Spring Boot 声明式事务结合相关拦截器
Posted 起名什么的...
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring Boot 声明式事务结合相关拦截器相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
我这项目的读写分离方式在使用ThreadLocal实现的读写分离在迁移后的偶发错误里提了,我不再说一次了,这次是有要求读写分离与事务部分要完全脱离配置文件,程序员折腾了很久,于是我就查了一下,由于我还是比较喜欢使用xml的方式,所以就随便。。。(过程省略吧),然而,似乎是一定要声明式的方式,所以,无奈之下就只好干了。
首先,在之前的博客里提到过,我们的读写分离方式要求我们自己的AOP拦截器必须在事务拦截器之前执行,在配置文件的方式下很容易,在aop的配置里设置一下Order就好了。然而,Spring Boot的@EnableTransactionManagement注解中已经把这部分固定了,官方文档似乎说它是和@Transactional配合使用的,总之几乎没有留下什么插手的余地(如果大家有好办法,希望能告诉我一下):

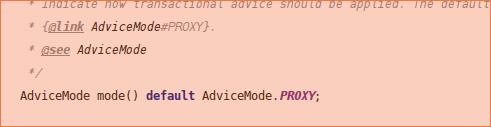
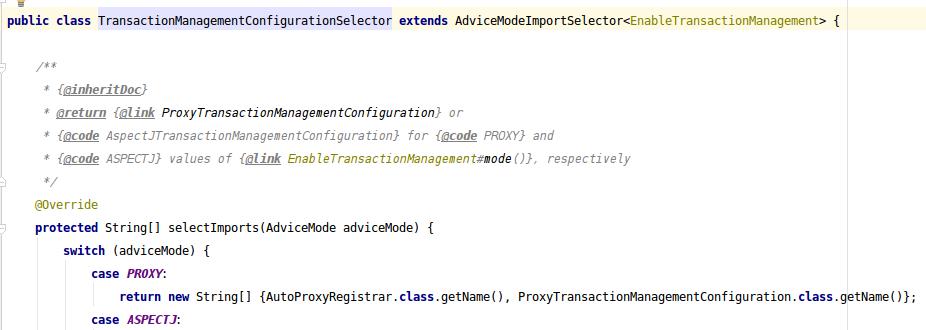
这个ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration类中,就直接手new了TransactionInterceptor:
public TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor() { TransactionInterceptor interceptor = new TransactionInterceptor(); interceptor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource()); if (this.txManager != null) { interceptor.setTransactionManager(this.txManager); } return interceptor; }
虽然这里可以通过上图的方式加点什么,但这个事务体系本身是非常独立的,而且在启动过程中就已经确定下来了,既然要调节它和自定义的aop的执行顺序,我想只能先统一他们的执行策略。之前自定义的aop是在启动过程中就被加入到一个拦截器的调用链中:
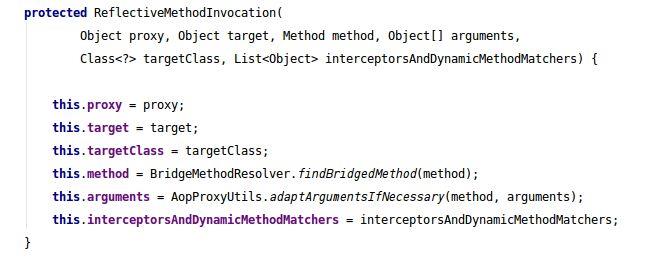
由于Spring Boot很多东西并没有留什么扩展的余地(就好像前面那个new),如果完全不用配置文件,使用Spring Boot的方式,虽然没有什么顺眼的方法,其实也还是能做的,先提个建议,能不用的情况下,最好不要用。方法是自定义一个事务拦截器,抛弃@EnableTransactionManagement,测试代码如下,不要在意命名,图方便直接在原来的上面改的:
@Bean(name = "newDataSourceAop") public NewDataSourceAop newDataSourceAop(){ return new NewDataSourceAop(); } @Bean(name = "tInterceptor") public TInterceptor tInterceptor(){ return new TInterceptor(); } /** * 代理 * @return */ @Bean public BeanNameAutoProxyCreator transactionAutoProxy() { BeanNameAutoProxyCreator autoProxy = new BeanNameAutoProxyCreator(); autoProxy.setProxyTargetClass(true);// 这个属性为true时,表示被代理的是目标类本身而不是目标类的接口 autoProxy.setBeanNames("*ServiceImpl"); autoProxy.setInterceptorNames("newDataSourceAop", "tInterceptor"); return autoProxy; }
注意,拦截器的顺序依赖于名字字符串传入的先后顺序,@Order什么的是完全没用的,因为保存这些拦截器的是一个字符串数组。自定义的事务AOP Advice:
public class TInterceptor extends TransactionAspectSupport implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable { public TInterceptor() { setTransactionAttributes(getAttrs()); } private Properties getAttrs(){ Properties attributes = new Properties(); // 新增 attributes.setProperty("create*", "PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,ISOLATION_DEFAULT"); // 修改 attributes.setProperty("update*", "PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,ISOLATION_DEFAULT"); // 删除 attributes.setProperty("delete*", "PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,ISOLATION_DEFAULT"); //查询 attributes.setProperty("query*", "PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,ISOLATION_DEFAULT"); return attributes; } @Override public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable { Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null); // Adapt to TransactionAspectSupport\'s invokeWithinTransaction... return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, () -> invocation.proceed()); } }
自定义的读写分离Advice:
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ReadDBPathProperties.class) public class NewDataSourceAop implements MethodBeforeAdvice { private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(NewDataSourceAop.class); @Autowired private ReadDBPathProperties readDBPathProperties; @Override public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable { String clazzName = method.getDeclaringClass().getSimpleName(); String runner = clazzName + "." + method.getName(); this.chooseDataSource(runner); } private void chooseDataSource(String runner){ runner += ","; String read = readDBPathProperties.getReadPath()+","; log.info("case : read path, vo : readPath = {}", read); int index = read.indexOf(runner); if (index == -1){ log.info("case : choose write DB, runner : {}, tid={}", runner, Thread.currentThread().getId()); HandleDataSource.putDataSource("write"); return; } log.info("case : choose read DB, runner : {}, tid={}", runner, Thread.currentThread().getId()); HandleDataSource.putDataSource("read"); } }
最后再特别说一下,关于这个功能的单元测试,这个单元测试有一点意思,如果是直接运行测试方法,启动过程和执行过程在同一个线程是测试不出效果的,因为启动过程中加载Bean的时候会对下图中的resources初始化,写入默认的数据源:
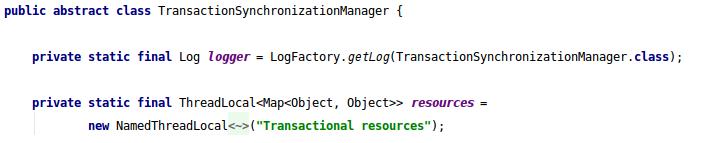
就会导致后续执行的读写分离拦截器失效,只要保证执行线程和启动线程不在同一线程就好。
==========================================================
咱最近用的github:https://github.com/saaavsaaa
微信公众号:

以上是关于Spring Boot 声明式事务结合相关拦截器的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Spring Boot 中使用 @Transactional 注解配置事务管理
Spring Boot 中使用 @Transactional 注解配置事务管理