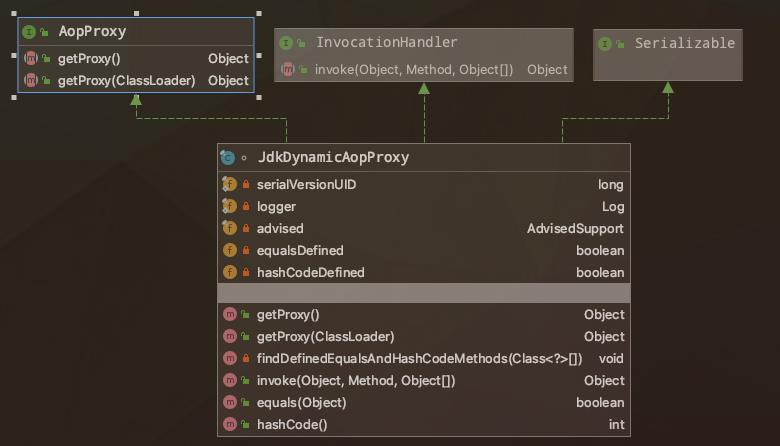
通过上图可以了解到JdkDynamicAopProxy通过实现接口AopProxy的getProxy方法获取代理对象。来看下这个方法,可以看出跟我们demo中实现的一模一样。
@Override
public Object getProxy() {
return getProxy(ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
@Override
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
//代理的接口,比如PersonService
Class<?>[] proxiedInterfaces = AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised, true);
findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(proxiedInterfaces);
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, proxiedInterfaces, this);
}
那么,这个JdkDynamicAopProxy#getProxy是被谁调用的呢?答案是ProxyFactory类,看下边。
//ProxyFactory.java
/**
* Create a new proxy according to the settings in this factory.
* <p>Can be called repeatedly. Effect will vary if we've added
* or removed interfaces. Can add and remove interceptors.
* <p>Uses a default class loader: Usually, the thread context class loader
* (if necessary for proxy creation).
* @return the proxy object
*/
public Object getProxy() {
return createAopProxy().getProxy();
}
既然是在ProxyFactory的getProxy方法中调用到,那么你一定可以想到createAopProxy()这个方法在这里返回的就是JdkDynamicAopProxy了。其实ProxyFactory的这个createAopProxy方法是由其父类ProxyCreatorSuppot提供的。
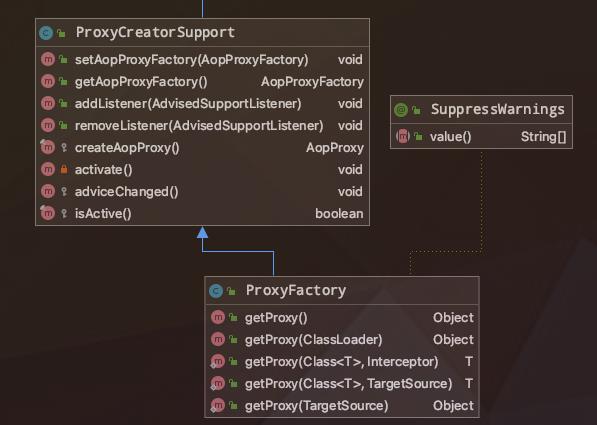
//ProxyCreatorSupport.java
/**
* Subclasses should call this to get a new AOP proxy. They should <b>not</b>
* create an AOP proxy with {@code this} as an argument.
*/
protected final synchronized AopProxy createAopProxy() {
if (!this.active) {
activate();
}
return getAopProxyFactory().createAopProxy(this);
}
通过AOP代理Factory创建代理
我们重点分析下ProxyCreatorSupport#createAopProxy方法,看到是先获取一个AopProxyfactory来创建代理,同时传入当前对象ProxyCreatorSupport,这是因为它继承了ProxyConfig类,封装了创建代理的配置属性。
getAopProxyFactory()方法返回的是DefaultAopProxyFactory类,这是一个SpringAOP提供的默认代理类创建Factory实现,作用是创建JDK代理或者cglib代理。
创建规则就不多说了,如果目标对象实现了接口那就默认是JDK代理。
public class DefaultAopProxyFactory implements AopProxyFactory, Serializable {
@Override
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {
Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +
"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
}
if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);
}
else {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
}
/**
* Determine whether the supplied {@link AdvisedSupport} has only the
* {@link org.springframework.aop.SpringProxy} interface specified
* (or no proxy interfaces specified at all).
*/
private boolean hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(AdvisedSupport config) {
Class<?>[] ifcs = config.getProxiedInterfaces();
return (ifcs.length == 0 || (ifcs.length == 1 && SpringProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(ifcs[0])));
}
}
经过一波三折终于获取到了JdkDynamicAopProxy,那么ProxyFactory#getProxy方法就可以获取代理了。前边我们已经说过了JdkDynamicAopProxy中是如何根据接口生成目标对象代理实现类了,这里不再赘述。
JDK代理对目标方法切面的拦截
知道了如何获取jdk基于接口的代理对象,那么当代理对象执行目标方法时又会发生什么?当然是执行JdkDynamicAopProxy#invoke方法了。在执行过程中,目标方法会被AOP切面拦截,也就是会执行前置通知,后置通知,环绕通知等等拦截执行。我们看下是怎么做到的?
package com.jeff.study.spring.aop;
import com.jeff.study.spring.aop.interceptor.EchoServiceMethodInterceptor;
import com.jeff.study.spring.aop.pointcut.EchoServicePointcut;
import com.jeff.study.spring.aop.service.DefaultEchoService;
import com.jeff.study.spring.aop.service.EchoService;
import org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice;
import org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice;
import org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactory;
import org.springframework.aop.support.DefaultPointcutAdvisor;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* Pointcut接口Demo
*
* @Date 2021/1/10 9:20 下午
* @Author jeff.sheng
*/
public class PointcutDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// EchoServiceStaticPointcut echoServicePointcut = new EchoServiceStaticPointcut("echo", EchoService.class);
EchoServicePointcut echoServicePointcut = new EchoServicePointcut();
//将Pointcut适配成Advisor,也就是说advice和pointcut之间需要一个advisor来做一个承载
DefaultPointcutAdvisor defaultPointcutAdvisor = new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(echoServicePointcut, new EchoServiceMethodInterceptor());
DefaultEchoService defaultEchoService = new DefaultEchoService();
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory(defaultEchoService);
//添加advisor
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(defaultPointcutAdvisor);
proxyFactory.addAdvice(new MethodBeforeAdvice() {
@Override
public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
System.out.printf("[MethodBeforeAdvice] 当前将要执行的方法是:%s , 参数key:[%s]\\r\\n", method.getName(), args[0]);
}
});
proxyFactory.addAdvice(new AfterReturningAdvice() {
@Override
public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
System.out.printf("[AfterReturningAdvice] 当前将要执行的方法是:%s , 参数key:[%s],value:[%s]\\r\\n", method.getName(), args[0], returnValue);
}
});
//获取代理对象
EchoService echoService = (EchoService) proxyFactory.getProxy();
System.out.println(echoService.echo("hello,world"));
}
}
ackage com.jeff.study.spring.aop.interceptor;
import com.jeff.study.spring.aop.service.EchoService;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation;
/**
* @Description 实现 {@link EchoService} 的拦截器对象
* @Date 2021/1/1 11:03 上午
* @Author jeff.sheng
* @see MethodInterceptor 继承了{@link org.aopalliance.intercept.Interceptor}
* @see org.aopalliance.intercept.Interceptor 继承了 {@link org.aopalliance.aop.Advice}
*/
public class EchoServiceMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("[EchoServiceMethodInterceptor] 当前执行的方法是:" + methodInvocation.getMethod());
return methodInvocation.proceed();
}
}
代码中我只设置了EchoServiceMethodInterceptor、MethodBeforeAdvice、AfterReturningAdvice三个Advive。
注意,EchoServiceMethodInterceptor实现了MethodInterceptor接口,而MethodInterceptor最终也是实现了Advice,这里不再解释。
当我们调用ProxyFactory#addAdvice方法时,advice会封装为DefaultPointcutAdvisor并保存在父类AdvisedSupport私有属性advisors列表中。
//AdvisedSupport.java
/**
* List of Advisors. If an Advice is added, it will be wrapped
* in an Advisor before being added to this List.
*/
private List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();
这个AdviseSupport会作为JdkDynamicAopProxy的构造器参数传入。在JdkDynamicAopProxy#invoke执行时会作为一个chain拦截器链被执行。
/**
* Construct a new JdkDynamicAopProxy for the given AOP configuration.
* @param config the AOP configuration as AdvisedSupport object
* @throws AopConfigException if the config is invalid. We try to throw an informative
* exception in this case, rather than let a mysterious failure happen later.
*/
public JdkDynamicAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
Assert.notNull(config, "AdvisedSupport must not be null");
if (config.getAdvisors().length == 0 && config.getTargetSource() == AdvisedSupport.EMPTY_TARGET_SOURCE) {
throw new AopConfigException("No advisors and no TargetSource specified");
}
this.advised = config;
}
过滤器模式的实践
看下invoke方法中如何执行Advice的?这里封装了一个ReflectiveMethodInvocation对象来执行具体逻辑(参看proceed方法)。
// We need to create a method invocation...
MethodInvocation invocation =
new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);
// Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain.
retVal = invocation.proceed();
//ReflectiveMethodInvocation.java
@Override
@Nullable
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
Class<?> targetClass = (this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass());
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
// Dynamic matching failed.
// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
return proceed();
}
}
else {
// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
这里用到了过滤器模式,在当前例子中过滤器有三个,封装在interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers列表中。
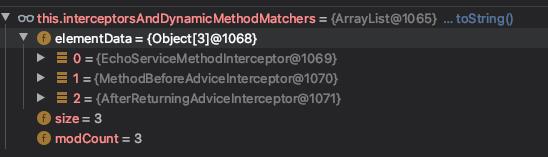
先执行环绕通知,再执行前置通知,然后是后置通知。执行完毕后满足ReflectiveMethodInvocation#proceed方法的退出条件。反射执行目标对象的目标方法,return返回结果。
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
/**
* Invoke the joinpoint using reflection.
* Subclasses can override this to use custom invocation.
* @return the return value of the joinpoint
* @throws Throwable if invoking the joinpoint resulted in an exception
*/
@Nullable
protected Object invokeJoinpoint() throws Throwable {
return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.target, this.method, this.arguments);
}
到此,关于JDK动态代理如何执行AOP切面的拦截流程已经完成,其实cglib的流程也是一样的,不同的是生成代理的方式不一样,cglib是根据asm字节码来生成目标对象的代理子类,无所谓是否实现接口。
以上是关于源码分析:Spring是如何跟JDK动态代理结合的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章