C++---设计模式(MARK一下)
Posted 4nc414g0n
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C++---设计模式(MARK一下)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
设计特殊类
1)引入设计模式
①设计一个不能被拷贝的类
拷贝只会放生在两个场景中:拷贝构造函数以及赋值运算符重载,因此想要让一个类禁止拷贝,只需让该类
不能调用拷贝构造函数以及赋值运算符重载即可
在使用库函数copy时会调用拷贝构造,在栈上创建空间
参考:
test::heap_only2* ptr = test::heap_only2::Create(); test::heap_only2 copy(*ptr); delete ptr;防止拷贝,只声明,不实现,声明为私有
C++98:private: heap_only2(const heap_only2& obj);//私有拷贝构造 heap_only2& operator=(const heap_only2& obj);//私有赋值运算符重载
C++11:heap_only2(const heap_only2& obj)=delete; //C++11 heap_only2& operator=(const heap_only2& obj)=delete;
②设计一个不能被继承的类
C++98中构造函数私有化,派生类中调不到基类的构造函数。则无法继承
- 子类可以继承,但是创建子类的时候才会报错
C++11中使用final关键字即可class NonInherit final;
③设计一个只能在堆上创建空间的类
法一(简单但不通用)
思路:私有化析构函数,再公有一个Destruct函数,用来delete this指针
代码:class heap_only1 public: void Desruct() delete this; //this = nullptr; private: ~heap_only1() //int _a; ;
法二(标准且通用)
思路:私有化构造函数,公有一个Create函数,用来创建类
注意:
heap_only2* ptr = Create();会报错,还没有实例化对象就调用成员函数,所以公有的Create函数要设置为static的(静态成员函数只需要指定类域即可,不需要创建对象)- 注意加上 “
不能被拷贝的类” 条件,声明私有构造函数,防止通过拷贝构造在栈上创建空间
代码如下:class heap_only2 public: static heap_only2* Create() return new heap_only2; ~heap_only2() cout << "~heap_only2" << endl; private: heap_only2() :_a(0) heap_only2(const heap_only2& obj);//私有拷贝构造 int _a = 0; ;
④设计一个只能在栈上创建空间的类
法一(标准)
思路:私有构造函数,创建一个公有Create函数,返回构造函数
代码如下:class stack_only1 public: static stack_only1 Create() return stack_only1(); private: stack_only1() :_a(0) ; int _a = 0; ;
调用:test::stack_only1 st = test::stack_only1::Create();//正常 test::stack_only1* ptr1 = new test::stack_only1;//报错
法二 (缺陷)
思路:重载类专属的new/delete,将其私有,只声明,不实现
缺点:可以在静态区创建对象
代码如下:class stack_only2 public: stack_only2() :_a(0) private: void* operator new(size_t size);//c++98只声明不实现 void operator delete(void* ptr); int _a = 0; ;
C++11可以使用=delete,删除函数,不让调用void* operator new(size_t size)=delete; void operator delete(void* ptr)=delete;
2)设计模式
设计模式(Design Pattern)是一套被反复使用、多数人知晓的、经过分类的、代码设计经验的总结
使用设计模式的目的:为了代码可重用性、让代码更容易被他人理解、保证代码可靠性
之前的STL里就接触过一种模式“
迭代器模式”:在不暴露(知晓)底层代码的情况下提供统一的接口
常见有三类模式,23种设计模式
创建型模式(Creational Patterns) | 结构型模式(Structural Patterns) | 行为型模式(Behavioral Patterns) | J2EE 设计模式 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 工厂模式(Factory Pattern) | 桥接模式(Bridge Pattern) | 责任链模式(Chain of Responsibility Pattern) | MVC 模式(MVC Pattern) |
| 抽象工厂模式(Abstract Factory Pattern) | 适配器模式(Adapter Pattern) | 命令模式(Command Pattern) | 业务代表模式(Business Delegate Pattern) |
| 单例模式(Singleton Pattern) | 过滤器模式(Filter、Criteria Pattern) | 解释器模式(Interpreter Pattern) | … … |
| 建造者模式(Builder Pattern) | 组合模式(Composite Pattern) | 迭代器模式(Iterator Pattern) | … … |
| 原型模式(Prototype Pattern) | … … | … … | … … |
Ⅰ单例模式
单例模式:
一个类只能创建一个对象,即单例模式,该模式可以保证系统中该类只有一个实例,并提供一个访问它的全局访问点,该实例被所有程序模块共享。比如在某个服务器程序中,该服务器的配置信息存放在一个文件中,这些配置数据由一个单例对象统一读取,然后服务进程中的其他对象再通过这个单例对象获取这些配置信息这种方式简化了在复杂环境下的配置管理
为什么不使用全局变量?
全局变量缺陷:全局变量在所有的文件都是可见的
有两cpp文件都包含一个single_pattern.h
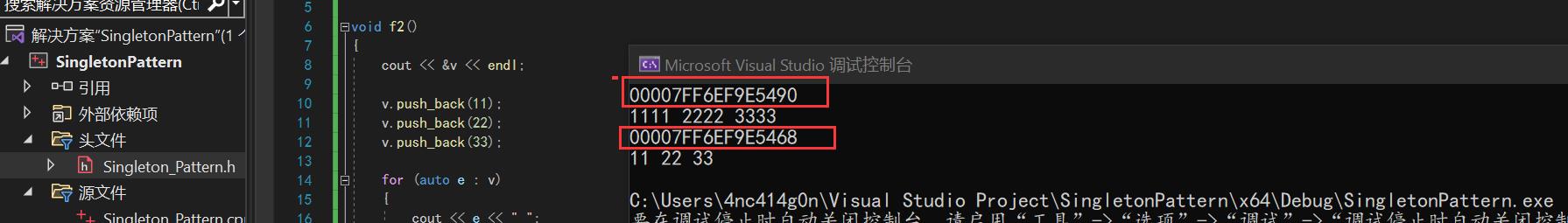
test1.cpp:#include "Singleton_Pattern.h" using namespace std; void f1() cout << &v << endl; v.push_back(1111); v.push_back(2222); v.push_back(3333); for (auto e : v) cout << e << " "; cout << endl;
test2.cpp#include "Singleton_Pattern.h" void f2() cout << &v << endl; v.push_back(11); v.push_back(22); v.push_back(33); for (auto e : v) cout << e << " "; cout << endl;
single_pattern.h//全局链接报错 std::vector<int> v; //全局静态,不再是同一个对象,每个cpp文件各自是一个对象 static std::vector<int> v; void f1(); void f2();全局会链接报错
全局静态不同文件不是同一个vector v
①饿汉模式
思路:
- 私有构造函数,每个单例模式只能创建一个类
- 私有拷贝构造和赋值重载,公有一个静态GetInstance成员函数供其他cpp文件调用
- 声明一个私有的
static singleton_pattern_hunger static_instance;,static成员函数不能访问this只能访问static成员变量- 只能在一个cpp文件中定义(所有的只能定义一次,重复包含会报链接错误,且不能在.h文件中定义),
代码如下:
Singleton_Pattern.h/// 饿汉 / class singleton_pattern_hunger public: static singleton_pattern_hunger& GetInstance(); vector<int > v; private: singleton_pattern_hunger() //防拷贝 singleton_pattern_hunger(const singleton_pattern_hunger& obj) = delete; singleton_pattern_hunger& operator=(const singleton_pattern_hunger& obj) = delete; static singleton_pattern_hunger static_instance; ;Singleton_Pattern.cpp
#include "Singleton_Pattern.h" using namespace test_single; singleton_pattern_hunger singleton_pattern_hunger::static_instance; //singleton_pattern_hunger static_instance;//定义 singleton_pattern_hunger& singleton_pattern_hunger::GetInstance() return static_instance;test1.cpp
void f1() cout << &test_single::singleton_pattern_hunger::GetInstance() << endl; test_single::singleton_pattern_hunger::GetInstance().v.push_back(11111); test_single::singleton_pattern_hunger::GetInstance().v.push_back(222222); test_single::singleton_pattern_hunger::GetInstance().v.push_back(33333); for (auto e : test_single::singleton_pattern_hunger::GetInstance().v) cout << e << " "; cout << endl;test2.cpp
void f2() cout << &test_single::singleton_pattern_hunger::GetInstance() << endl; test_single::singleton_pattern_hunger::GetInstance().v.push_back(11); test_single::singleton_pattern_hunger::GetInstance().v.push_back(22); test_single::singleton_pattern_hunger::GetInstance().v.push_back(33); for (auto e : test_single::singleton_pattern_hunger::GetInstance().v) cout << e << " "; cout << endl;
优点:简单
缺点:
- 单例对象时main函数之前创建初始化的
- 如果单例对象的构造函数中要做很多工作,可能会导致程序启动慢
- 且如果有多个单例类对象实例启动顺序不确定,如果多个单例类,并且他们之前有依赖关系,那么饿汉模式无法保证
②懒汉模式
思路:
- 类似饿汉,但是私有的是静态成员指针
- GetInstance()改为当第一次调用的时候创建单例对象
代码如下:
Singleton_Pattern.hclass singleton_pattern_lazy public: static singleton_pattern_lazy& GetInstance(); static void Del Instance() vector<int > v; private: singleton_pattern_lazy() //防拷贝 singleton_pattern_lazy(const singleton_pattern_lazy& obj) = delete; singleton_pattern_lazy& operator=(const singleton_pattern_lazy& obj) = delete; static singleton_pattern_lazy* pstatic_instance; ;Singleton_Pattern.cpp
singleton_pattern_lazy* singleton_pattern_lazy::pstatic_instance = nullptr; singleton_pattern_lazy& singleton_pattern_lazy::GetInstance() if (singleton_pattern_lazy::pstatic_instance == nullptr) //第一次调用才会创建初始化单例对象 singleton_pattern_lazy::pstatic_instance = new singleton_pattern_lazy; return *(singleton_pattern_lazy::pstatic_instance);
优点:不存在可能会导致启动慢的问题,也可以控制顺序依赖的问题
缺点:
- 不同于饿汉模式(main函数之前没有多线程)
- 懒汉模式在多线程的情况下会造成数据丢失/内存泄漏,需要加锁
加锁:
双检查比单检查效率高 (保证线程安全)singleton_pattern_lazy* singleton_pattern_lazy::pstatic_instance = nullptr; singleton_pattern_lazy& singleton_pattern_lazy::GetInstance() if (singleton_pattern_lazy::pstatic_instance == nullptr) singleton_pattern_lazy::_mtx.lock(); if (singleton_pattern_lazy::pstatic_instance == nullptr) //第一次调用才会创建初始化单例对象 singleton_pattern_lazy::pstatic_instance = new singleton_pattern_lazy; singleton_pattern_lazy::_mtx.unlock(); return *(singleton_pattern_lazy::pstatic_instance); //删除 void singleton_pattern_lazy::Del Instance() if (singleton_pattern_lazy::pstatic_instance != nullptr) singleton_pattern_lazy::_mtx.lock(); if (singleton_pattern_lazy::pstatic_instance != nullptr) delete singleton_pattern_lazy::pstatic_instance; singleton_pattern_lazy::pstatic_instance = nullptr; singleton_pattern_lazy::_mtx.lock();
Ⅱ工厂模式(MARK一下)
这里是引用
Ⅲ观察者模式(MARK一下)
这里是引用
以上是关于C++---设计模式(MARK一下)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章