使用Identity Server 4建立Authorization Server - js(angular5) 客户端
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了使用Identity Server 4建立Authorization Server - js(angular5) 客户端相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
预备知识: http://www.cnblogs.com/cgzl/p/7746496.html
第一部分: http://www.cnblogs.com/cgzl/p/7780559.html
第二部分: http://www.cnblogs.com/cgzl/p/7788636.html
第三部分: http://www.cnblogs.com/cgzl/p/7793241.html
第四部分: http://www.cnblogs.com/cgzl/p/7795121.html
第五部分: http://www.cnblogs.com/cgzl/p/7799567.html
由于手头目前用项目, 所以与前几篇文章不同, 这次要讲的js客户端这部分是通过我刚刚开发的真是项目的代码来讲解的.
这是后端的代码: https://github.com/solenovex/asp.net-core-2.0-web-api-boilerplate
这里面有几个dbcontext, 需要分别对Identity Server和Sales.DataContext进行update-database, 如果使用的是Package Manager Console的话.
进行update-database的时候, 如果是针对IdentityServer这个项目的要把IdentityServer设为启动项目, 如果是针对Sales.DataContext的, 那么要把SalesApi.Web设为启动项目, 然后再进行update-database.
项目结构如图:
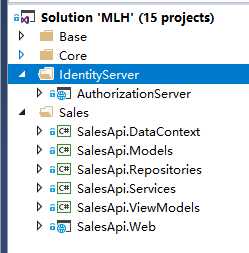
目前项目只用到AuthorizationServer和Sales这两部分.
首先查看AuthorizationServer的相关配置: 打开Configuration/Config.cs
ApiResource:
public static IEnumerable<ApiResource> GetApiResources() { return new List<ApiResource> { new ApiResource(CoreApiSettings.ApiResource.Name, CoreApiSettings.ApiResource.DisplayName) { }, new ApiResource(SalesApiSettings.ApiResource.Name, SalesApiSettings.ApiResource.DisplayName) { UserClaims = { JwtClaimTypes.Name, JwtClaimTypes.PreferredUserName, JwtClaimTypes.Email } } }; }
红色部分是相关代码, 是所需要的ApiResource的定义.
其中需要注意的是, 像user的name, email等这些claims按理说应该可以通过id_token传递给js客户端, 也就是IdentityResource应该负责的. 但是我之所以这样做是因为想把这些信息包含在access_token里面, 以便js可以使用包含这些信息的access_token去访问web api, 这样 web api就可以直接获得到当前的用户名(name), email了. 标准的做法应该是web api通过访问authorization server的user profile节点来获得用户信息, 我这么做就是图简单而已.
所以我把这几个claims添加到了ApiResource里面.
配置好整个项目之后你可以把 name 去掉试试, 如果去掉的话, 在web api的controller里面就无法取得到user的name了, 因为js收到的access token里面没有name这个claim, 所以js传给web api的token里面也没有name. 这个一定要自己修改下试试.
然后配置Client:
public static IEnumerable<Client> GetClients() { return new List<Client> { // Core javascript Client new Client { ClientId = CoreApiSettings.Client.ClientId, ClientName = CoreApiSettings.Client.ClientName, AllowedGrantTypes = GrantTypes.Implicit, AllowAccessTokensViaBrowser = true, RedirectUris = { CoreApiSettings.Client.RedirectUri, CoreApiSettings.Client.SilentRedirectUri }, PostLogoutRedirectUris = { CoreApiSettings.Client.PostLogoutRedirectUris }, AllowedCorsOrigins = { CoreApiSettings.Client.AllowedCorsOrigins }, AllowedScopes = { IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.OpenId, IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Profile, IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Email, CoreApiSettings.ApiResource.Name } }, // Sales JavaScript Client new Client { ClientId = SalesApiSettings.Client.ClientId, ClientName = SalesApiSettings.Client.ClientName, AllowedGrantTypes = GrantTypes.Implicit, AllowAccessTokensViaBrowser = true, AccessTokenLifetime = 60 * 10, AllowOfflineAccess = true, RedirectUris = { SalesApiSettings.Client.RedirectUri, SalesApiSettings.Client.SilentRedirectUri }, PostLogoutRedirectUris = { SalesApiSettings.Client.PostLogoutRedirectUris }, AllowedCorsOrigins = { SalesApiSettings.Client.AllowedCorsOrigins }, //AlwaysIncludeUserClaimsInIdToken = true, AllowedScopes = { IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.OpenId, IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Profile, IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Email, SalesApiSettings.ApiResource.Name, CoreApiSettings.ApiResource.Name } } }; }
红色部分是相关的代码.
AccessTokenLifeTime是token的有效期, 单位是秒, 这里设置的是 10 分钟.
AlwaysIncludeUserClaimsInIdToken默认是false, 如果写true的话, 那么返回给客户端的id_token里面就会有user的name, email等等user相关的claims信息.
然后是IdentityResource:
public static IEnumerable<IdentityResource> GetIdentityResources() { return new List<IdentityResource> { new IdentityResources.OpenId(), new IdentityResources.Profile(), new IdentityResources.Email() }; }
这里需要这三个IdentityResource, 其中的openId scope(identity resource)是必须要加上的, 如果没有这个openid scope, 那么这个请求也许是一个合理的OAuth2.0请求, 但它肯定不会被当作OpenId Connect 请求.
如果你把profile这项去掉, 其他相关代码也去掉profile, 那么客户端新请求的id_token是无论如何也不会包括profile所包含的信息的(name等), 但是并不影响api resource里面包含相关的claim(access_token还是可以获得到user的name等的).
其他的Identity Scopes(Identity Resource)所代表的内容请看文档: http://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-core-1_0.html#ScopeClaims:
profile: name, family_name, given_name, middle_name, nickname, preferred_username,profile, picture, website, gender, birthdate, zoneinfo, locale, and updated_at.
email: email and email_verified Claims.
address: address Claim.
phone: phone_number and phone_number_verified Claims.
看一下Authorization Server的Startup.cs:
namespace AuthorizationServer { public class Startup { public Startup(IConfiguration configuration) { Configuration = configuration; } public IConfiguration Configuration { get; } public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { var connectionString = Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection"); var migrationsAssembly = typeof(Startup).GetTypeInfo().Assembly.GetName().Name; services.AddDbContext<ApplicationDbContext>(options => options.UseSqlServer(connectionString)); services.AddIdentity<ApplicationUser, IdentityRole>(options => { // Password settings options.Password.RequireDigit = false; options.Password.RequiredLength = 4; options.Password.RequireNonAlphanumeric = false; options.Password.RequireUppercase = false; options.Password.RequireLowercase = false; options.Password.RequiredUniqueChars = 1; // Lockout settings options.Lockout.DefaultLockoutTimeSpan = TimeSpan.FromMinutes(5); options.Lockout.MaxFailedAccessAttempts = 5; options.Lockout.AllowedForNewUsers = true; // Signin settings options.SignIn.RequireConfirmedEmail = false; options.SignIn.RequireConfirmedPhoneNumber = false; // User settings options.User.RequireUniqueEmail = false; }) .AddEntityFrameworkStores<ApplicationDbContext>() .AddDefaultTokenProviders(); services.ConfigureApplicationCookie(options => { options.Cookie.Name = "MLHAuthorizationServerCookie"; options.Cookie.HttpOnly = true; options.ExpireTimeSpan = TimeSpan.FromMinutes(60); options.LoginPath = "/Account/Login"; options.LogoutPath = "/Account/Logout"; options.AccessDeniedPath = "/Account/AccessDenied"; options.SlidingExpiration = true; options.ReturnUrlParameter = CookieAuthenticationDefaults.ReturnUrlParameter; }); services.AddTransient<IEmailSender, EmailSender>(); services.AddMvc(); services.AddAutoMapper(); services.AddIdentityServer() #if DEBUG .AddDeveloperSigningCredential() #else .AddSigningCredential(new System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.X509Certificate2( SharedSettings.Settings.AuthorizationServerSettings.Certificate.Path, SharedSettings.Settings.AuthorizationServerSettings.Certificate.Password)) #endif .AddInMemoryIdentityResources(Config.GetIdentityResources()) .AddInMemoryApiResources(Config.GetApiResources()) .AddInMemoryClients(Config.GetClients()) .AddOperationalStore(options => { options.ConfigureDbContext = builder => builder.UseSqlServer(connectionString, sql => sql.MigrationsAssembly(migrationsAssembly)); options.EnableTokenCleanup = true; options.TokenCleanupInterval = 30; }) .AddAspNetIdentity<ApplicationUser>(); services.AddAuthorization(options => { options.AddPolicy(CoreApiAuthorizationPolicy.PolicyName, policy => policy.RequireClaim(CoreApiAuthorizationPolicy.ClaimName, CoreApiAuthorizationPolicy.ClaimValue)); }); } public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env) { app.InitializeDatabase(); if (env.IsDevelopment()) { app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage(); app.UseBrowserLink(); app.UseDatabaseErrorPage(); } else { app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error"); } app.UseStaticFiles(); app.UseIdentityServer(); app.UseMvc(routes => { routes.MapRoute( name: "default", template: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}"); }); } } }
这里我只将Operation数据保存到了数据库. 而Client和ApiResource, IdentityResource等定义还是放在了内存中, 我感觉这样比较适合我.
Sales Web Api:
打开SalesApi.Web的Startup ConfigureServices: 这个非常简单:
services.AddAuthentication("Bearer") .AddIdentityServerAuthentication(options => { options.Authority = AuthorizationServerSettings.AuthorizationServerBase; options.RequireHttpsMetadata = false; options.ApiName = SalesApiSettings.ApiResource.Name; });
没什么可说的.
js 客户端 和 oidc-client.js
无论你使用什么样的前端框架, 最后都使用oidc-client.js来和identity server 4来配套操作.
我使用的是 angular 5: 由于这个代码是公司的项目, 后端处于早期阶段, 被我开源了, 没什么问题.
但是前端是某机构买的一套收费的皮肤, 所以没法开源, 这里我尝试提供部分代码, 我相信您一定可以从头搭建出完整的js客户端的.
我的前端应用流程是:
访问前端地址, 如果没有登录用户, 那么跳转到Authorization Server进行登陆, 同意后, 返回到前端的网站.
如果前端网站有登录的用户, 那么在用户快过期的时候自动刷新token. 以免登陆过期.
前端应用访问api时, 自动拦截所有请求, 把登陆用户的access token添加到请求的authorization header, 然后再发送给 web api.
我把前端精简了一下, 放到了网盘,是好用的
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1minARgc 密码: ipyw
首先需要安装angular-cli:
npm install -g @angular/cli
然后在项目根目录执行:
npm install
虽然npm有点慢, 但是也不要使用cnpm, 有bug.
js客户端参考
你可以参考官方文档: http://docs.identityserver.io/en/release/quickstarts/7_javascript_client.html
安装oidc-client:
地址是: https://github.com/IdentityModel/oidc-client-js, 查看文档的话点wiki即可.
在你的框架里面执行:
npm install oidc-client --save
配置oidc-client:
我的配置放在了angular5项目的environments里面, 因为这个配置根据环境的不同(开发和生产)里面的设定是不同的:
import { WebStorageStateStore } from ‘oidc-client‘;
// The file contents for the current environment will overwrite these during build.
// The build system defaults to the dev environment which uses `environment.ts`, but if you do
// `ng build --env=prod` then `environment.prod.ts` will be used instead.
// The list of which env maps to which file can be found in `angular-cli.json`.
export const environment = {
production: false,
authConfig: {
authority: ‘http://localhost:5000‘,
client_id: ‘sales‘,
redirect_uri: ‘http://localhost:4200/login-callback‘,
response_type: ‘id_token token‘,
scope: ‘openid profile salesapi email‘,
post_logout_redirect_uri: ‘http://localhost:4200‘,
silent_redirect_uri: ‘http://localhost:4200/silent-renew.html‘,
automaticSilentRenew: true,
accessTokenExpiringNotificationTime: 4,
// silentRequestTimeout:10000,
userStore: new WebStorageStateStore({ store: window.localStorage })
},
salesApiBase: ‘http://localhost:5100/api/sales/‘,
themeKey: ‘MLHSalesApiClientThemeKeyForDevelopment‘
};
authority就是authorization server的地址.
redirect_url是登陆成功后跳转回来的地址.
silent_redirect_uri是自动刷新token的回掉地址.
automaticSilentRenew为true是启用自动安静刷新token.
userStore默认是放在sessionStorage里面的, 我需要使用localStorage, 所以改了.
建立AuthService:
import { Injectable, EventEmitter } from ‘@angular/core‘;
import { Router } from ‘@angular/router‘;
import { Observable } from ‘rxjs/Observable‘;
import { User, UserManager, Log } from ‘oidc-client‘;
import ‘rxjs/add/observable/fromPromise‘;
import { environment } from ‘../../../environments/environment‘;
Log.logger = console;
Log.level = Log.DEBUG;
@Injectable()
export class AuthService {
private manager: UserManager = new UserManager(environment.authConfig);
public loginStatusChanged: EventEmitter<User> = new EventEmitter();
private userKey = `oidc.user:${environment.authConfig.authority}:${environment.authConfig.client_id}`;
constructor(
private router: Router
) {
this.manager.events.addAccessTokenExpired(() => {
this.login();
});
}
login() {
this.manager.signinRedirect();
}
loginCallBack() {
return Observable.create(observer => {
Observable.fromPromise(this.manager.signinRedirectCallback())
.subscribe((user: User) => {
this.loginStatusChanged.emit(user);
observer.next(user);
observer.complete();
});
});
}
tryGetUser() {
return Observable.fromPromise(this.manager.getUser());
}
logout() {
this.manager.signoutRedirect();
}
get type(): string {
return ‘Bearer‘;
}
get token(): string | null {
const temp = localStorage.getItem(this.userKey);
if (temp) {
const user: User = JSON.parse(temp);
return user.access_token;
}
return null;
}
get authorizationHeader(): string | null {
if (this.token) {
return `${this.type} ${this.token}`;
}
return null;
}
}
UserManager就是oidc-client里面的东西. 我们主要是用它来操作.
constructor里面那个事件是表示, 如果用户登录已经失效了或者没登录, 那么自动调用login()登陆方法.
login()方法里面的signInRedirect()会直接跳转到Authorization Server的登陆窗口.
logout()里的signoutRedirect()就会跳转到AuthorizationServer并执行登出.
其中的userKey字符串是oidc-client在localStorage默认存放用户信息的key, 这个可以通过oidc-client的配置来更改.
我没有改, 所以key是这样的: "oidc.user:http://localhost:5000:sales":
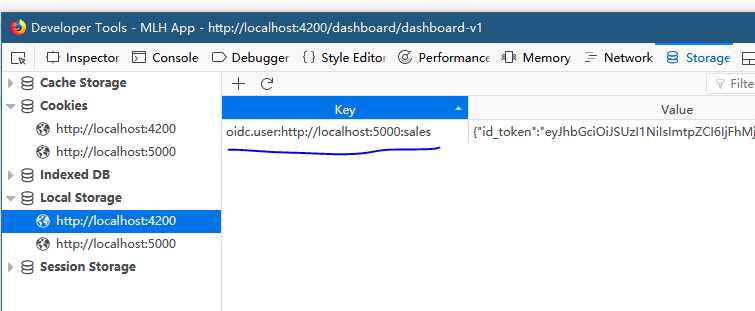
Token Interceptor 请求拦截器:
针对angular 5 所有的请求, 都应该加上authorization header, 其内容就是 access token, 所以token.interceptor.ts就是做这个工作的:
import { Injectable } from ‘@angular/core‘;
import { HttpEvent, HttpInterceptor, HttpHandler, HttpRequest } from ‘@angular/common/http‘;
import { Observable } from ‘rxjs/Observable‘;
import { User } from ‘oidc-client‘;
import { environment } from ‘../../../environments/environment‘;
import { AuthService } from ‘./auth.service‘;
@Injectable()
export class TokenInterceptor implements HttpInterceptor {
constructor(
private authService: AuthService
) { }
intercept(req: HttpRequest<any>, next: HttpHandler): Observable<HttpEvent<any>> {
const authHeader = this.authService.authorizationHeader;
const authReq = req.clone({ headers: req.headers.set(‘Authorization‘, authHeader) });
return next.handle(authReq);
}
}
angular 5 的interceptor不会修改request, 所以只能clone.
设置AuthGuard:
angular5的authguard就是里面有个方法, 如果返回true就可以访问这个路由, 否则就不可以访问.
所以我在几乎最外层添加了这个authguard, 里面的代码是:
import { Injectable } from ‘@angular/core‘;
import { CanActivate } from ‘@angular/router‘;
import { Router } from ‘@angular/router‘;
import { User } from ‘oidc-client‘;
import { AuthService } from ‘./../services/auth.service‘;
import { Observable } from ‘rxjs/Observable‘;
import ‘rxjs/add/operator/map‘;
@Injectable()
export class AuthGuard implements CanActivate {
constructor(
private router: Router,
private authService: AuthService) { }
canActivate(): Observable<boolean> {
return this.authService.tryGetUser().map((user: User) => {
if (user) {
return true;
}
this.authService.login();
return false;
});
}
}
意思就是, 取当前用户, 如果有用户那么就可以继续访问路由, 否走执行登陆动作.
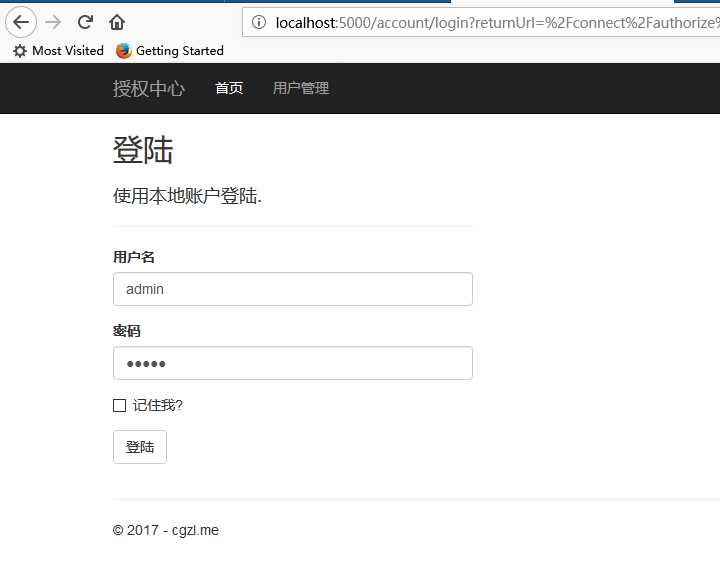
所以访问访问网站后会跳转到这, 这里有个内置用户 admin 密码也是admin, 可以使用它登陆.
外层路由代码app-routing.module.ts:
import { NgModule } from ‘@angular/core‘;
import { Routes } from ‘@angular/router‘;
import { AuthGuard } from ‘./shared/guards/auth.guard‘;
import { MainComponent } from ‘./main/main.component‘;
import { LoginCallbackComponent } from ‘./shared/components/login-callback/login-callback.component‘;
import { NotFoundComponent } from ‘./shared/components/not-found/not-found.component‘;
export const AppRoutes: Routes = [{
path: ‘‘,
redirectTo: ‘dashboard‘,
pathMatch: ‘full‘,
}, {
path: ‘login-callback‘,
component: LoginCallbackComponent
}, {
path: ‘‘,
component: MainComponent,
canActivate: [AuthGuard],
children: [{
path: ‘dashboard‘,
loadChildren: ‘./dashboard/dashboard.module#DashboardModule‘
}, {
path: ‘settings‘,
loadChildren: ‘./settings/settings.module#SettingsModule‘
}]
},
{ path: ‘**‘, component: NotFoundComponent }];
登陆成功后首先会跳转到设置好的redirect_uri, 这里就是login-callback这个路由地址对应的component:
import { Component, OnInit } from ‘@angular/core‘;
import { AuthService } from ‘../../../shared/services/auth.service‘;
import { User } from ‘oidc-client‘;
import { ToastrService } from ‘ngx-toastr‘;
@Component({
selector: ‘app-login-callback‘,
templateUrl: ‘./login-callback.component.html‘,
styleUrls: [‘./login-callback.component.css‘]
})
export class LoginCallbackComponent implements OnInit {
constructor(
private authService: AuthService,
private toastr: ToastrService
) { }
ngOnInit() {
this.authService.loginCallBack().subscribe(
(user: User) => {
this.toastr.info(‘登陆成功, 跳转中...‘, ‘登陆成功‘);
if (user) {
window.location.href = ‘/‘;
}
}
);
}
}
我在这里没做什么, 就是重新加载了一下页面, 我感觉这并不是好的做法.
您可以单独建立一个简单的页面就像官方文档那样, 然后再跳转到angular5项目里面.
这个页面一闪而过:
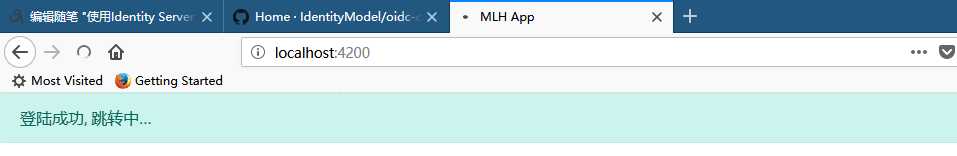
回到angular5项目后就可以正常访问api了.
自动刷新Token:
oidc-client的自动刷新token是只要配置好了, 你就不用再做什么操作了.
刷新的时候, 它好像是会在页面上弄一个iframe, 然后在iframe里面操作.
不过还是需要建立一个页面, 用于刷新:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title></title> </head> <body> <h1 id="waiting">Waiting...</h1> <div id="error"></div> <script src="assets/js/oidc-client.min.js"></script> <script> new Oidc.UserManager().signinSilentCallback(); </script> </body> </html>
很简单就这些.
最后操作一下试试: 最好自己调试一下:

菜单那几个都是好用的页面.
以上是关于使用Identity Server 4建立Authorization Server - js(angular5) 客户端的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
使用Identity Server 4建立Authorization Server
使用Identity Server 4建立Authorization Server - js(angular5) 客户端
使用 Identity Server 4 和 ASP.NET Identity 添加外部登录