求数据结构(C语言版)建立二叉树的代码~~急~~谢谢了
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了求数据结构(C语言版)建立二叉树的代码~~急~~谢谢了相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
建立一个二叉树:
(1)输出其对应的中,先,后根序列
(2)输出树中结点所在的层数
(3)输出树中叶子数
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <conio.h>
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define ERROR 0
#define OK 1
#define Stack_Size 50
#define NUM 50
#define MAXSIZE 50 //队列的最大长度
//定义二叉树
typedef char DataType;
typedef struct Node
DataType data;
struct Node *LChild;
struct Node *RChild;
BiTNode, *BiTree;
//定义stack
typedef BiTree StackElementType;
typedef struct
StackElementType elem[Stack_Size];
int top;
SeqStack;
//定义队列
typedef BiTree QueueElementType;
typedef struct
QueueElementType element[MAXSIZE];
int front;
int rear;
SeqQueue;
//队列的抽象
void InitQueue(SeqQueue *Q)
Q->front=Q->rear=0;
int EnterQueue(SeqQueue *Q, QueueElementType x)
if((Q->rear+1)%MAXSIZE==Q->front)
return(FALSE);
Q->element[Q->rear]=x;
Q->rear=(Q->rear+1)%MAXSIZE;
return(TRUE);
参考技术A 第一个是一个cpp文件
#include "bt.h"
void main()
BiTree T;
int layer=0;
printf("按扩展先序遍历序列建立二叉树,请输入序列:\n");
CreateBiTree(&T);
//三个递归
printf("先序递归遍历输出序列为:");
PreOrder(T);
printf("\n中序递归遍历输出序列为:");
InOrder(T);
printf("\n后序递归遍历输出序列为:");
PostOrder(T);
//三个非递归
printf("\n先序非递归遍历输出序列为:");
PreNoOrder(T);
printf("\n中序非递归遍历输出序列为:");
InNoOrder(T);
printf("\n后序非递归遍历输出序列为:");
PostNoOrder(T);
//一个层次
printf("\n层次遍历输出结点为:");
LayerOrder(T);
printf("\n按树状打印二叉树\n");
PrintTree(T,layer);
int h=PostTreeDepth(T);
printf("\n二叉树高度为: %d\n",h);
int lc=leaf(T);
printf("二叉树的叶子节点数目: %d\n",lc);
参考技术B 再接
//中序非递归
void InNoOrder(BiTree root)
int top=0;
BiTree p;
BiTree s[Stack_Size];
int m;
m = Stack_Size-1;
p = root;
do
while(p!=NULL)
if (top>m) return;
top=top+1;
s[top]=p;
p=p->LChild;
;
if(top!=0)
p=s[top];
top=top-1;
Visit(p->data);
p=p->RChild;
while(p!=NULL || top!=0);
//后序非递归
void PostNoOrder(BiTree root)
BiTNode *p,*q;
BiTNode **s;
int top=0;
q=NULL;
p=root;
s=(BiTNode**)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode*)*NUM);
while(p!=NULL || top!=0)
while(p!=NULL)
top++;
s[top]=p;
p=p->LChild;
if(top>0)
p=s[top];
if((p->RChild==NULL) ||(p->RChild==q))
Visit(p->data);
q=p;
top--;
p=NULL;
else
p=p->RChild;
free(s);
//层次遍历二叉树
int LayerOrder(BiTree bt)
SeqQueue *Q;
BiTree p;
Q=(SeqQueue *)malloc(sizeof(SeqQueue));
InitQueue(Q);
if(bt == NULL)
return ERROR;
EnterQueue(Q, bt);
while(!IsEmpty(Q))
DeleteQueue(Q, &p);
printf("%c ",p->data);
if(p->LChild )
EnterQueue(Q, p->LChild);
if(p->RChild )
EnterQueue(Q, p->RChild);
return OK;
//后序求二叉树高度
int PostTreeDepth(BiTree bt)
int hl,hr,max;
if(bt!=NULL)
hl=PostTreeDepth(bt->LChild);
hr=PostTreeDepth(bt->RChild);
max=hl>hr?hl:hr;
return(max+1);
else return(0);
//
int leaf(BiTree root)
int LeafCount;
if(root==NULL)
LeafCount=0;
else if((root->LChild==NULL)&&(root->RChild==NULL))
LeafCount=1;
else
LeafCount=leaf(root->LChild)+leaf(root->RChild);
return LeafCount;
//按树状打印二叉树
void PrintTree(BiTree bt,int nLayer)
if(bt==NULL)return;
PrintTree(bt->RChild,nLayer+1);
for(int i=0;i<nLayer;i++)
printf(" ");
printf("%c\n",bt->data);
PrintTree(bt->LChild,nLayer+1);
参考技术C 接着上面的
int DeleteQueue(SeqQueue *Q, QueueElementType *x)
if(Q->front==Q->rear)
return(FALSE);
*x=Q->element[Q->front];
Q->front=(Q->front+1)%MAXSIZE;
return(TRUE);
int IsEmpty(SeqQueue *Q)
if(Q->front==Q->rear)
return(TRUE);
else
return(FALSE);
//输出函数
void Visit(char ch)
printf("%c ",ch);
//扩展先序遍历创建二叉树
void CreateBiTree(BiTree *bt)
char ch;
ch = getchar();
if(ch=='.') *bt=NULL;
else
*bt=(BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
(*bt)->data=ch;
CreateBiTree(&((*bt)->LChild));
CreateBiTree(&((*bt)->RChild));
//先序递归遍历输出二叉树
void PreOrder(BiTree root)
if (root!=NULL)
Visit(root->data);
PreOrder(root ->LChild);
PreOrder(root ->RChild);
//中序递归遍历输出二叉树
void InOrder(BiTree root)
if(root!=NULL)
InOrder(root->LChild);
Visit(root->data);
InOrder(root->RChild);
//后序递归
void PostOrder(BiTree root)
if(root!=NULL)
PostOrder(root->LChild);
PostOrder(root->RChild);
Visit(root->data);
//先序非递归
void PreNoOrder(BiTree root)
int top=0;
BiTree p;
BiTree s[Stack_Size];
int m;
m = Stack_Size-1;
p = root;
do
while(p!=NULL)
if (top>m) return;
Visit(p->data);
top=top+1;
s[top]=p;
p=p->LChild;
;
if(top!=0)
p=s[top];
top=top-1;
p=p->RChild;
while(p!=NULL || top!=0);
数据结构C语言版——链式二叉树的基本操作实现
文章目录
链式二叉树
1. 概念
设计不同的节点结构可构成不同形式的链式存储结构。由二叉树的定义可知,二叉树的节点由一个数据元素分别指向其左右子树的两个分支构成,则表示二叉树的链表中的结点至少包含3个域:数据域和左右指针域,左右指针分别指向左右孩子所在的链节点的存储地址。

typedef char BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
BTDataType data;
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
BTNode;
2. 链式二叉树的基本操作
前序遍历
前序遍历又叫先根遍历,先遍历根节点再遍历左子树和右子树,而左子树和右子树又有根节点,这就是一个递归操作。就是按根左右的遍历方法。
比如下面这棵数的前序遍历就是ABDEHCFG
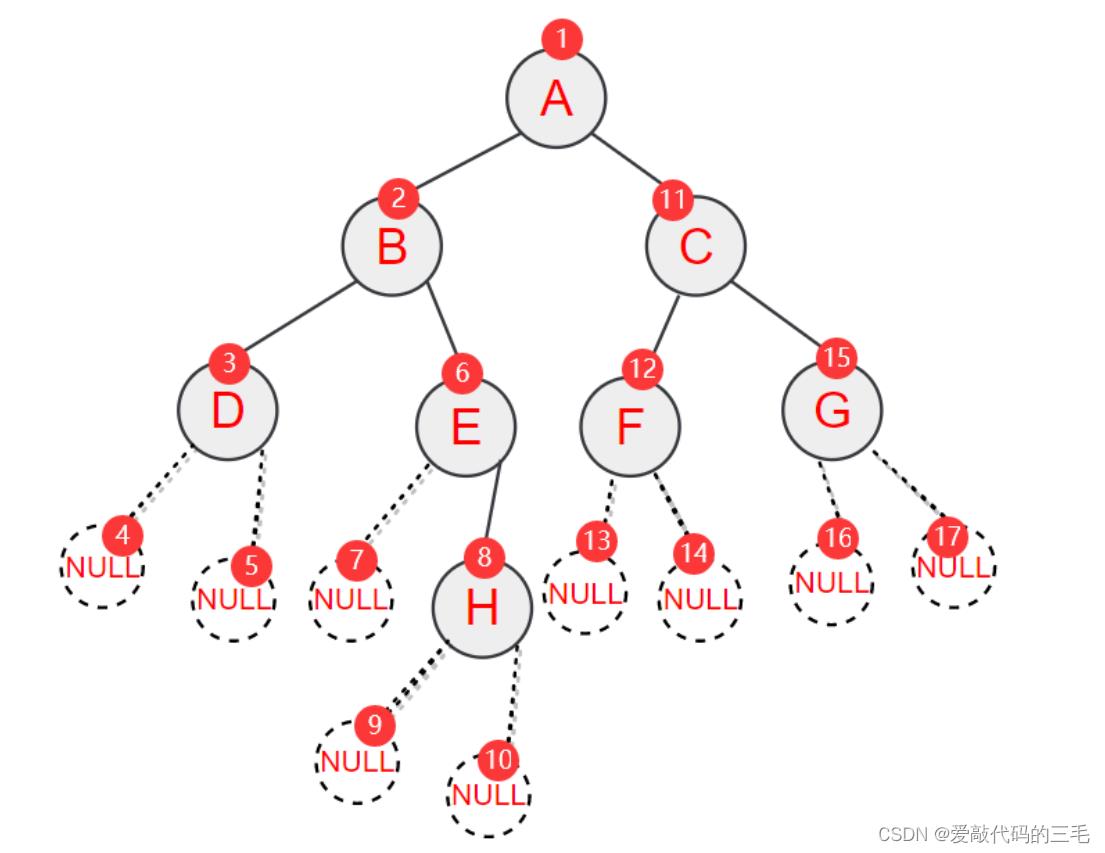
// 二叉树前序遍历
void BinaryTreePrevOrder(BTNode* root)
if (root == NULL)
return;
printf("%c ", root->data);
BinaryTreePrevOrder(root->left);
BinaryTreePrevOrder(root->right);
中序遍历
中序遍历中根遍历,它的遍历顺序就是先遍历左子树再遍历根节点再遍历右子树,也就是左根右。
这棵树的中序遍历就是DBEHAFCG

// 二叉树中序遍历
void BinaryTreeInOrder(BTNode* root)
if (root == NULL)
return;
BinaryTreeInOrder(root->left);
printf("%c ", root->data);
BinaryTreeInOrder(root->right);
后续遍历
后续遍历也叫后根遍历,遍历的顺序是先左子树再右子树最后根节点,按照左右根来遍历二叉树。
下面这棵树的后续遍历就是DHEBFGCA
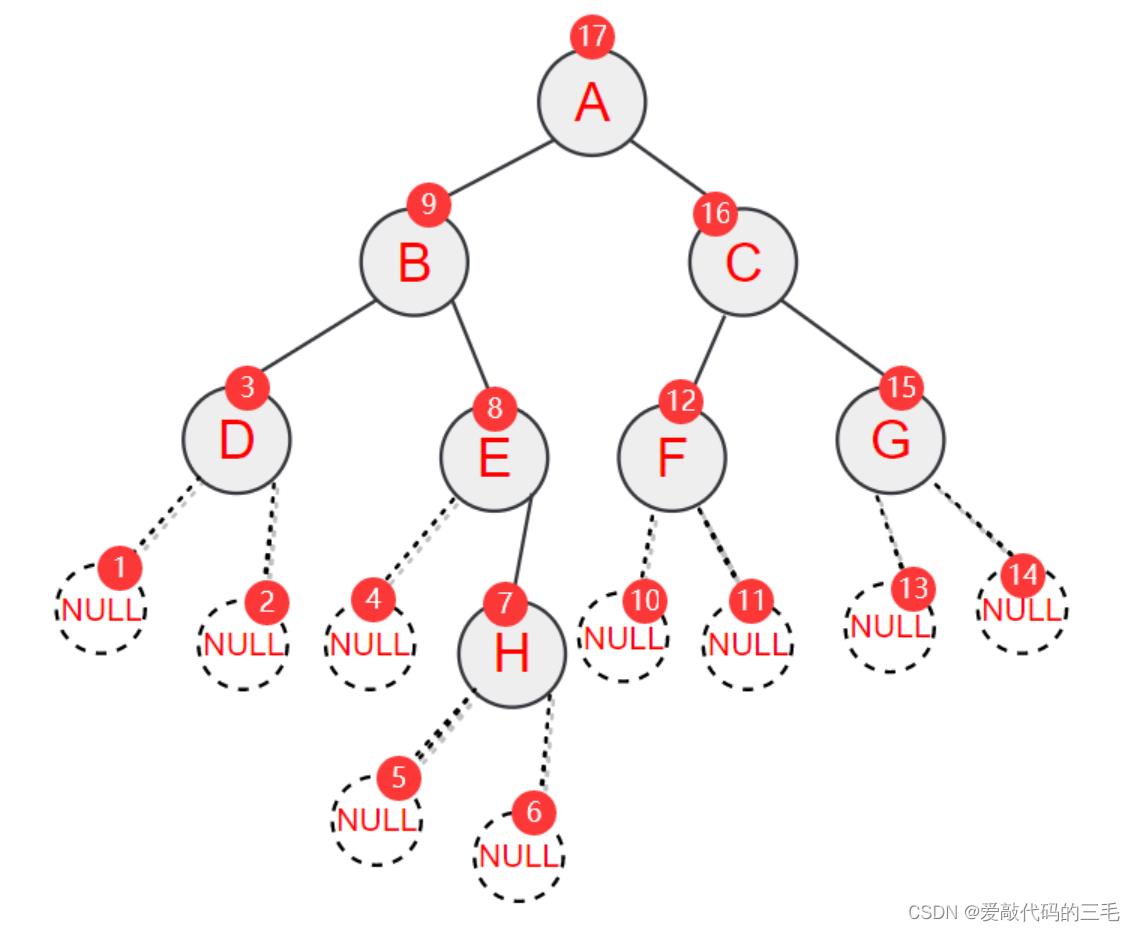
// 二叉树后序遍历
void BinaryTreePostOrder(BTNode* root)
if (root == NULL)
return;
BinaryTreePostOrder(root->left);
BinaryTreePostOrder(root->right);
printf("%c ", root->data);
根据前序遍历构建二叉树
给定一个字符串。是二叉树树的前序遍历ABD##E#H##CF##G##,其中#代表NULL,通过这个字符串构造一颗二叉树。

实现思路:
- 函数三个参数,数组、字符串长度、数组下标,通过递归来构建
- 递归的结束条件,数组遍历完了、或者是遇到
#了 - 每调用一次函数就让index加一
- 最后返回节点
// 根据前序遍历构建二叉树
BTNode* BinaryTreeCreate(BTDataType* arr, int n, int* index)
if (*index >= n || arr[*index] == '#')
return NULL;
BTNode* root = (BTNode*)(malloc(sizeof(BTNode)));
root->data = arr[*index];
(*index)++;
root->left = BinaryTreeCreate(arr, n, index);
(*index)++;
root->right = BinaryTreeCreate(arr, n, index);
return root;
层序遍历
层序遍历就是将二叉树按层一层一层遍历。
下面这个二叉树的层序遍历为ABCDEFGH

思路:
同过队列来进行广度优先搜索。
- 首先将根节点如队列,然后出队出队的同时将左右孩子入队列(注意左右孩子不为空)
- 出队前记录当前队列元素个数,出当前队列中的元素(避免刚入队的左右子树出队列)
- 当队列为空时说明层序遍历完成
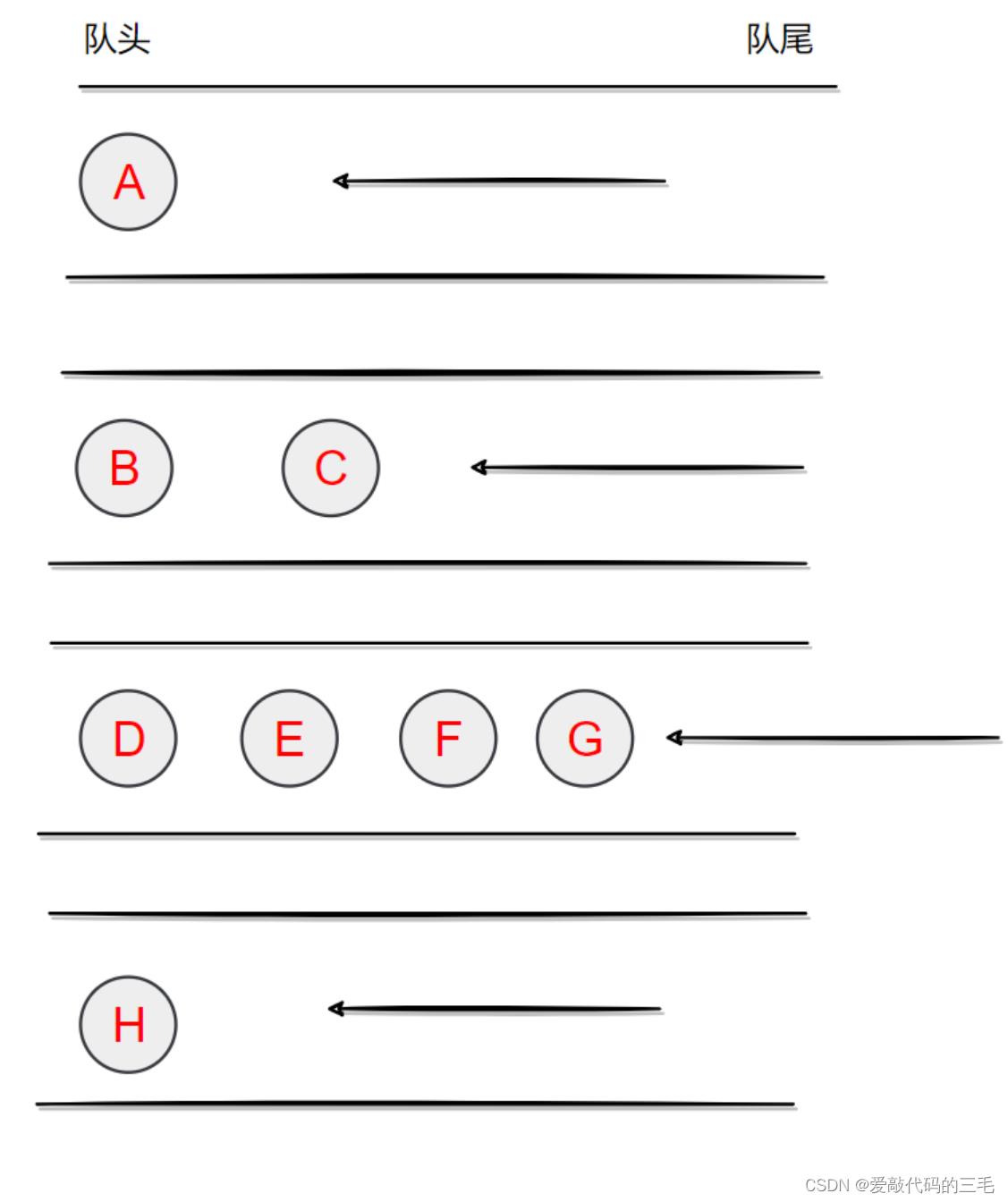
// 层序遍历
void BinaryTreeLevelOrder(BTNode* root)
Queue q = NULL,NULL;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q,root);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
int size = QueueSize(&q);
while (size--)
BTNode* root = QueueFront(&q);
printf("%c ", root->data);
if (root->left != NULL)
QueuePush(&q, root->left);
if (root->right != NULL)
QueuePush(&q, root->right);
QueuePop(&q);
在二叉树中查找指定值
直接递归遍历二叉树,先找根节点再找左子树和右子树。
// 二叉树查找值为x的节点
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
if (root->data == x)
return root;
BTNode* left = BinaryTreeFind(root->left, x);
if (left != NULL)
return left;
BTNode* right = BinaryTreeFind(root->right, x);
if (right != NULL)
return right;
return NULL;
获取二叉树节点个数
这其实就时一个普通的遍历,通过递归将大事化小。整棵树的节点个数会等于:它的左子树节点个数加上右子树的节点个数再加上自己,也就是加一。
// 二叉树节点个数
int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root)
return root == NULL ? 0 : BinaryTreeSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeSize(root->right) + 1;
获取叶子节点个数
叶子节点右一个特点,就是它的左子树和右子树都为空,通过递归如果左右子树都为NULL就返回1,否则返回0,就能得到叶子节点个数。
// 二叉树叶子节点个数
int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
return 1;
return BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->right);
求二叉树的高度
二叉树的高度就是它的最大深度,相求一颗树的最大深度,就得先求出它的左右子树的最大深度,通过后续遍历到达叶子节点,从叶子节点开始不断求出左右子树的较大的那一棵子树再加一,开始不断向上返回就能得到一颗二叉树的最大深度。
int maxDepth(BTNode* root)
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
int left = maxDepth(root->left);
int right = maxDepth(root->right);
return left > right ? left+1 : right+1;
从叶子节点开始不断求出左右子树的较大的那一棵子树再加一,开始不断向上返回就能得到一颗二叉树的最大深度。
int maxDepth(BTNode* root)
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
int left = maxDepth(root->left);
int right = maxDepth(root->right);
return left > right ? left+1 : right+1;
以上是关于求数据结构(C语言版)建立二叉树的代码~~急~~谢谢了的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
急!高分悬赏!求c语言高手!!!二叉树输入中如何判断输入是不是合法?
急!二叉树的存储结构,并完成:建立、查找、计算结点数、求高度、三种遍历方式