TensorFlow学习笔记
Posted sereasuesue
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了TensorFlow学习笔记相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
TensorFlow版本2发布后,使用TensorFlow变得更简单和方便,但看网上的很多代码是使用的TensorFlow1进行完成的,每次遇到不懂的函数去查,理解记忆的一般,感觉还是有点不清楚
所以又快速看了一下TensorFlow1常用的方法,感觉似乎比之前清楚了一下。整理记录下方便阅读代码
这个TensorFlow教程挺好的 https://www.w3cschool.cn/tensorflow_python/
课程的话个人感觉莫凡系列的挺好懂
TensorFlow 的特点:
- 使用图 (graph) 来表示计算任务.
- 在被称之为
会话 (Session)的上下文 (context) 中执行图. - 使用 tensor 表示数据.
- 通过
变量 (Variable)维护状态. - 使用 feed 和 fetch 可以为任意的操作(arbitrary operation) 赋值或者从其中获取数据
TensorFlow基本使用之创建图 ,在会话中使用图
import tensorflow as tf
#
# 创建一个常量,产生1*2的矩阵
m1 = tf.constant([[2, 2]])
m2 = tf.constant([[3],
[3]])
product = tf.matmul(m1, m2)
print(product) # wrong! no result
# 在一个会话中启动图
# 调用 sess 的 'run()' 方法来执行矩阵乘法 op, 传入 'product' 作为该方法的参数.
# method1 use session
sess = tf.Session()
result = sess.run(product)
# 上面提到, 'product' 代表了矩阵乘法 op 的输出, 传入它是向方法表明, 我们希望取回矩阵乘法 op 的输出.
print(result) # 返回值 'result' 是一个 numpy `ndarray` 对象
sess.close()
# method2 use session
with tf.Session() as sess:
result_ = sess.run(product)
print(result_)使用cpu,GPU
如果机器上有超过一个可用的 GPU, 除第一个外的其它 GPU 默认是不参与计算的. 为了让 TensorFlow 使用这些 GPU, 你必须将 op 明确指派给它们执行. with...Device 语句用来指派特定的 CPU 或 GPU 执行操作:
with tf.Session() as sess:
with tf.device("/gpu:1"):
matrix1 = tf.constant([[3., 3.]])
matrix2 = tf.constant([[2.],[2.]])
product = tf.matmul(matrix1, matrix2)
...
设备用字符串进行标识. 目前支持的设备包括:
"/cpu:0": 机器的 CPU."/gpu:0": 机器的第一个 GPU, 如果有的话."/gpu:1": 机器的第二个 GPU, 以此类推.
变量or feed
import tensorflow as tf
input1 = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32)
input2 = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32)
output = tf.multiply(input1, input2)
with tf.Session() as sess:
result=sess.run([output], feed_dict={input1:[7.], input2:[2.]})
print(result)
import tensorflow as tf
# 创建一个变量
var = tf.Variable(0) # our first variable in the "global_variable" set
add_operation = tf.add(var, 1)
update_operation = tf.assign(var, add_operation)
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 必须初始化 once define variables, you have to initialize them by doing this
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for _ in range(3):
sess.run(update_operation)
print(sess.run(var))激活函数
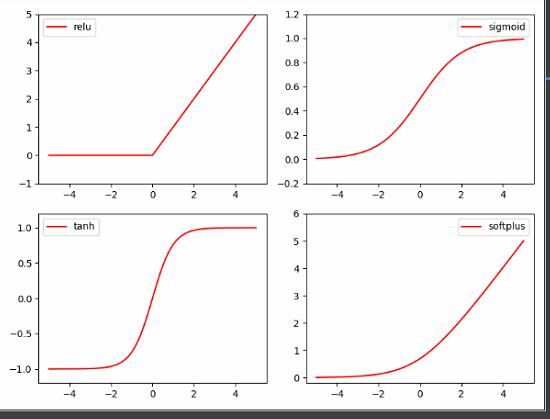
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# fake data
x = np.linspace(-5, 5, 200) # x data, shape=(100, 1)
# following are popular activation functions
y_relu = tf.nn.relu(x)
y_sigmoid = tf.nn.sigmoid(x)
y_tanh = tf.nn.tanh(x)
y_softplus = tf.nn.softplus(x)
# y_softmax = tf.nn.softmax(x) softmax is a special kind of activation function, it is about probability
sess = tf.Session()
y_relu, y_sigmoid, y_tanh, y_softplus = sess.run([y_relu, y_sigmoid, y_tanh, y_softplus])
# plt to visualize these activation function
plt.figure(1, figsize=(8, 6))
plt.subplot(221)
plt.plot(x, y_relu, c='red', label='relu')
plt.ylim((-1, 5))
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.subplot(222)
plt.plot(x, y_sigmoid, c='red', label='sigmoid')
plt.ylim((-0.2, 1.2))
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.subplot(223)
plt.plot(x, y_tanh, c='red', label='tanh')
plt.ylim((-1.2, 1.2))
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.subplot(224)
plt.plot(x, y_softplus, c='red', label='softplus')
plt.ylim((-0.2, 6))
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()简单神经网络构造
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
tf.set_random_seed(1)
np.random.seed(1)
# fake data
x = np.linspace(-1, 1, 100)[:, np.newaxis] # shape (100, 1)
noise = np.random.normal(0, 0.1, size=x.shape)
y = np.power(x, 2) + noise # shape (100, 1) + some noise
# plot data
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.show()
tf_x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, x.shape) # input x
tf_y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, y.shape) # input y
# neural network layers
l1 = tf.layers.dense(tf_x, 10, tf.nn.relu) # hidden layer
output = tf.layers.dense(l1, 1) # output layer
loss = tf.losses.mean_squared_error(tf_y, output) # compute cost
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.5)
train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss)
sess = tf.Session() # control training and others
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) # initialize var in graph
plt.ion() # something about plotting 打开交互模式
for step in range(100):
# train and net output
_, l, pred = sess.run([train_op, loss, output], {tf_x: x, tf_y: y})
if step % 5 == 0:
# plot and show learning process
plt.cla()#清除活动轴
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.plot(x, pred, 'r-', lw=5)
plt.text(0.5, 0, 'Loss=%.4f' % l, fontdict={'size': 20, 'color': 'red'})
plt.pause(0.1)
plt.ioff()#关闭交互模式用于阻塞程序,不让图片关闭
plt.show()优化器
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
tf.set_random_seed(1)
np.random.seed(1)
LR = 0.01
BATCH_SIZE = 32
# fake data
x = np.linspace(-1, 1, 100)[:, np.newaxis] # shape (100, 1)
noise = np.random.normal(0, 0.1, size=x.shape)
y = np.power(x, 2) + noise # shape (100, 1) + some noise
# plot dataset
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.show()
# default network
class Net:
def __init__(self, opt, **kwargs):
self.x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1])
self.y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1])
l = tf.layers.dense(self.x, 20, tf.nn.relu)
out = tf.layers.dense(l, 1)
self.loss = tf.losses.mean_squared_error(self.y, out)
self.train = opt(LR, **kwargs).minimize(self.loss)
# different nets
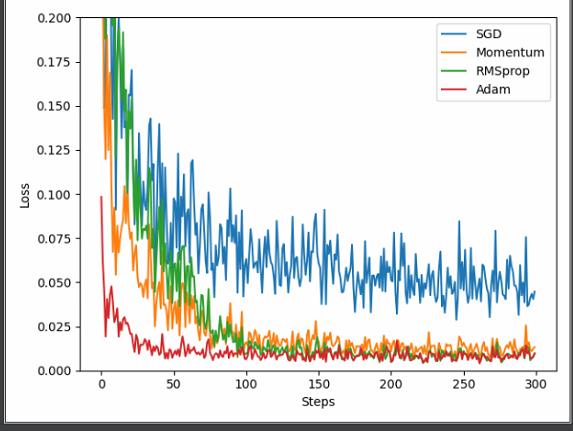
net_SGD = Net(tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer)
net_Momentum = Net(tf.train.MomentumOptimizer, momentum=0.9)
net_RMSprop = Net(tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer)
net_Adam = Net(tf.train.AdamOptimizer)
nets = [net_SGD, net_Momentum, net_RMSprop, net_Adam]
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
losses_his = [[], [], [], []] # record loss
# training
for step in range(300): # for each training step
index = np.random.randint(0, x.shape[0], BATCH_SIZE)
b_x = x[index]
b_y = y[index]
for net, l_his in zip(nets, losses_his):
_, l = sess.run([net.train, net.loss], {net.x: b_x, net.y: b_y})
l_his.append(l) # loss recoder
# plot loss history
labels = ['SGD', 'Momentum', 'RMSprop', 'Adam']
for i, l_his in enumerate(losses_his):
plt.plot(l_his, label=labels[i])
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.xlabel('Steps')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.ylim((0, 0.2))
plt.show()
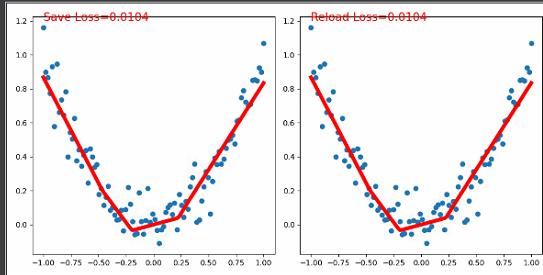
保存模型与加载模型
"""
Know more, visit my Python tutorial page: https://morvanzhou.github.io/tutorials/
My Youtube Channel: https://www.youtube.com/user/MorvanZhou
Dependencies:
tensorflow: 1.1.0
matplotlib
numpy
"""
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
tf.set_random_seed(1)
np.random.seed(1)
# fake data
x = np.linspace(-1, 1, 100)[:, np.newaxis] # shape (100, 1)
noise = np.random.normal(0, 0.1, size=x.shape)
y = np.power(x, 2) + noise # shape (100, 1) + some noise
def save():
print('This is save')
# build neural network
tf_x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, x.shape) # input x
tf_y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, y.shape) # input y
l = tf.layers.dense(tf_x, 10, tf.nn.relu) # hidden layer
o = tf.layers.dense(l, 1) # output layer
loss = tf.losses.mean_squared_error(tf_y, o) # compute cost
train_op = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.5).minimize(loss)
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) # initialize var in graph
saver = tf.train.Saver() # define a saver for saving and restoring
for step in range(100): # train
sess.run(train_op, {tf_x: x, tf_y: y})
saver.save(sess, './params', write_meta_graph=False) # meta_graph is not recommended
# plotting
pred, l = sess.run([o, loss], {tf_x: x, tf_y: y})
plt.figure(1, figsize=(10, 5))
plt.subplot(121)
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.plot(x, pred, 'r-', lw=5)
plt.text(-1, 1.2, 'Save Loss=%.4f' % l, fontdict={'size': 15, 'color': 'red'})
def reload():
print('This is reload')
# build entire net again and restore
tf_x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, x.shape) # input x
tf_y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, y.shape) # input y
l_ = tf.layers.dense(tf_x, 10, tf.nn.relu) # hidden layer
o_ = tf.layers.dense(l_, 1) # output layer
loss_ = tf.losses.mean_squared_error(tf_y, o_) # compute cost
sess = tf.Session()
# don't need to initialize variables, just restoring trained variables
saver = tf.train.Saver() # define a saver for saving and restoring
saver.restore(sess, './params')
# plotting
pred, l = sess.run([o_, loss_], {tf_x: x, tf_y: y})
plt.subplot(122)
plt.scatter(x, y)
plt.plot(x, pred, 'r-', lw=5)
plt.text(-1, 1.2, 'Reload Loss=%.4f' % l, fontdict={'size': 15, 'color': 'red'})
plt.show()
save()
# destroy previous net
tf.reset_default_graph()
reload()
tensorboard可视化
参考文档:TensorBoard:图表可视化 - TensorFlow官方文档中文版 (pythontab.com)
1.创建writer,写日志文件
writer=tf.summary.FileWriter('/path/to/logs', tf.get_default_graph())
2.保存日志文件
writer.close()
3.运行可视化命令,启动服务
tensorboard –logdir /path/to/logs
4.打开可视化界面
通过浏览器打开服务器访问端口http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:6006TensorBoard的使用流程
- 添加记录节点:
tf.summary.scalar/image/histogram()等 - 汇总记录节点:
merged = tf.summary.merge_all() - 运行汇总节点:
summary = sess.run(merged),得到汇总结果 - 日志书写器实例化:
summary_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(logdir, graph=sess.graph),实例化的同时传入 graph 将当前计算图写入日志 - 调用日志书写器实例对象
summary_writer的add_summary(summary, global_step=i)方法将所有汇总日志写入文件 - 调用日志书写器实例对象
summary_writer的close()方法写入内存,否则它每隔120s写入一次
"""
Know more, visit my Python tutorial page: https://morvanzhou.github.io/tutorials/
My Youtube Channel: https://www.youtube.com/user/MorvanZhou
Dependencies:
tensorflow: 1.1.0
numpy
"""
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
tf.set_random_seed(1)
np.random.seed(1)
# fake data
x = np.linspace(-1, 1, 100)[:, np.newaxis] # shape (100, 1)
noise = np.random.normal(0, 0.1, size=x.shape)
y = np.power(x, 2) + noise # shape (100, 1) + some noise
with tf.variable_scope('Inputs'):#用tf.variable_scope命名Inputs(名称),x,y属于Inputs层级下的节点
tf_x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, x.shape, name='x')
tf_y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, y.shape, name='y')
with tf.variable_scope('Net'):
l1 = tf.layers.dense(tf_x, 10, tf.nn.relu, name='hidden_layer')
output = tf.layers.dense(l1, 1, name='output_layer')
# add to histogram summary
tf.summary.histogram('h_out', l1)
tf.summary.histogram('pred', output)
loss = tf.losses.mean_squared_error(tf_y, output, scope='loss')
train_op = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.5).minimize(loss)
tf.summary.scalar('loss', loss) # add loss to scalar summary
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('./log', sess.graph) # write to file
merge_op = tf.summary.merge_all() # operation to merge all summary
for step in range(100):
# train and net output
_, result = sess.run([train_op, merge_op], {tf_x: x, tf_y: y})
writer.add_summary(result, step)
# Lastly, in your terminal or CMD, type this :
# $ tensorboard --logdir path/to/log
# open you google chrome, type the link shown on your terminal or CMD. (something like this: http://localhost:6006)注意:节点域:tf2使用tf.name_scope('XX'):使可视化更简洁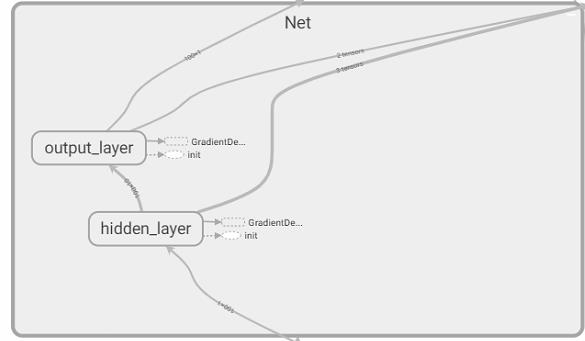
启动TensorBoard
输入下面的指令来启动TensorBoard
tensorboard --logdir=/path/to/log-directory
这里的参数 logdir 指向 SummaryWriter 序列化数据的存储路径。如果logdir目录的子目录中包含另一次运行时的数据,那么 TensorBoard 会展示所有运行的数据。一旦 TensorBoard 开始运行,你可以通过在浏览器中输入 localhost:6006 来查看 TensorBoard。
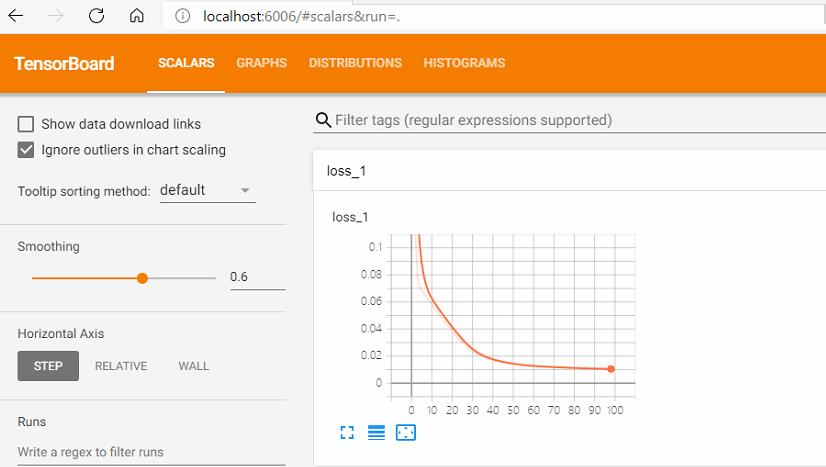
梯度下降
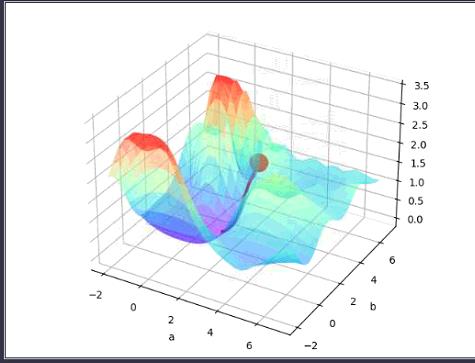
"""
Know more, visit my Python tutorial page: https://morvanzhou.github.io/tutorials/
My Youtube Channel: https://www.youtube.com/user/MorvanZhou
Dependencies:
tensorflow: 1.1.0
matplotlib
numpy
"""
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
LR = 0.1
REAL_PARAMS = [1.2, 2.5]
INIT_PARAMS = [[5, 4],
[5, 1],
[2, 4.5]][2]
x = np.linspace(-1, 1, 200, dtype=np.float32) # x data
# Test (1): Visualize a simple linear function with two parameters,
# you can change LR to 1 to see the different pattern in gradient descent.
# y_fun = lambda a, b: a * x + b
# tf_y_fun = lambda a, b: a * x + b
# Test (2): Using Tensorflow as a calibrating tool for empirical formula like following.
# y_fun = lambda a, b: a * x**3 + b * x**2
# tf_y_fun = lambda a, b: a * x**3 + b * x**2
# Test (3): Most simplest two parameters and two layers Neural Net, and their local & global minimum,
# you can try different INIT_PARAMS set to visualize the gradient descent.
y_fun = lambda a, b: np.sin(b*np.cos(a*x))
tf_y_fun = lambda a, b: tf.sin(b*tf.cos(a*x))
noise = np.random.randn(200)/10
y = y_fun(*REAL_PARAMS) + noise # target
# tensorflow graph
a, b = [tf.Variable(initial_value=p, dtype=tf.float32) for p in INIT_PARAMS]
pred = tf_y_fun(a, b)
mse = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-pred))
train_op = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(LR).minimize(mse)
a_list, b_list, cost_list = [], [], []
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for t in range(400):
a_, b_, mse_ = sess.run([a, b, mse])
a_list.append(a_); b_list.append(b_); cost_list.append(mse_) # record parameter changes
result, _ = sess.run([pred, train_op]) # training
# visualization codes:
print('a=', a_, 'b=', b_)
plt.figure(1)
plt.scatter(x, y, c='b') # plot data
plt.plot(x, result, 'r-', lw=2) # plot line fitting
# 3D cost figure
fig = plt.figure(2); ax = Axes3D(fig)
a3D, b3D = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-2, 7, 30), np.linspace(-2, 7, 30)) # parameter space
cost3D = np.array([np.mean(np.square(y_fun(a_, b_) - y)) for a_, b_ in zip(a3D.flatten(), b3D.flatten())]).reshape(a3D.shape)
ax.plot_surface(a3D, b3D, cost3D, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap=plt.get_cmap('rainbow'), alpha=0.5)
ax.scatter(a_list[0], b_list[0], zs=cost_list[0], s=300, c='r') # initial parameter place
ax.set_xlabel('a'); ax.set_ylabel('b')
ax.plot(a_list, b_list, zs=cost_list, zdir='z', c='r', lw=3) # plot 3D gradient descent
plt.show()
以上是关于TensorFlow学习笔记的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章