Web APIs DOM 时间对象
Posted 黑马程序员官方
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Web APIs DOM 时间对象相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前期更新笔记内容: Web API 基本认知 / 获取DOM元素 / 设置/修改DOM元素内容和元素属性 / 定时器-间歇函数 / 事件基础 / 高阶函数 / 环境对象 / 综合案例-Tab栏切换 / DOM节点
一、Web APIs 时间对象:
时间对象:用来表示时间的对象
作用:可以得到当前系统时间
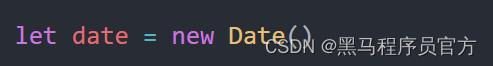
1.1 实例化

- 在代码中发现了 new 关键字时,一般将这个操作称为实例化
- 创建一个时间对象并获取时间
☞ 获得指定时间
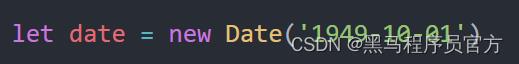
时间对象代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// let arr = []
// let arr = new Array()
// let obj =
// let obj = new Object()
// new 实例化 时间对象
// 小括号为空可以得到当前的时间
let date = new Date()
console.log(date)
// 小括号里面写上时间,可以返回指定的时间
let last = new Date('2021-8-29 18:30:00')
console.log(last)
</script>
</body>
</html>
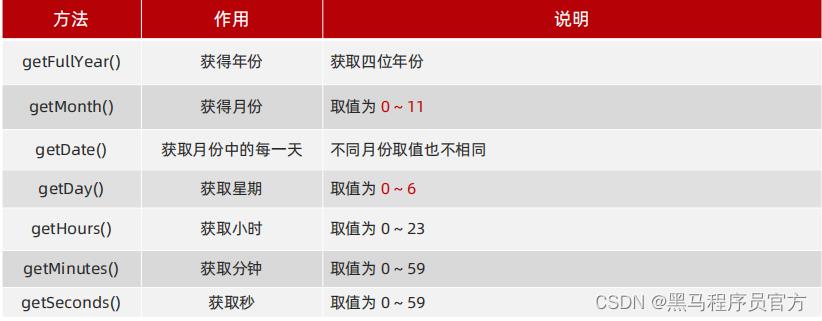
1.2 时间对象方法
因为时间对象返回的数据我们不能直接使用,所以需要转换为实际开发中常用的格式
时间对象常用方法代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// new 实例化 时间对象
// 小括号为空可以得到当前的时间
let date = new Date()
console.log(date.getFullYear())
console.log(date.getMonth() + 1)
console.log(date.getDate())
// 时分秒
console.log(date.getHours())
console.log(date.getMinutes())
console.log(date.getSeconds())
// 星期几
console.log(date.getDay())
</script>
</body>
</html>
【案例】 页面显示时间
需求:
将当前时间以:YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm 形式显示在页面
分析:
- 调用时间对象方法进行转换
- 字符串拼接后,通过 innerText 给 标签
代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
div
width: 400px;
height: 50px;
background-color: pink;
text-align: center;
line-height: 50px;
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<script>
let arr = ['星期日', '星期一', '星期二', '星期三', '星期四', '星期五', '星期六']
let div = document.querySelector('div')
// 先调用,就省去了1秒的空白期
getTime()
setInterval(getTime, 1000)
function getTime()
// 1. 实例化时间对象 一定写到定时器里面才可以额
let date = new Date()
let year = date.getFullYear()
let month = date.getMonth() + 1
let date1 = date.getDate()
let hour = date.getHours()
let min = date.getMinutes()
let sec = date.getSeconds()
let day = date.getDay()
div.innerHTML = `今天是: $year年$month月$date1日 $hour:$min:$sec $arr[day]`
</script>
</body>
</html>1.3 时间戳
什么是时间戳?
- 是指1970年01月01日00时00分00秒起至现在的毫秒数,它是一种特殊的计量时间的方式
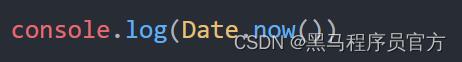
三种方式获取时间戳
1. 使用 getTime() 方法
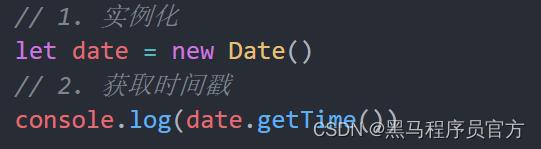
2. 简写 +new Date()
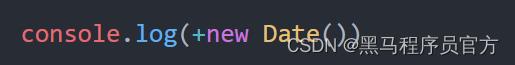
- 无需实例化
- 但是只能得到当前的时间戳, 而前面两种可以返回指定时间的时间戳
时间戳代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 时间戳是总的毫秒数 是独一无二的
// 计算倒计时: 核心思想:
// 将来时间 9.1 12:00 有一个时间戳 2000000
// 现在的时间 8.29 15:00 有一个时间戳 1000000
// 可以利用将来的时间戳 减去 现在的时间戳 就是剩余的时间毫秒数
// 转换为时分秒就是剩余的时间了
// 1. getTime()
// let date = new Date()
// console.log(date.getTime())
// 2. +new Date()
console.log(+new Date()) // 当前的时间戳
console.log(+new Date('2021-8-30 12:00:00')) // 指定时间的时间戳
// 3. 只能得到当前的
// console.log(Date.now())
</script>
</body>
</html>案例 :毕业倒计时效果
需求:计算到下课还有多少时间 分析: ①:用将来时间减去现在时间就是剩余的时间 ②:核心: 使用将来的时间戳减去现在的时间戳 ③:把剩余的时间转换为 天 时 分 秒注意:
1. 通过时间戳得到是毫秒,需要转换为秒在计算
2. 转换公式:
- d = parseInt(总秒数/ 60/60 /24); // 计算天数
- h = parseInt(总秒数/ 60/60 %24) // 计算小时
- m = parseInt(总秒数 /60 %60 ); // 计算分数
- s = parseInt(总秒数%60); // 计算当前秒数

案例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.countdown
width: 240px;
height: 305px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 1;
color: #fff;
background-color: brown;
/* background-size: 240px; */
/* float: left; */
overflow: hidden;
.countdown .next
font-size: 16px;
margin: 25px 0 14px;
.countdown .title
font-size: 33px;
.countdown .tips
margin-top: 80px;
font-size: 23px;
.countdown small
font-size: 17px;
.countdown .clock
width: 142px;
margin: 18px auto 0;
overflow: hidden;
.countdown .clock span,
.countdown .clock i
display: block;
text-align: center;
line-height: 34px;
font-size: 23px;
float: left;
.countdown .clock span
width: 34px;
height: 34px;
border-radius: 2px;
background-color: #303430;
.countdown .clock i
width: 20px;
font-style: normal;
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="countdown">
<p class="next">今天是2021年8月28日</p>
<p class="title">下班倒计时</p>
<p class="clock">
<span id="hour">00</span>
<i>:</i>
<span id="minutes">25</span>
<i>:</i>
<span id="scond">20</span>
</p>
<p class="tips">
现在是18:30:00
</p>
</div>
<script>
let hour = document.querySelector('#hour')
let minutes = document.querySelector('#minutes')
let scond = document.querySelector('#scond')
time()
setInterval(time, 1000)
function time()
// 1. 得到现在的时间戳
let now = +new Date()
// 2. 得到指定时间的时间戳
let last = +new Date('2021-8-29 18:30:00')
// 3. (计算剩余的毫秒数) / 1000 === 剩余的秒数
let count = (last - now) / 1000
// console.log(count)
// 4. 转换为时分秒
// h = parseInt(总秒数 / 60 / 60 % 24) // 计算小时
let h = parseInt(count / 60 / 60 % 24)
h = h < 10 ? '0' + h : h
// m = parseInt(总秒数 / 60 % 60); // 计算分数
let m = parseInt(count / 60 % 60)
m = m < 10 ? '0' + m : m
// s = parseInt(总秒数 % 60); // 计算当前秒数
let s = parseInt(count % 60);
s = s < 10 ? '0' + s : s
// console.log(h, m, s)
hour.innerHTML = h
minutes.innerHTML = m
scond.innerHTML = s
</script>
</body>
</html>黑马前端专栏干货多多,关注再学,好方便~
2022年前端学习路线图:课程、源码、笔记,技术栈 另外此线路图实时更新!需要课后资料的友友们,可以直接告诉我。

以上是关于Web APIs DOM 时间对象的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章