Spark中文手册8:spark GraphX编程指南
Posted wanmeilingdu
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spark中文手册8:spark GraphX编程指南相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
问题导读1.什么是GraphX?
2.如何将Spark和GraphX引入到项目中?
3.从一个图中取出顶点特征加入到另外一个图中如何实现?

GraphX编程指南
GraphX是一个新的(alpha)Spark API,它用于图和并行图(graph-parallel)的计算。GraphX通过引入 Resilient Distributed Property Graph:带有 顶点和边属性的有向多重图,来扩展Spark RDD。为了支持图计算,GraphX公开一组基本的功能操作以及Pregel API的一个优化。另外,GraphX包含了一个日益增长的图算法和图builders的 集合,用以简化图分析任务。 从社交网络到语言建模,不断增长的规模和图形数据的重要性已经推动了许多新的 graph-parallel系统(如 Giraph和 GraphLab)的发展。 通过限制可表达的计算类型和引入新的技术来划分和分配图,这些系统可以高效地执行复杂的图形算法,比一般的 data-parallel系统快很多。

然而,通过这种限制可以提高性能,但是很难表示典型的图分析途径(构造图、修改它的结构或者表示跨多个图的计算)中很多重要的stages。另外,我们如何看待数据取决于我们的目标,并且同一原始数据可能有许多不同表和图的视图。

结论是,图和表之间经常需要能够相互移动。然而,现有的图分析管道必须组成 graph-parallel和 data- parallel系统`,从而实现大数据的迁移和复制并生成一个复杂的编程模型。
 GraphX项目的目的就是将
graph-parallel和
data-parallel统一到一个系统中,这个系统拥有一个唯一的组合API。GraphX允许用户将数据当做一个图和一个集合(RDD),而不需要数据移动或者复制。通过将最新的进展整合进
graph-parallel系统,GraphX能够优化图操作的执行。
GraphX项目的目的就是将
graph-parallel和
data-parallel统一到一个系统中,这个系统拥有一个唯一的组合API。GraphX允许用户将数据当做一个图和一个集合(RDD),而不需要数据移动或者复制。通过将最新的进展整合进
graph-parallel系统,GraphX能够优化图操作的执行。
- 开始
- 属性图
- 图操作符
- Pregel API
- 图构造者
- 顶点和边RDDs
- 图算法
- 例子
开始
开始的第一步是引入Spark和GraphX到你的项目中,如下面所示
- mport org.apache.spark._
- import org.apache.spark.graphx._
- // To make some of the examples work we will also need RDD
- import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
如果你没有用到Spark shell,你还将需要SparkContext。
属性图
属性图是一个有向多重图,它带有连接到每个顶点和边的用户定义的对象。 有向多重图中多个并行(parallel)的边共享相同的源和目的地顶点。支持并行边的能力简化了建模场景,这个场景中,相同的顶点存在多种关系(例如co-worker和friend)。每个顶点由一个 唯一的64位长的标识符(VertexID)作为key。GraphX并没有对顶点标识强加任何排序。同样,顶点拥有相应的源和目的顶点标识符。 属性图通过vertex(VD)和edge(ED)类型参数化,这些类型是分别与每个顶点和边相关联的对象的类型。 在某些情况下,在相同的图形中,可能希望顶点拥有不同的属性类型。这可以通过继承完成。例如,将用户和产品建模成一个二分图,我们可以用如下方式
- class VertexProperty()
- case class UserProperty(val name: String) extends VertexProperty
- case class ProductProperty(val name: String, val price: Double) extends VertexProperty
- // The graph might then have the type:
- var graph: Graph[VertexProperty, String] = null
和RDD一样,属性图是不可变的、分布式的、容错的。图的值或者结构的改变需要按期望的生成一个新的图来实现。注意,原始图的大部分都可以在新图中重用,用来减少这种固有的功能数据结构的成本。 执行者使用一系列顶点分区试探法来对图进行分区。如RDD一样,图中的每个分区可以在发生故障的情况下被重新创建在不同的机器上。 逻辑上的属性图对应于一对类型化的集合(RDD),这个集合编码了每一个顶点和边的属性。因此,图类包含访问图中顶点和边的成员.
- class Graph[VD, ED]
- val vertices: VertexRDD[VD]
- val edges: EdgeRDD[ED]
VertexRDD[VD]和EdgeRDD[ED]类分别继承和优化自RDD[(VertexID, VD)]和RDD[Edge[ED]]。VertexRDD[VD]和EdgeRDD[ED]都支持额外的功能来建立在图计算和利用内部优化。 属性图的例子 在GraphX项目中,假设我们想构造一个包括不同合作者的属性图。顶点属性可能包含用户名和职业。我们可以用描述合作者之间关系的字符串标注边缘。
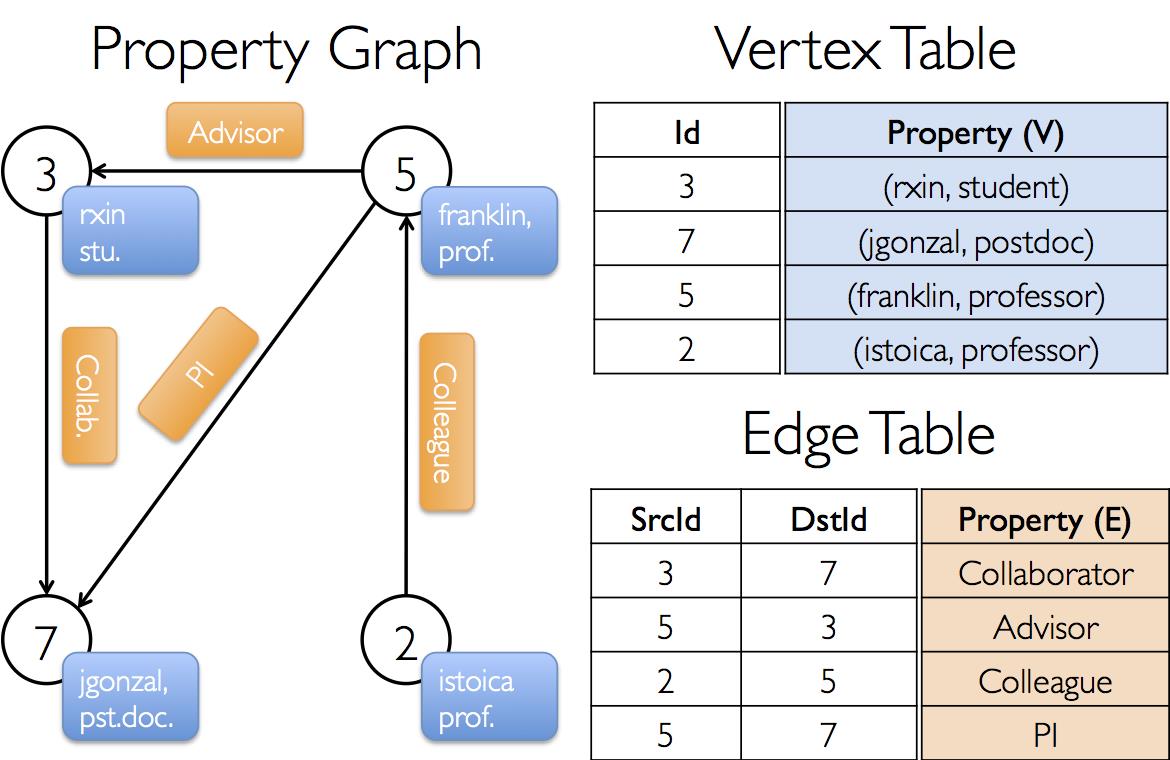 所得的图形将具有类型签名
所得的图形将具有类型签名
- val userGraph: Graph[(String, String), String]
有很多方式从一个原始文件、RDD构造一个属性图。最一般的方法是利用 Graph object。 下面的代码从RDD集合生成属性图。
- // Assume the SparkContext has already been constructed
- val sc: SparkContext
- // Create an RDD for the vertices
- val users: RDD[(VertexId, (String, String))] =
- sc.parallelize(Array((3L, ("rxin", "student")), (7L, ("jgonzal", "postdoc")),
- (5L, ("franklin", "prof")), (2L, ("istoica", "prof"))))
- // Create an RDD for edges
- val relationships: RDD[Edge[String]] =
- sc.parallelize(Array(Edge(3L, 7L, "collab"), Edge(5L, 3L, "advisor"),
- Edge(2L, 5L, "colleague"), Edge(5L, 7L, "pi")))
- // Define a default user in case there are relationship with missing user
- val defaultUser = ("John Doe", "Missing")
- // Build the initial Graph
- val graph = Graph(users, relationships, defaultUser)
在上面的例子中,我们用到了 Edge样本类。边有一个srcId和dstId分别对应 于源和目标顶点的标示符。另外,Edge类有一个attr成员用来存储边属性。 我们可以分别用graph.vertices和graph.edges成员将一个图解构为相应的顶点和边。
- val graph: Graph[(String, String), String] // Constructed from above
- // Count all users which are postdocs
- graph.vertices.filter case (id, (name, pos)) => pos == "postdoc" .count
- // Count all the edges where src > dst
- graph.edges.filter(e => e.srcId > e.dstId).count
注意,graph.vertices返回一个VertexRDD[(String, String)],它继承于 RDD[(VertexID, (String, String))]。所以我们可以用scala的case表达式解构这个元组。另一方面, graph.edges返回一个包含Edge[String]对象的EdgeRDD。我们也可以用到case类的类型构造器,如下例所示。
- graph.edges.filter case Edge(src, dst, prop) => src > dst .count
除了属性图的顶点和边视图,GraphX也包含了一个三元组视图,三元视图逻辑上将顶点和边的属性保存为一个RDD[EdgeTriplet[VD, ED]],它包含EdgeTriplet类的实例。 可以通过下面的Sql表达式表示这个连接。
- SELECT src.id, dst.id, src.attr, e.attr, dst.attr
- FROM edges AS e LEFT JOIN vertices AS src, vertices AS dst
- ON e.srcId = src.Id AND e.dstId = dst.Id
除了属性图的顶点和边视图,GraphX也包含了一个三元组视图,三元视图逻辑上将顶点和边的属性保存为一个RDD[EdgeTriplet[VD, ED]],它包含 EdgeTriplet类的实例。 可以通过下面的Sql表达式表示这个连接。
- SELECT src.id, dst.id, src.attr, e.attr, dst.attr
- FROM edges AS e LEFT JOIN vertices AS src, vertices AS dst
- ON e.srcId = src.Id AND e.dstId = dst.Id
或者通过下面的图来表示。
 EdgeTriplet类继承于Edge类,并且加入了srcAttr和dstAttr成员,这两个成员分别包含源和目的的属性。我们可以用一个三元组视图渲染字符串集合用来描述用户之间的关系。
EdgeTriplet类继承于Edge类,并且加入了srcAttr和dstAttr成员,这两个成员分别包含源和目的的属性。我们可以用一个三元组视图渲染字符串集合用来描述用户之间的关系。
- val graph: Graph[(String, String), String] // Constructed from above
- // Use the triplets view to create an RDD of facts.
- val facts: RDD[String] =
- graph.triplets.map(triplet =>
- triplet.srcAttr._1 + " is the " + triplet.attr + " of " + triplet.dstAttr._1)
- facts.collect.foreach(println(_))
图操作符
正如RDDs有基本的操作map, filter和reduceByKey一样,属性图也有基本的集合操作,这些操作采用用户自定义的函数并产生包含转换特征和结构的新图。定义在 Graph中的 核心操作是经过优化的实现。表示为核心操作的组合的便捷操作定义在 GraphOps中。然而, 因为有Scala的隐式转换,定义在GraphOps中的操作可以作为Graph的成员自动使用。例如,我们可以通过下面的方式计算每个顶点(定义在GraphOps中)的入度。
- val graph: Graph[(String, String), String]
- // Use the implicit GraphOps.inDegrees operator
- val inDegrees: VertexRDD[Int] = graph.inDegrees
区分核心图操作和GraphOps的原因是为了在将来支持不同的图表示。每个图表示都必须提供核心操作的实现并重用很多定义在GraphOps中的有用操作。 操作一览 一下是定义在Graph和GraphOps中(为了简单起见,表现为图的成员)的功能的快速浏览。注意,某些函数签名已经简化(如默认参数和类型的限制已删除),一些更高级的功能已经被 删除,所以请参阅API文档了解官方的操作列表。
- /** Summary of the functionality in the property graph */
- class Graph[VD, ED]
- // Information about the Graph ===================================================================
- val numEdges: Long
- val numVertices: Long
- val inDegrees: VertexRDD[Int]
- val outDegrees: VertexRDD[Int]
- val degrees: VertexRDD[Int]
- // Views of the graph as collections =============================================================
- val vertices: VertexRDD[VD]
- val edges: EdgeRDD[ED]
- val triplets: RDD[EdgeTriplet[VD, ED]]
- // Functions for caching graphs ==================================================================
- def persist(newLevel: StorageLevel = StorageLevel.MEMORY_ONLY): Graph[VD, ED]
- def cache(): Graph[VD, ED]
- def unpersistVertices(blocking: Boolean = true): Graph[VD, ED]
- // Change the partitioning heuristic ============================================================
- def partitionBy(partitionStrategy: PartitionStrategy): Graph[VD, ED]
- // Transform vertex and edge attributes ==========================================================
- def mapVertices[VD2](map: (VertexID, VD) => VD2): Graph[VD2, ED]
- def mapEdges[ED2](map: Edge[ED] => ED2): Graph[VD, ED2]
- def mapEdges[ED2](map: (PartitionID, Iterator[Edge[ED]]) => Iterator[ED2]): Graph[VD, ED2]
- def mapTriplets[ED2](map: EdgeTriplet[VD, ED] => ED2): Graph[VD, ED2]
- def mapTriplets[ED2](map: (PartitionID, Iterator[EdgeTriplet[VD, ED]]) => Iterator[ED2])
- : Graph[VD, ED2]
- // Modify the graph structure ====================================================================
- def reverse: Graph[VD, ED]
- def subgraph(
- epred: EdgeTriplet[VD,ED] => Boolean = (x => true),
- vpred: (VertexID, VD) => Boolean = ((v, d) => true))
- : Graph[VD, ED]
- def mask[VD2, ED2](other: Graph[VD2, ED2]): Graph[VD, ED]
- def groupEdges(merge: (ED, ED) => ED): Graph[VD, ED]
- // Join RDDs with the graph ======================================================================
- def joinVertices[U](table: RDD[(VertexID, U)])(mapFunc: (VertexID, VD, U) => VD): Graph[VD, ED]
- def outerJoinVertices[U, VD2](other: RDD[(VertexID, U)])
- (mapFunc: (VertexID, VD, Option[U]) => VD2)
- : Graph[VD2, ED]
- // Aggregate information about adjacent triplets =================================================
- def collectNeighborIds(edgeDirection: EdgeDirection): VertexRDD[Array[VertexID]]
- def collectNeighbors(edgeDirection: EdgeDirection): VertexRDD[Array[(VertexID, VD)]]
- def aggregateMessages[Msg: ClassTag](
- sendMsg: EdgeContext[VD, ED, Msg] => Unit,
- mergeMsg: (Msg, Msg) => Msg,
- tripletFields: TripletFields = TripletFields.All)
- : VertexRDD[A]
- // Iterative graph-parallel computation ==========================================================
- def pregel[A](initialMsg: A, maxIterations: Int, activeDirection: EdgeDirection)(
- vprog: (VertexID, VD, A) => VD,
- sendMsg: EdgeTriplet[VD, ED] => Iterator[(VertexID,A)],
- mergeMsg: (A, A) => A)
- : Graph[VD, ED]
- // Basic graph algorithms ========================================================================
- def pageRank(tol: Double, resetProb: Double = 0.15): Graph[Double, Double]
- def connectedComponents(): Graph[VertexID, ED]
- def triangleCount(): Graph[Int, ED]
- def stronglyConnectedComponents(numIter: Int): Graph[VertexID, ED]
属性操作 如RDD的map操作一样,属性图包含下面的操作:
- class Graph[VD, ED]
- def mapVertices[VD2](map: (VertexId, VD) => VD2): Graph[VD2, ED]
- def mapEdges[ED2](map: Edge[ED] => ED2): Graph[VD, ED2]
- def mapTriplets[ED2](map: EdgeTriplet[VD, ED] => ED2): Graph[VD, ED2]
每个操作都产生一个新的图,这个新的图包含通过用户自定义的map操作修改后的顶点或边的属性。 注意,每种情况下图结构都不受影响。这些操作的一个重要特征是它允许所得图形重用原有图形的结构索引(indices)。下面的两行代码在逻辑上是等价的,但是第一个不保存结构索引,所以 不会从GraphX系统优化中受益。
- val newVertices = graph.vertices.map case (id, attr) => (id, mapUdf(id, attr))
- val newGraph = Graph(newVertices, graph.edges)
另一种方法是用[url=http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/api/scala/index.html#org.apache.spark.graphx.Graph@mapVertices[VD2]((VertexId,VD]mapVertices[/ur
以上是关于Spark中文手册8:spark GraphX编程指南的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章