main主函数参数解析
Posted Half-up
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了main主函数参数解析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
默认的main函数参数
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
// 主函数的代码逻辑
return 0;
-
其中,int 是主函数的返回值类型,主函数执行完后会返回一个整数值给操作系统,通常
返回值为 0 表示程序正常结束,非 0 的返回值表示程序运行出现错误。 -
argc 和 argv[]是主函数的参数列表: 主要用于命令行
-
argc:表示命令行参数的个数(argument count),即程序被调用时在命令行中输入的参数的总数(包括程序本身),其中至少有一个参数,即程序本身。
例如,输入命令 “./my_program file1.txt file2.txt”,则 argc 的值为 3。 -
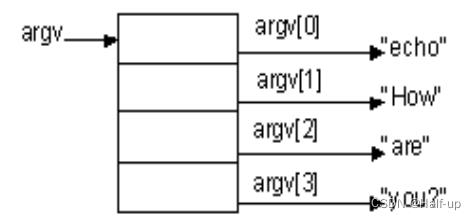
argv[]:表示命令行参数的数组(argument vector),存放着每个参数字符串的指针,其中 argv[0] 指向程序名本身,argv[1] 指向第一个参数字符串,argv[2] 指向第二个参数字符串, 以此类推。
例如,输入命令 “./my_program file1.txt file2.txt”,则 argv[0] 的值为 “./my_program”,argv[1] 的值为 “file1.txt”,argv[2] 的值为 “file2.txt”。
通过这两个参数,我们可以在命令行中以不同的方式指定程序运行时需要的参数,从而使程序能够更加灵活地运行。同时,我们也可以通过遍历 argv 数组来获取各个命令行参数的值,并进行相应的处理,例如将其中的文件名作为输入文件读入程序中进行处理。
举例:回显命令行参数的程序
//回显命令行参数的代码
#include<stdio.h>
int main(int argc,char* argv[])
int i;
for ( i = 0; i < argc; i++)
fputs(argv[i],stdin);
return 0;
生成了编译程序test.exe,在终端下输入"echo what day is today?“。这个命令行向echo的main函数传递了5个参数,所以argc的值是5.其中,argc[0]指向echo,argv[4]指向"today?”

也就是这样:
调用main函数过程(汇编层面)
在可执行文件被加载之后,控制权立即交给由编译器插入的 _start函数, _start函数初始化系统相关资源并调用main()函数:
- 设置栈指针
- 初始化static静态和全局变量,即data段的内容
- 将未初始化部分的赋初值
- 将main函数的参数argc、argv等传递给main函数,然后才真正运行main函数
在其他程序中调用应用程序 system
// aa.cpp
#include<stdio.h>
int main(int argc,char* argv[])
printf("Hello");
puts(*(argv+1));
return 0;
//test.cpp
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
system("/Users/apple/C_program/C_source/C语言main函数参数解析/在其他程序中调用应用程序/aa __halfup");
return 0;
运行后:
调用连接了;
也可以调用其他可执行程序
system函数调用作用
以下是几个常用的 system 函数调用和它们的作用:
| 函数调用 | 作用说明 |
|---|---|
system("dir") | 显示当前目录的内容 |
system("cls") | 清屏(常用) |
system("color 2") | 设置命令窗口字体颜色 |
system("shutdown /r /t 1000") | 在 1000 秒之后重启计算机 |
system("shutdown /a") | 取消计划中的关机指令 |
system("D:\\\\win Word.exe") | 打开 D 盘根目录下的 Word.exe 应用程序 |
补充一些:
| 函数调用 | 作用说明 |
|---|---|
system("ipconfig") | 显示网络配置信息 |
system("ping www.google.com") | ping指定域名或IP地址 |
system("tasklist") | 列出正在运行的进程和应用程序 |
system("taskkill /im app.exe /f") | 强制关闭指定名称的进程或应用程序 |
system("del /F /S /Q C:\\\\*.tmp") | 删除指定盘符下所有的 .tmp 文件 |
system("date") | 显示当前日期 |
system("time") | 显示当前时间 |
system("ver") | 查看操作系统版本信息 |
x264代码剖析:主函数main()解析函数parse()与编码函数encode()
x264代码剖析(三):主函数main()、解析函数parse()与编码函数encode()
x264的入口函数为main()。main()函数首先调用parse()解析输入的参数,然后调用encode()编码YUV数据。parse()首先调用x264_param_default()为保存参数的x264_param_t结构体赋默认值;然后在一个大循环中通过getopt_long()解析通过命令行传递来的存储在argv[]中的参数,并作相应的设置工作;最后调用select_input()和select_output()完成输入文件格式(yuv,y4m等)和输出文件格式(裸流,mp4,mkv,FLV等)的设置。encode()首先调用x264_encoder_open()打开编码器;接着在一个循环中反复调用encode_frame()一帧一帧地进行编码;最后在编码完成后调用x264_encoder_close()关闭编码器。encode_frame()则调用x264_encoder_encode()将存储YUV数据的x264_picture_t编码为存储H.264数据的x264_nal_t。具体函数关系如下图所示:
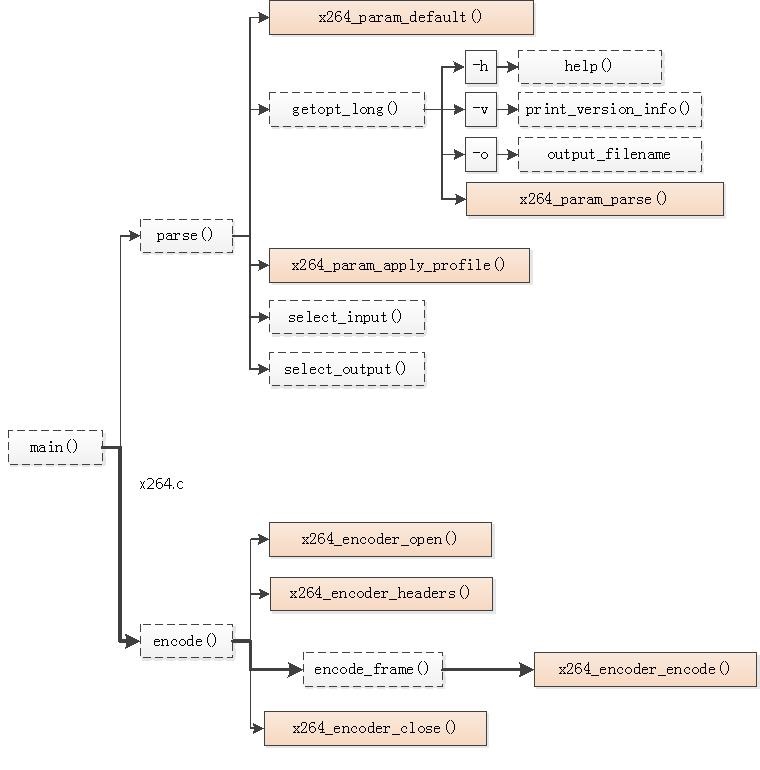
下面对该函数关系图中的主函数main()、解析函数parse()与编码函数encode()做详细的分析。
1、主函数main()
主函数主要调用了两个函数:parse()和encode()。main()首先调用parse()解析输入的命令行参数,然后调用encode()进行编码。对应代码如下:
/******************************************************************/
/******************************************************************/
/*
======Analysed by RuiDong Fang
======Csdn Blog:http://blog.csdn.net/frd2009041510
======Date:2016.03.07
*/
/******************************************************************/
/******************************************************************/
/************====== 主函数 ======************/
/*
功能:主要调用了两个函数:parse()和encode()。
main()首先调用parse()解析输入的命令行参数,然后调用encode()进行编码。
*/
int main( int argc, char **argv )
{
x264_param_t param; //参数集
cli_opt_t opt = {0};
int ret = 0;
FAIL_IF_ERROR( x264_threading_init(), "unable to initialize threading\\n" )
#ifdef _WIN32
FAIL_IF_ERROR( !get_argv_utf8( &argc, &argv ), "unable to convert command line to UTF-8\\n" )
GetConsoleTitleW( org_console_title, CONSOLE_TITLE_SIZE );
_setmode( _fileno( stdin ), _O_BINARY );
_setmode( _fileno( stdout ), _O_BINARY );
_setmode( _fileno( stderr ), _O_BINARY );
#endif
/* Parse command line */
if( parse( argc, argv, ¶m, &opt ) < 0 ) ///解析命令行输入,调用parse()
ret = -1;
#ifdef _WIN32
/* Restore title; it can be changed by input modules */
SetConsoleTitleW( org_console_title );
#endif
/* Control-C handler */
signal( SIGINT, sigint_handler );
if( !ret )
ret = encode( ¶m, &opt ); ///编码,调用encode()
/* clean up handles */
if( filter.free )
filter.free( opt.hin );
else if( opt.hin )
cli_input.close_file( opt.hin );
if( opt.hout )
cli_output.close_file( opt.hout, 0, 0 );
if( opt.tcfile_out )
fclose( opt.tcfile_out );
if( opt.qpfile )
fclose( opt.qpfile );
#ifdef _WIN32
SetConsoleTitleW( org_console_title );
free( argv );
#endif
return ret;
}
2、解析函数parse()
解析函数parse()解析输入的命令行参数,存储于argv[]中,对应的代码如下:
/************====== 解析函数 ======************/
/*
功能:parse()解析输入的命令行参数,存储于argv[]中
*/
static int parse( int argc, char **argv, x264_param_t *param, cli_opt_t *opt )
{
char *input_filename = NULL;
const char *demuxer = demuxer_names[0];
char *output_filename = NULL;
const char *muxer = muxer_names[0];
char *tcfile_name = NULL;
x264_param_t defaults; //默认值设为x264_param_t结构体
char *profile = NULL;
char *vid_filters = NULL;
int b_thread_input = 0;
int b_turbo = 1;
int b_user_ref = 0;
int b_user_fps = 0;
int b_user_interlaced = 0;
cli_input_opt_t input_opt;
cli_output_opt_t output_opt;
char *preset = NULL;
char *tune = NULL;
//x264_param_default()是一个x264的API,调用x264_param_default()为保存参数的x264_param_t结构体赋默认值
x264_param_default( &defaults ); ///初始化参数默认值
cli_log_level = defaults.i_log_level;
memset( &input_opt, 0, sizeof(cli_input_opt_t) );
memset( &output_opt, 0, sizeof(cli_output_opt_t) );
input_opt.bit_depth = 8;
input_opt.input_range = input_opt.output_range = param->vui.b_fullrange = RANGE_AUTO;
int output_csp = defaults.i_csp;
opt->b_progress = 1;
/* Presets are applied before all other options. */
for( optind = 0;; )
{
//通过getopt_long()解析通过命令行传递来的存储在argv[]中的参数,并作相应的设置工作
int c = getopt_long( argc, argv, short_options, long_options, NULL ); ///getopt_long()
if( c == -1 )
break;
if( c == OPT_PRESET )
preset = optarg;
if( c == OPT_TUNE )
tune = optarg;
else if( c == '?' )
return -1;
}
if( preset && !strcasecmp( preset, "placebo" ) )
b_turbo = 0;
//x264_param_default_preset()是一个libx264的API,用于设置x264的preset和tune。
if( x264_param_default_preset( param, preset, tune ) < 0 ) //设置preset、tune
return -1;
/* Parse command line options */
//解析命令行选项
for( optind = 0;; )
{
int b_error = 0;
int long_options_index = -1;
int c = getopt_long( argc, argv, short_options, long_options, &long_options_index );
if( c == -1 )
{
break;
}
//不同的选项做不同的处理
switch( c )
{
//"-h"帮助菜单
case 'h':
help( &defaults, 0 );
exit(0);
case OPT_LONGHELP:
help( &defaults, 1 );
exit(0);
case OPT_FULLHELP:
help( &defaults, 2 );
exit(0);
//"-V"打印版本信息
case 'V':
print_version_info();
exit(0);
case OPT_FRAMES:
param->i_frame_total = X264_MAX( atoi( optarg ), 0 );
break;
case OPT_SEEK:
opt->i_seek = X264_MAX( atoi( optarg ), 0 );
break;
//"-o"输出文件路径
case 'o':
output_filename = optarg;
break;
case OPT_MUXER:
FAIL_IF_ERROR( parse_enum_name( optarg, muxer_names, &muxer ), "Unknown muxer `%s'\\n", optarg )
break;
case OPT_DEMUXER:
FAIL_IF_ERROR( parse_enum_name( optarg, demuxer_names, &demuxer ), "Unknown demuxer `%s'\\n", optarg )
break;
case OPT_INDEX:
input_opt.index_file = optarg;
break;
case OPT_QPFILE:
opt->qpfile = x264_fopen( optarg, "rb" );
FAIL_IF_ERROR( !opt->qpfile, "can't open qpfile `%s'\\n", optarg )
if( !x264_is_regular_file( opt->qpfile ) )
{
x264_cli_log( "x264", X264_LOG_ERROR, "qpfile incompatible with non-regular file `%s'\\n", optarg );
fclose( opt->qpfile );
return -1;
}
break;
case OPT_THREAD_INPUT:
b_thread_input = 1;
break;
case OPT_QUIET:
cli_log_level = param->i_log_level = X264_LOG_NONE; //设置log级别
break;
//"-v"
case 'v':
cli_log_level = param->i_log_level = X264_LOG_DEBUG; //设置log级别
break;
case OPT_LOG_LEVEL:
if( !parse_enum_value( optarg, log_level_names, &cli_log_level ) )
cli_log_level += X264_LOG_NONE;
else
cli_log_level = atoi( optarg );
param->i_log_level = cli_log_level; //设置log级别
break;
case OPT_NOPROGRESS:
opt->b_progress = 0;
break;
case OPT_TUNE:
case OPT_PRESET:
break;
case OPT_PROFILE:
profile = optarg;
break;
case OPT_SLOWFIRSTPASS:
b_turbo = 0;
break;
//"-r"
case 'r':
b_user_ref = 1;
goto generic_option;
case OPT_FPS:
b_user_fps = 1;
param->b_vfr_input = 0;
goto generic_option;
case OPT_INTERLACED:
b_user_interlaced = 1;
goto generic_option;
case OPT_TCFILE_IN:
tcfile_name = optarg;
break;
case OPT_TCFILE_OUT:
opt->tcfile_out = x264_fopen( optarg, "wb" );
FAIL_IF_ERROR( !opt->tcfile_out, "can't open `%s'\\n", optarg )
break;
case OPT_TIMEBASE:
input_opt.timebase = optarg;
break;
case OPT_PULLDOWN:
FAIL_IF_ERROR( parse_enum_value( optarg, pulldown_names, &opt->i_pulldown ), "Unknown pulldown `%s'\\n", optarg )
break;
case OPT_VIDEO_FILTER:
vid_filters = optarg;
break;
case OPT_INPUT_FMT:
input_opt.format = optarg; //输入文件格式
break;
case OPT_INPUT_RES:
input_opt.resolution = optarg; //输入分辨率
break;
case OPT_INPUT_CSP:
input_opt.colorspace = optarg; //输入色域
break;
case OPT_INPUT_DEPTH:
input_opt.bit_depth = atoi( optarg ); //输入颜色位深
break;
case OPT_DTS_COMPRESSION:
output_opt.use_dts_compress = 1;
break;
case OPT_OUTPUT_CSP:
FAIL_IF_ERROR( parse_enum_value( optarg, output_csp_names, &output_csp ), "Unknown output csp `%s'\\n", optarg )
// correct the parsed value to the libx264 csp value
#if X264_CHROMA_FORMAT
static const uint8_t output_csp_fix[] = { X264_CHROMA_FORMAT, X264_CSP_RGB };
#else
static const uint8_t output_csp_fix[] = { X264_CSP_I420, X264_CSP_I422, X264_CSP_I444, X264_CSP_RGB };
#endif
param->i_csp = output_csp = output_csp_fix[output_csp];
break;
case OPT_INPUT_RANGE:
FAIL_IF_ERROR( parse_enum_value( optarg, range_names, &input_opt.input_range ), "Unknown input range `%s'\\n", optarg )
input_opt.input_range += RANGE_AUTO;
break;
case OPT_RANGE:
FAIL_IF_ERROR( parse_enum_value( optarg, range_names, ¶m->vui.b_fullrange ), "Unknown range `%s'\\n", optarg );
input_opt.output_range = param->vui.b_fullrange += RANGE_AUTO;
break;
default:
generic_option:
{
if( long_options_index < 0 )
{
for( int i = 0; long_options[i].name; i++ )
if( long_options[i].val == c )
{
long_options_index = i;
break;
}
if( long_options_index < 0 )
{
/* getopt_long already printed an error message */
return -1;
}
}
//解析以字符串方式输入的参数
//即选项名称和选项值都是字符串
//实质就是通过strcmp()方法
b_error |= x264_param_parse( param, long_options[long_options_index].name, optarg ); ///x264_param_parse()
}
}
if( b_error )
{
const char *name = long_options_index > 0 ? long_options[long_options_index].name : argv[optind-2];
x264_cli_log( "x264", X264_LOG_ERROR, "invalid argument: %s = %s\\n", name, optarg );
return -1;
}
}
/* If first pass mode is used, apply faster settings. */
if( b_turbo )
x264_param_apply_fastfirstpass( param );
/* Apply profile restrictions. */
//x264_param_apply_profile()是一个x264的API,该函数用于设置x264的profile.
if( x264_param_apply_profile( param, profile ) < 0 ) ///设置profile
return -1;
/* Get the file name */
FAIL_IF_ERROR( optind > argc - 1 || !output_filename, "No %s file. Run x264 --help for a list of options.\\n",
optind > argc - 1 ? "input" : "output" )
//根据文件名的后缀确定输出的文件格式(raw H264,flv,mp4...)
if( select_output( muxer, output_filename, param ) ) ///select_output()
return -1;
FAIL_IF_ERROR( cli_output.open_file( output_filename, &opt->hout, &output_opt ), "could not open output file `%s'\\n", output_filename )
//输入文件路径
input_filename = argv[optind++];
video_info_t info = {0};
char demuxername[5];
/* set info flags to be overwritten by demuxer as necessary. */
//设置info结构体
info.csp = param->i_csp;
info.fps_num = param->i_fps_num;
info.fps_den = param->i_fps_den;
info.fullrange = input_opt.input_range == RANGE_PC;
info.interlaced = param->b_interlaced;
if( param->vui.i_sar_width > 0 && param->vui.i_sar_height > 0 )
{
info.sar_width = param->vui.i_sar_width;
info.sar_height = param->vui.i_sar_height;
}
info.tff = param->b_tff;
info.vfr = param->b_vfr_input;
input_opt.seek = opt->i_seek;
input_opt.progress = opt->b_progress;
input_opt.output_csp = output_csp;
//设置输入文件的格式(yuv,y4m...)
if( select_input( demuxer, demuxername, input_filename, &opt->hin, &info, &input_opt ) ) ///select_input()
return -1;
FAIL_IF_ERROR( !opt->hin && cli_input.open_file( input_filename, &opt->hin, &info, &input_opt ),
"could not open input file `%s'\\n", input_filename )
x264_reduce_fraction( &info.sar_width, &info.sar_height );
x264_reduce_fraction( &info.fps_num, &info.fps_den );
x264_cli_log( demuxername, X264_LOG_INFO, "%dx%d%c %u:%u @ %u/%u fps (%cfr)\\n", info.width,
info.height, info.interlaced ? 'i' : 'p', info.sar_width, info.sar_height,
info.fps_num, info.fps_den, info.vfr ? 'v' : 'c' );
if( tcfile_name )
{
FAIL_IF_ERROR( b_user_fps, "--fps + --tcfile-in is incompatible.\\n" )
FAIL_IF_ERROR( timecode_input.open_file( tcfile_name, &opt->hin, &info, &input_opt ), "timecode input failed\\n" )
cli_input = timecode_input;
}
else FAIL_IF_ERROR( !info.vfr && input_opt.timebase, "--timebase is incompatible with cfr input\\n" )
/* init threaded input while the information about the input video is unaltered by filtering */
#if HAVE_THREAD
if( info.thread_safe && (b_thread_input || param->i_threads > 1
|| (param->i_threads == X264_THREADS_AUTO && x264_cpu_num_processors() > 1)) )
{
if( thread_input.open_file( NULL, &opt->hin, &info, NULL ) )
{
fprintf( stderr, "x264 [error]: threaded input failed\\n" );
return -1;
}
cli_input = thread_input;
}
#endif
/* override detected values by those specified by the user */
if( param->vui.i_sar_width > 0 && param->vui.i_sar_height > 0 )
{
info.sar_width = param->vui.i_sar_width;
info.sar_height = param->vui.i_sar_height;
}
if( b_user_fps )
{
info.fps_num = param->i_fps_num;
info.fps_den = param->i_fps_den;
}
if( !info.vfr )
{
info.timebase_num = info.fps_den;
info.timebase_den = info.fps_num;
}
if( !tcfile_name && input_opt.timebase )
{
uint64_t i_user_timebase_num;
uint64_t i_user_timebase_den;
int ret = sscanf( input_opt.timebase, "%"SCNu64"/%"SCNu64, &i_user_timebase_num, &i_user_timebase_den );
FAIL_IF_ERROR( !ret, "invalid argument: timebase = %s\\n", input_opt.timebase )
else if( ret == 1 )
{
i_user_timebase_num = info.timebase_num;
i_user_timebase_den = strtoul( input_opt.timebase, NULL, 10 );
}
FAIL_IF_ERROR( i_user_timebase_num > UINT32_MAX || i_user_timebase_den > UINT32_MAX,
"timebase you specified exceeds H.264 maximum\\n" )
opt->timebase_convert_multiplier = ((double)i_user_timebase_den / info.timebase_den)
* ((double)info.timebase_num / i_user_timebase_num);
info.timebase_num = i_user_timebase_num;
info.timebase_den = i_user_timebase_den;
info.vfr = 1;
}
if( b_user_interlaced )
{
info.interlaced = param->b_interlaced;
info.tff = param->b_tff;
}
if( input_opt.input_range != RANGE_AUTO )
info.fullrange = input_opt.input_range;
//初始化滤镜filter
//filter可以认为是一种“扩展”了的输入源
if( init_vid_filters( vid_filters, &opt->hin, &info, param, output_csp ) )
return -1;
/* set param flags from the post-filtered video */
param->b_vfr_input = info.vfr;
param->i_fps_num = info.fps_num;
param->i_fps_den = info.fps_den;
param->i_timebase_num = info.timebase_num;
param->i_timebase_den = info.timebase_den;
param->vui.i_sar_width = info.sar_width;
param->vui.i_sar_height = info.sar_height;
info.num_frames = X264_MAX( info.num_frames - opt->i_seek, 0 );
if( (!info.num_frames || param->i_frame_total < info.num_frames)
&& param->i_frame_total > 0 )
info.num_frames = param->i_frame_total;
param->i_frame_total = info.num_frames;
if( !b_user_interlaced && info.interlaced )
{
#if HAVE_INTERLACED
x264_cli_log( "x264", X264_LOG_WARNING, "input appears to be interlaced, enabling %cff interlaced mode.\\n"
" If you want otherwise, use --no-interlaced or --%cff\\n",
info.tff ? 't' : 'b', info.tff ? 'b' : 't' );
param->b_interlaced = 1;
param->b_tff = !!info.tff;
#else
x264_cli_log( "x264", X264_LOG_WARNING, "input appears to be interlaced, but not compiled with interlaced support\\n" );
#endif
}
/* if the user never specified the output range and the input is now rgb, default it to pc */
int csp = param->i_csp & X264_CSP_MASK;
if( csp >= X264_CSP_BGR && csp <= X264_CSP_RGB )
{
if( input_opt.output_range == RANGE_AUTO )
param->vui.b_fullrange = RANGE_PC;
/* otherwise fail if they specified tv */
FAIL_IF_ERROR( !param->vui.b_fullrange, "RGB must be PC range" )
}
/* Automatically reduce reference frame count to match the user's target level
* if the user didn't explicitly set a reference frame count. */
if( !b_user_ref )
{
int mbs = (((param->i_width)+15)>>4) * (((param->i_height)+15)>>4);
for( int i = 0; x264_levels[i].level_idc != 0; i++ )
if( param->i_level_idc == x264_levels[i].level_idc )
{
while( mbs * param->i_frame_reference > x264_levels[i].dpb && param->i_frame_reference > 1 )
param->i_frame_reference--;
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
3、编码函数encode()
编码函数encode()主要用于设置正式编码前的一些参数,并且调用了encode_frame()函数,而encode_frame()又调用了x264_encoder_encode()函数进行正式编码。对应的代码如下:
/************====== encode函数 ======************/
/*
功能:编码(在内部有一个循环用于一帧一帧编码)
*/
static int encode( x264_param_t *param, cli_opt_t *opt )
{
x264_t *h = NULL;
x264_picture_t pic;
cli_pic_t cli_pic;
const cli_pulldown_t *pulldown = NULL; // shut up gcc
int i_frame = 0;
int i_frame_output = 0;
int64_t i_end, i_previous = 0, i_start = 0;
int64_t i_file = 0;
int i_frame_size;
int64_t last_dts = 0;
int64_t prev_dts = 0;
int64_t first_dts = 0;
# define MAX_PTS_WARNING 3 /* arbitrary */
int pts_warning_cnt = 0;
int64_t largest_pts = -1;
int64_t second_largest_pts = -1;
int64_t ticks_per_frame;
double duration;
double pulldown_pts = 0;
int retval = 0;
opt->b_progress &= param->i_log_level < X264_LOG_DEBUG;
/* set up pulldown */
if( opt->i_pulldown && !param->b_vfr_input )
{
param->b_pulldown = 1;
param->b_pic_struct = 1;
pulldown = &pulldown_values[opt->i_pulldown];
param->i_timebase_num = param->i_fps_den;
FAIL_IF_ERROR2( fmod( param->i_fps_num * pulldown->fps_factor, 1 ),
"unsupported framerate for chosen pulldown\\n" )
param->i_timebase_den = param->i_fps_num * pulldown->fps_factor;
}
h = x264_encoder_open( param ); /x264_encoder_open():打开编码器
FAIL_IF_ERROR2( !h, "x264_encoder_open failed\\n" );
//获得参数
x264_encoder_parameters( h, param );
//一些不是裸流的封转格式(FLV,MP4等)需要一些参数,例如宽高等等
//cli_output_t是代表输出媒体文件的结构体
FAIL_IF_ERROR2( cli_output.set_param( opt->hout, param ), "can't set outfile param\\n" );
//计时开始
i_start = x264_mdate();
/* ticks/frame = ticks/second / frames/second */
ticks_per_frame = (int64_t)param->i_timebase_den * param->i_fps_den / param->i_timebase_num / param->i_fps_num;
FAIL_IF_ERROR2( ticks_per_frame < 1 && !param->b_vfr_input, "ticks_per_frame invalid: %"PRId64"\\n", ticks_per_frame )
ticks_per_frame = X264_MAX( ticks_per_frame, 1 );
//如果不是在每个keyframe前面都增加SPS/PPS/SEI的话,就在整个码流前面加SPS/PPS/SEI
//Header指的就是SPS/PPS/SEI
if( !param->b_repeat_headers )
{
// Write SPS/PPS/SEI
x264_nal_t *headers;
int i_nal;
//获得文件头(SPS、PPS、SEI)
FAIL_IF_ERROR2( x264_encoder_headers( h, &headers, &i_nal ) < 0, "x264_encoder_headers failed\\n" ) /x264_encoder_headers():输出SPS,PPS,SEI等信息
//把文件头写入输出文件
FAIL_IF_ERROR2( (i_file = cli_output.write_headers( opt->hout, headers )) < 0, "error writing headers to output file\\n" );
}
if( opt->tcfile_out )
fprintf( opt->tcfile_out, "# timecode format v2\\n" );
/* Encode frames */
//循环进行编码
for( ; !b_ctrl_c && (i_frame < param->i_frame_total || !param->i_frame_total); i_frame++ )
{
//从输入源中获取1帧YUV数据,存于cli_pic
//cli_vid_filter_t可以认为是x264一种“扩展”后的输入源,可以在像素域对图像进行拉伸裁剪等工作。
//原本代表输入源的结构体是cli_input_t
if( filter.get_frame( opt->hin, &cli_pic, i_frame + opt->i_seek ) )
break;
//初始化x264_picture_t结构体pic
x264_picture_init( &pic );
//cli_pic到pic
convert_cli_to_lib_pic( &pic, &cli_pic );
if( !param->b_vfr_input )
pic.i_pts = i_frame;
if( opt->i_pulldown && !param->b_vfr_input )
{
pic.i_pic_struct = pulldown->pattern[ i_frame % pulldown->mod ];
pic.i_pts = (int64_t)( pulldown_pts + 0.5 );
pulldown_pts += pulldown_frame_duration[pic.i_pic_struct];
}
else if( opt->timebase_convert_multiplier )
pic.i_pts = (int64_t)( pic.i_pts * opt->timebase_convert_multiplier + 0.5 );
if( pic.i_pts <= largest_pts )
{
if( cli_log_level >= X264_LOG_DEBUG || pts_warning_cnt < MAX_PTS_WARNING )
x264_cli_log( "x264", X264_LOG_WARNING, "non-strictly-monotonic pts at frame %d (%"PRId64" <= %"PRId64")\\n",
i_frame, pic.i_pts, largest_pts );
else if( pts_warning_cnt == MAX_PTS_WARNING )
x264_cli_log( "x264", X264_LOG_WARNING, "too many nonmonotonic pts warnings, suppressing further ones\\n" );
pts_warning_cnt++;
pic.i_pts = largest_pts + ticks_per_frame;
}
second_largest_pts = largest_pts;
largest_pts = pic.i_pts;
if( opt->tcfile_out )
fprintf( opt->tcfile_out, "%.6f\\n", pic.i_pts * ((double)param->i_timebase_num / param->i_timebase_den) * 1e3 );
if( opt->qpfile )
parse_qpfile( opt, &pic, i_frame + opt->i_seek );
prev_dts = last_dts;
//编码pic中存储的1帧YUV数据
i_frame_size = encode_frame( h, opt->hout, &pic, &last_dts ); /encode_frame()
if( i_frame_size < 0 )
{
b_ctrl_c = 1; /* lie to exit the loop */
retval = -1;
}
else if( i_frame_size )
{
i_file += i_frame_size;
i_frame_output++;
if( i_frame_output == 1 )
first_dts = prev_dts = last_dts;
}
//释放处理完的YUV数据
if( filter.release_frame( opt->hin, &cli_pic, i_frame + opt->i_seek ) )
break;
/* update status line (up to 1000 times per input file) */
if( opt->b_progress && i_frame_output )
i_previous = print_status( i_start, i_previous, i_frame_output, param->i_frame_total, i_file, param, 2 * last_dts - prev_dts - first_dts );
}
/* Flush delayed frames */
//输出编码器中剩余的帧
//x264_encoder_delayed_frames()返回剩余的帧的个数
while( !b_ctrl_c && x264_encoder_delayed_frames( h ) )
{
prev_dts = last_dts;
//编码
//注意第3个参数为NULL
i_frame_size = encode_frame( h, opt->hout, NULL, &last_dts ); /encode_frame()
if( i_frame_size < 0 )
{
b_ctrl_c = 1; /* lie to exit the loop */
retval = -1;
}
else if( i_frame_size )
{
i_file += i_frame_size;
i_frame_output++;
if( i_frame_output == 1 )
first_dts = prev_dts = last_dts;
}
//输出一些统计信息
if( opt->b_progress && i_frame_output )
i_previous = print_status( i_start, i_previous, i_frame_output, param->i_frame_total, i_file, param, 2 * last_dts - prev_dts - first_dts );
}
fail:
if( pts_warning_cnt >= MAX_PTS_WARNING && cli_log_level < X264_LOG_DEBUG )
x264_cli_log( "x264", X264_LOG_WARNING, "%d suppressed nonmonotonic pts warnings\\n", pts_warning_cnt-MAX_PTS_WARNING );
/* duration algorithm fails when only 1 frame is output */
if( i_frame_output == 1 )
duration = (double)param->i_fps_den / param->i_fps_num;
else if( b_ctrl_c )
duration = (double)(2 * last_dts - prev_dts - first_dts) * param->i_timebase_num / param->i_timebase_den;
else
duration = (double)(2 * largest_pts - second_largest_pts) * param->i_timebase_num / param->i_timebase_den;
//计时结束
i_end = x264_mdate();
/* Erase progress indicator before printing encoding stats. */
if( opt->b_progress )
fprintf( stderr, " \\r" );
if( h )
x264_encoder_close( h ); /x264_encoder_close():关闭编码器
fprintf( stderr, "\\n" );
if( b_ctrl_c )
fprintf( stderr, "aborted at input frame %d, output frame %d\\n", opt->i_seek + i_frame, i_frame_output );
//关闭输出文件
cli_output.close_file( opt->hout, largest_pts, second_largest_pts );
opt->hout = NULL;
if( i_frame_output > 0 )
{
double fps = (double)i_frame_output * (double)1000000 /
(double)( i_end - i_start );
fprintf( stderr, "encoded %d frames, %.2f fps, %.2f kb/s\\n", i_frame_output, fps,
(double) i_file * 8 / ( 1000 * duration ) );
}
return retval;
}
/************====== 编码函数 ======************/
/*
功能:encode_frame()内部调用x264_encoder_encode()完成编码工作,
调用输出格式对应cli_output_t结构体的write_frame()完成了输出工作。
*/
static int encode_frame( x264_t *h, hnd_t hout, x264_picture_t *pic, int64_t *last_dts )
{
x264_picture_t pic_out;
x264_nal_t *nal;
int i_nal;
int i_frame_size = 0;
//编码API
//编码x264_picture_t为x264_nal_t
i_frame_size = x264_encoder_encode( h, &nal, &i_nal, pic, &pic_out ); //x264_encoder_encode()
FAIL_IF_ERROR( i_frame_size < 0, "x264_encoder_encode failed\\n" );
if( i_frame_size )
{
//通过cli_output_t中的方法输出
//输出raw H.264流的话,等同于直接fwrite()
//其他封装格式,则还需进行一定的封装
i_frame_size = cli_output.write_frame( hout, nal[0].p_payload, i_frame_size, &pic_out );
*last_dts = pic_out.i_dts;
}
return i_frame_size;
}
4、总结
main()是x264控制台程序的入口函数,可以看出main()的定义很简单,它主要调用了两个函数:parse()和encode()。main()首先调用parse()解析输入的命令行参数,然后调用encode()进行编码。
parse()用于解析命令行输入的参数(存储于argv[]中)。parse()的流程大致为:
(1)调用x264_param_default()为存储参数的结构体x264_param_t赋默认值;
(2)调用x264_param_default_preset()为x264_param_t赋值;
(3)在一个大循环中调用getopt_long()逐个解析输入的参数,并作相应的处理。举几个例子:
a)“-h”:调用help()打开帮助菜单。
b)“-V”调用print_version_info()打印版本信息。
c)对于长选项,调用x264_param_parse()进行处理。
(4)调用select_input()解析输出文件格式(例如raw,flv,MP4…)
(5)调用select_output()解析输入文件格式(例如yuv,y4m…)
encode()编码YUV为H.264码流,主要流程为:
(1)调用x264_encoder_open()打开H.264编码器;
(2)调用x264_encoder_parameters()获得当前的参数集x264_param_t,用于后续步骤中的一些配置;
(3)调用输出格式(H.264裸流、FLV、mp4等)对应cli_output_t结构体的set_param()方法,为输出格式的封装器设定参数。其中参数源自于上一步骤得到的x264_param_t;
(4)如果不是在每个keyframe前面都增加SPS/PPS/SEI的话,就调用x264_encoder_headers()在整个码流前面加SPS/PPS/SEI;
(5)进入一个循环中进行一帧一帧的将YUV编码为H.264:
a)调用输入格式(YUV、Y4M等)对应的cli_vid_filter_t结构体get_frame()方法,获取一帧YUV数据。
b)调用encode_frame()编码该帧YUV数据为H.264数据,并且输出出来。该函数内部调用x264_encoder_encode()完成编码工作,调用输出格式对应cli_output_t结构体的write_frame()完成了输出工作。
c)调用输入格式(YUV、Y4M等)对应的cli_vid_filter_t结构体release_frame()方法,释放刚才获取的YUV数据。
d)调用print_status()输出一些统计信息。
(6)编码即将结束的时候,进入另一个循环,输出编码器中缓存的视频帧:
a)不再传递新的YUV数据,直接调用encode_frame(),将编码器中缓存的剩余几帧数据编码输出出来。
b)调用print_status()输出一些统计信息。
(7)调用x264_encoder_close()关闭H.264编码器。
以上是关于main主函数参数解析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
C语言中的“main”可以用别的字母代替吗?比如“mai”或"ain"等。