栈队列面试题
Posted nogos
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了栈队列面试题相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
栈、队列面试题
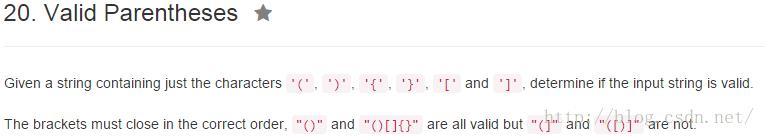 分析
基本思路:用栈保存没有匹配的左括号,遍历字符串中的字符。如果字符为左括号就入栈;如果是右括号,看栈顶元素是否与其匹配,匹配则出栈,否侧返回false。
注意:在处理过程中、处理后要小心检查栈空的情况。
分析
基本思路:用栈保存没有匹配的左括号,遍历字符串中的字符。如果字符为左括号就入栈;如果是右括号,看栈顶元素是否与其匹配,匹配则出栈,否侧返回false。
注意:在处理过程中、处理后要小心检查栈空的情况。
public boolean isValid(String s)
if(s.equalsIgnoreCase("")) return true;
Map<Character,Character> ps=new HashMap<Character,Character>();
ps.put('', '');ps.put('[', ']');ps.put('(', ')');
Stack<Character> stack=new Stack<Character>();
for(char c:s.toCharArray())
if(ps.containsKey(c))
stack.push(c);
else
if(stack.isEmpty())
return false;
else
Character top=stack.peek();
if(ps.get(top).equals(c))
stack.pop();
else
return false;
if(!stack.isEmpty())
return false;
else
return true;
 分析
想要O(1)时间内获取栈中的最小值,显然就暗示不允许我们通过遍历的方式来查找最小值。
我们能是否能用一个变量记录栈的最小值呢?如果8,2,5,1,6先依次入栈,然后再依次出栈,显然,用单个(常数个)变量是无法追踪栈当前最小值的。
方案一:O(1)时间内的查找,我们很容易联想到哈希表,我们可以维护这样一个哈希表<栈大小,栈的最小值>,这样我们就可以在O(1)时间内得到栈中的最小值。空间复杂度为O(K),K为栈的最大长度。
方案二:借鉴方案一的思路,我们可以始终维护一个与元素栈大小相同的最小值栈,保持最小值栈的栈顶元素为元素栈的最小值,并且同步入栈出栈。空间复杂度为O(K),K为栈的最大长度。
代码一
分析
想要O(1)时间内获取栈中的最小值,显然就暗示不允许我们通过遍历的方式来查找最小值。
我们能是否能用一个变量记录栈的最小值呢?如果8,2,5,1,6先依次入栈,然后再依次出栈,显然,用单个(常数个)变量是无法追踪栈当前最小值的。
方案一:O(1)时间内的查找,我们很容易联想到哈希表,我们可以维护这样一个哈希表<栈大小,栈的最小值>,这样我们就可以在O(1)时间内得到栈中的最小值。空间复杂度为O(K),K为栈的最大长度。
方案二:借鉴方案一的思路,我们可以始终维护一个与元素栈大小相同的最小值栈,保持最小值栈的栈顶元素为元素栈的最小值,并且同步入栈出栈。空间复杂度为O(K),K为栈的最大长度。
代码一
public class MinStack
private Stack<Integer> stack;
private Map<Integer,Integer> minMap;
public MinStack()
this.stack=new Stack<Integer>();
this.minMap=new HashMap<Integer,Integer>();
public void push(int x)
if(stack.isEmpty())
stack.push(x);
minMap.put(stack.size(), x);
else
int preMin=minMap.get(stack.size());
stack.push(x);
minMap.put(stack.size(), Math.min(preMin, x));
public void pop()
stack.pop();
public int top()
return stack.peek();
public int getMin()
return minMap.get(stack.size());
public class MinStack
private Stack<Integer> stack;
private Stack<Integer> minStack;;
public MinStack()
this.stack=new Stack<Integer>();
this.minStack=new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int x)
if(stack.isEmpty())
stack.push(x);
minStack.push(x);
else
stack.push(x);
int preMin=minStack.peek();
minStack.push(Math.min(preMin, x));
public void pop()
stack.pop();
minStack.pop();
public int top()
return stack.peek();
public int getMin()
return minStack.peek();
 方案一
内部用队列保存数据,入栈操作时对应内部队列的入队操作,出栈我们需要获取队列最后一个元素,我们将队列之前的元素先出队到一个临时队列,获取队列末尾元素,然后将临时队列赋值给保存数据的队列。
方案一
内部用队列保存数据,入栈操作时对应内部队列的入队操作,出栈我们需要获取队列最后一个元素,我们将队列之前的元素先出队到一个临时队列,获取队列末尾元素,然后将临时队列赋值给保存数据的队列。
public class MyStack
private Queue<Integer> queueOne;
private Queue<Integer> queueTemp;
public MyStack()
queueOne=new LinkedList<Integer>();
queueTemp=new LinkedList<Integer>();
public void push(int x)
queueOne.add(x);
public void pop()
while(true)
Integer front=queueOne.poll();
if(queueOne.isEmpty())
Queue<Integer> t=queueOne;
queueOne=queueTemp;
queueTemp=t;
break;
else
queueTemp.add(front);
public int top()
Integer front=null;
while(true)
front=queueOne.poll();
if(queueOne.isEmpty())
Queue<Integer> t=queueOne;
queueOne=queueTemp;
queueTemp=t;
break;
else
queueTemp.add(front);
queueOne.add(front);
return front;
public boolean empty()
return queueOne.isEmpty();
public class MyStack
private Queue<Integer> queue;
public MyStack()
queue=new LinkedList<Integer>();
public void push(int x)
int size=queue.size();
queue.add(x);
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)
Integer t=queue.peek();
queue.poll();
queue.add(t);
public void pop()
queue.poll();
public int top()
return queue.peek();
public boolean empty()
return queue.isEmpty();

分析 队列是先入先出,栈是后入先出。这种特性与负负得正特性相似,负(后入先出),正(先入先出)。 将数据先后通过两个栈的处理就可以保证先入先出了,即用栈实现了队列的特性。但是,在之前用队列实现栈的例子中,队列先入先出的特性不能充分发挥来构造后入先出的特性,只能每次入栈时,处理整个队列才能保证先入后出。
class MyQueue
private Stack<Integer> stackIn;
private Stack<Integer> stackOut;
private void inToOut()
while(!stackIn.isEmpty())
Integer top=stackIn.peek();
stackIn.pop();
stackOut.push(top);
public MyQueue()
stackIn=new Stack<Integer>();
stackOut=new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int x)
stackIn.push(x);
public void pop()
if(stackOut.isEmpty())
inToOut();
stackOut.pop();
public int peek()
if(stackOut.isEmpty())
inToOut();
Integer top=stackOut.peek();
return top;
public boolean empty()
return stackIn.isEmpty()&&stackOut.isEmpty();
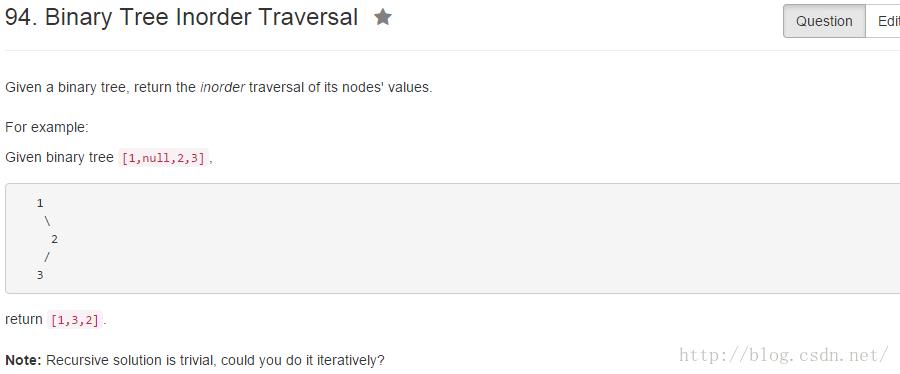
分析
深度优先遍历,利用栈记录遍历路径。
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root)
List<Integer> res=new LinkedList<Integer>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<TreeNode>();
TreeNode p=root;//当前处理的树根
while(p!=null||!stack.isEmpty())
while(p!=null)//先处理左子树
stack.push(p);
p=p.left;
p=stack.pop();
res.add(p.val);
//处理右子树
p=p.right;
return res;
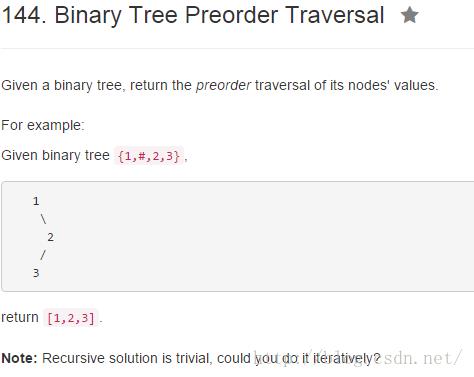
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root)
List<Integer> res=new LinkedList<Integer>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<TreeNode>();
TreeNode p=root;//当前处理的树根
while(p!=null||!stack.isEmpty())
while(p!=null)//先处理左子树
stack.push(p);
res.add(p.val);
p=p.left;
p=stack.pop();
//处理右子树
p=p.right;
return res;

分析 层次遍历即宽度优先遍历,用栈来记录访问路径。
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root)
List<List<Integer>> levels=new LinkedList<List<Integer>>();
if(root==null) return levels;
Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.add(root);
int mark=0;
while(!queue.isEmpty())
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<Integer>();
Queue<TreeNode> nextqueue=new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
while(!queue.isEmpty())
TreeNode node=queue.poll();
list.add(node.val);
if(node.left!=null)nextqueue.add(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)nextqueue.add(node.right);
queue=nextqueue;
if(mark==1)
Collections.reverse(list);
mark=(mark+1)%2;
levels.add(list);
return levels;
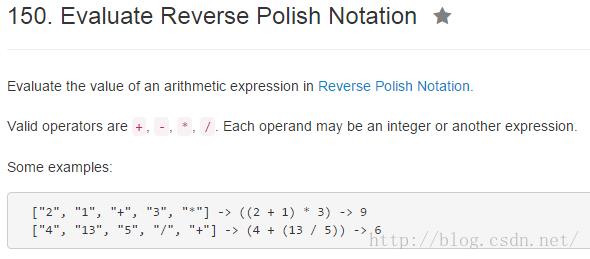
分析 经典的利用栈进行表达式计算。
public int evalRPN(String[] tokens)
Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack<Integer>();
for(String token:tokens)
if(token.equalsIgnoreCase("+"))
Integer second=stack.pop();
Integer first=stack.pop();
stack.push(first+second);
else if(token.equalsIgnoreCase("-"))
Integer second=stack.pop();
Integer first=stack.pop();
stack.push(first-second);
else if(token.equalsIgnoreCase("*"))
Integer second=stack.pop();
Integer first=stack.pop();
stack.push(first*second);
else if(token.equalsIgnoreCase("/"))
Integer second=stack.pop();
Integer first=stack.pop();
stack.push(first/second);
else
stack.push(Integer.parseInt(token));
return stack.pop();

分析 利用二分查找树中序遍历递增的特性,用栈记录遍历路径。
public class BSTIterator
private Stack<TreeNode> stack;
private TreeNode p;
public BSTIterator(TreeNode root)
p=root;
stack=new Stack<TreeNode>();
public boolean hasNext()
return !(p==null&&stack.isEmpty());
public int next()
while(p!=null)
stack.push(p);
p=p.left;
TreeNode top=stack.pop();
p=top.right;
return top.val;

分析 后续遍历同样是利用栈来记录访问路径。注:但是由于是左右中的遍历顺序,当某个根元素存在右子树时,该根元素会两次出现在栈顶,但是只有第二次出现在栈顶的时候才能出栈,因此我们需要利用哈希表标记根元素出现在栈顶的次数。
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root)
List<Integer> res=new LinkedList<Integer>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<TreeNode>();
Map<TreeNode,Integer> mark=new HashMap<TreeNode,Integer>();
TreeNode p=root;
while(p!=null||!stack.isEmpty())
while(p!=null)
stack.push(p);
p=p.left;
p=stack.peek();
if(p.right==null)
res.add(p.val);
stack.pop();
p=null;
else//有右子树
if(mark.get(p)==null)
mark.put(p, 1);
p=p.right;
else
res.add(p.val);
stack.pop();
mark.remove(p);
p=null;
return res;
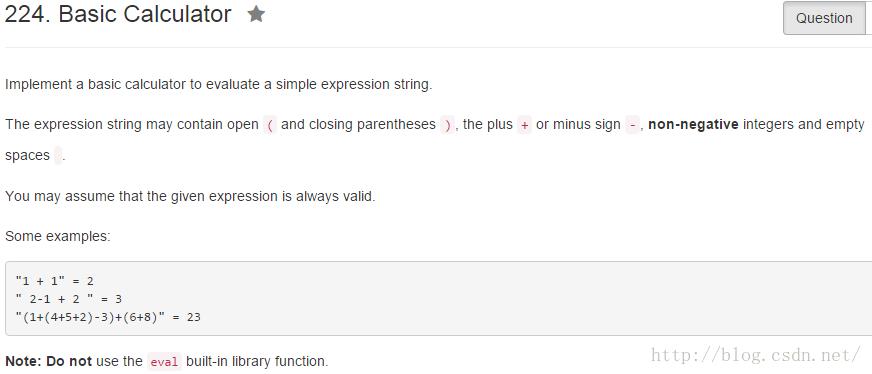
分析 对于表达式的计算(中序表达式),我们可以先将其转换成后序表达式,然后再对其进行计算。
public int calculate(String s)
if(s == null)
return 0;
s = reform(s);
int result = 0, num = 0, base = 1;
for(char c: s.toCharArray())
switch(c)
case '+': result += num; num = 0; base = 1; break;
case '-': result -= num; num = 0; base = 1; break;
default: num += (c - '0') * base; base *= 10;
return result;
private String reform(String s)
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Stack<Boolean> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(true);
boolean add = true;
for(char c: s.toCharArray())
switch(c)
case ' ': break;
case '(': stack.push(add); break;
case ')': stack.pop(); break;
case '+':
add = stack.peek();
sb.append(stack.peek() ? '+' : '-');
break;
case '-':
add = !stack.peek();
sb.append(stack.peek() ? '-' : '+');
break;
default: sb.append(c);
if(sb.charAt(0) != '+' || sb.charAt(0) != '-')
sb.insert(0, '+');
return sb.reverse().toString();

 分析
利用序列化后的字符串重构树,用栈记录路径。如果重构过程失败返回false。
分析
利用序列化后的字符串重构树,用栈记录路径。如果重构过程失败返回false。
public boolean isValidSerialization(String preorder)
Stack<String> stack=new Stack<String>();
if(preorder.equals("")) return false;
String[] values = preorder.split(",");
System.out.println(values.length);
if(values[0].equals("#")&&values.length==1) return true;
if(values[0].equals("#")) return false;
stack.push(values[0]);
int mark=0;
for(int i=1;i<values.length;i++)
if(stack.isEmpty())
return false;
String p=stack.peek();
if(mark==0)//左子树
if(values[i].equals("#"))
mark=(mark+1)%2;//左子树为空,转成处理右子树
else
stack.push(values[i]);//继续处理左子树的左子树
else//右子树
if(values[i].equals("#"))
stack.pop();//继续处理根元素的右子树
else
stack.push(values[i]);
if(!stack.isEmpty())
return false;
else
return true;
以上是关于栈队列面试题的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章