Java递归递推的应用
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java递归递推的应用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
利用阶乘公式来计算组合式:
程序设计思想:
根据公式来计算组合数的大小,从键盘输入n,k的值,设计一个计算阶乘的大小,如果输入的数a为1或0,则直接return 1,否则运用递归,计算a-1的阶乘,直到a为1时,递归结束。
程序流程图:
程序源代码:
public static void main(String args[]) { int n ,k,c; Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("输入从n个数中选k个数中n,k的值:"); n=in.nextInt(); k=in.nextInt(); System.out.println("结果为:"); c=jiecheng(n)/(jiecheng(k)*jiecheng(n-k)); System.out.println(c); }
public static int jiecheng(int x)
{
int y=1;
if(x==1||x==0)
y=1;
else y=jiecheng(x-1)*x;
return y;
}

根据杨辉三角递推求组合数
程序设计思想:
根据杨辉三角的规律,得出杨辉三角的第n行的第m个的值等于该位置的元素的上一行的左右两个输的和,然后根据杨辉三角与组合数的关系即c(n,m)等于杨辉三角的第n+1的第m+1个元素的值,根据这个来写出组合数的值。
程序流程图: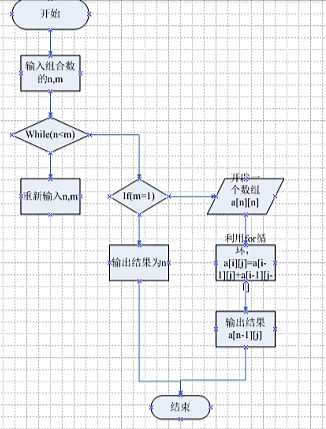
程序源代码:
public static void main(String args[]) { Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("输入N值:"); int n=sc.nextInt(); System.out.print("输入K值:"); int k=sc.nextInt(); int[][] a=new int[n+1][n+1]; for(int i=0;i<n+1;i++) { for(int j=0;j<=i;j++) { if(j==0||j==i) { a[i][j]=1; System.out.print(a[i][j]+" "); } else { a[i][j]=a[i-1][j-1]+a[i-1][j]; System.out.print(a[i][j]); System.out.print(" "); } } System.out.println(); } if(n<2||k==1) System.out.println("num=1"); else System.out.println("num="+a[n][k-1]+"="+a[n-1][k-2]+"+"+a[n-1][k-1]); }

运用公式计算组合数:
程序设计思想:
输入n,m,两个数(来组成要求出的组合数)(n>m),如果m=1,则输出结果n,如果m!=1,则进入递归,运用公式,直到进行到n-m=1的时候,结束递归,输出结果。
程序流程图
程序源代码:
public static void main(String args[]) { Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("输入N值:"); int n=sc.nextInt(); System.out.print("输入K值:"); int k=sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("结果为:"+C(n,k)); } public static int C(int n,int k) { if(n<0||k<0||n<k) return 0; if(n==k) return 1; if(k==1) return n; return C(n-1,k)+C(n-1,k-1); }
用Java实现汉诺塔:
程序设计思想:
1.首先输入盘子的数量n,如果盘子的数量是1,则直接将编号为1的圆盘从A移到C,递归结束。
2.否则:
递归,将A上编号为1至n-1的圆盘移到B,C做辅助塔;
直接将编号为n的圆盘从A到C;
递归,将B上的编号为1至n-1的圆盘移到C,A做辅助塔。
程序流程图: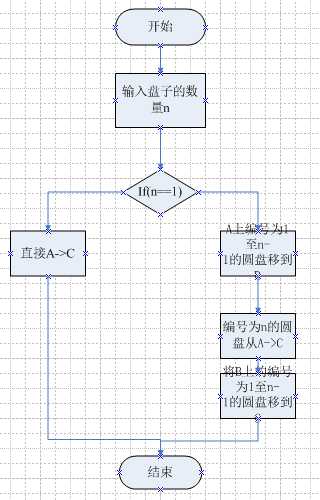
程序源代码:
public static void main(String[] args) { @SuppressWarnings("resource") Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); int n; System.out.println("Please enter the number of your dished(Hanoi Tower):"); n=sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("The number of the times you need to move the dishes is:"+new HanoiTower().hanoiTower(n)); HanoiTower HanoiTower = new HanoiTower(); HanoiTower.move(n, ‘A‘, ‘B‘, ‘C‘); } public int hanoiTower(int n) { if(n==1) return 1; else return hanoiTower(n-1)*2+1; } public void move(int n, char a, char b, char c) { if (n == 1) System.out.println("盘 " + n + " 由 " + a + " 移至 " + c); else { move(n - 1, a, c, b); System.out.println("盘 " + n + " 由 " + a + " 移至 " + c); move(n - 1, b, a, c); } }

随意输入一个任意大小的字符串,判断他是不是回文字符串。
程序设计思想:
从键盘随意输入一个字符串,并将其赋值给一个数组,然后用递归进行,若i=j,肯定是递归,否则从数组的首元素与尾元素进行比较,若相等,则进行i++与j--,不断向中间靠拢,直到达到判断条件 n>=len/2 ,中间若有一次不符合判断,直接跳出递归,结束进程,输出不是回文字符串。
程序设计流程图:
程序源代码:
public class huiwen { private static int len; private static char p[]; public static void main(String args[]){ Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); String str; str=sc.nextLine(); len=str.length(); p=str.toCharArray(); if(huiwen(0)) System.out.println(str+" is a palindrome!"); else System.out.println(str+" is not a palindrome!"); } public static boolean huiwen(int n){ if(n>=len/2) return true; if(p[n]==p[len-1-n]) return huiwen(n+1); else return false; } }

以上是关于Java递归递推的应用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章