一文带你搞懂C++如何操作文件对话框(附源码)
Posted dvlinker
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了一文带你搞懂C++如何操作文件对话框(附源码)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
在C++程序中有时需要通过系统的文件对话框去操作文件或者文件夹,我们有必要熟练掌握操作文件对话框的细节,去更好的为我们软件服务。本文我们就来讲述一下C++在操作文件夹对话框的相关细节,给大家借鉴和参考。
1、调用GetOpenFileName接口启动打开文件对话框
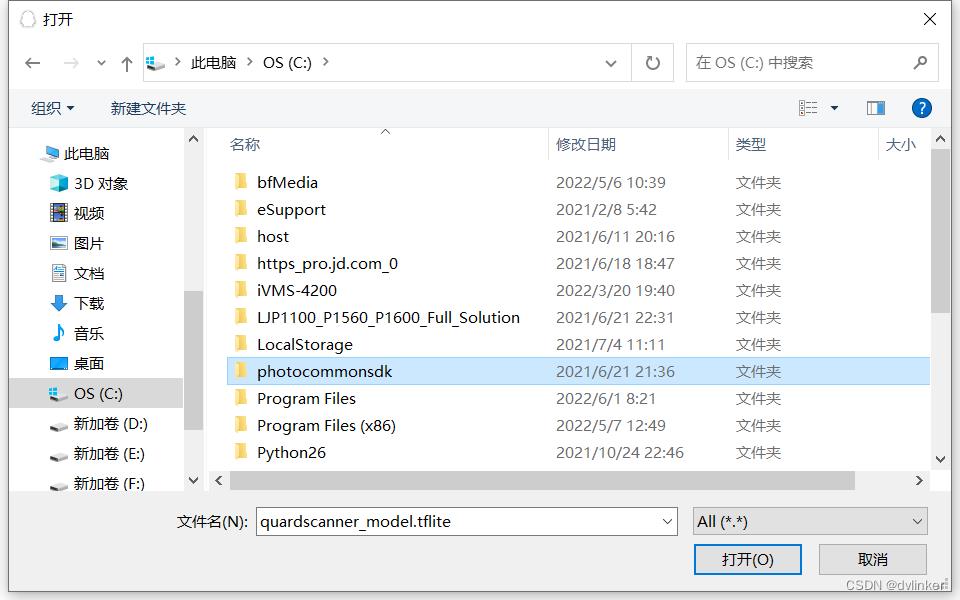
当我们需要使用文件对话框打开一个文件时,我们可以调用系统API函数GetOpenFileName来启动系统的打开文件对话框。调用该API函数时需要传入OPENFILENAME结构体对象,通过该结构体给打开文件对话框设置一些属性参数。
1.1、OPENFILENAME结构体说明
结构体OPENFILENAME的定义有两个版本,一个Unicode版本的OPENFILENAMEW,一个ANSI版本的OPENFILENAMEA,这个地方我们以Unicode版本的OPENFILENAMEW来说明,该结构体的定义如下:
typedef struct tagOFNW
DWORDlStructSize;
HWND hwndOwner;
HINSTANCEhInstance;
LPCWSTR lpstrFilter;
LPWSTR lpstrCustomFilter;
DWORDnMaxCustFilter;
DWORDnFilterIndex;
LPWSTR lpstrFile;
DWORDnMaxFile;
LPWSTR lpstrFileTitle;
DWORDnMaxFileTitle;
LPCWSTR lpstrInitialDir;
LPCWSTR lpstrTitle;
DWORDFlags;
WORD nFileOffset;
WORD nFileExtension;
LPCWSTR lpstrDefExt;
LPARAM lCustData;
LPOFNHOOKPROC lpfnHook;
LPCWSTR lpTemplateName;
#ifdef _MAC
LPEDITMENU lpEditInfo;
LPCSTR lpstrPrompt;
#endif
#if (_WIN32_WINNT >= 0x0500)
void *pvReserved;
DWORDdwReserved;
DWORDFlagsEx;
#endif // (_WIN32_WINNT >= 0x0500)
OPENFILENAMEW, *LPOPENFILENAMEW;这个地方我们讲一下几个我们使用到的字段:
- lStructSize字段[in]:用来存放当前结构体的长度。
- hwndOwner字段[in]:用来指定文件对话框的父窗口。
- lpstrFilter字段[in]:用来设置选择的文件类型,如果要选择所有文件,则设置“All Files(*.*)\\0*.*\\0\\0”;如果选择的是常用的图片文件,则可以设置“图片文件(*.bmp;*.jpg;*.jpeg;*.gif;*.png)\\0*.bmp;*.jpg;*.jpeg;*.gif;*.png\\0\\0”。
- lpstrFile字段[out]:该字段用来传出用户选择的文件信息,存放选择的文件信息的buffer是需要外部申请内存的,然后将buffer地址赋值给该字段,然后在GetOpenFileName调用完成后通过该字段指定的buffer输出用户选择的文件信息。
- nMaxFile字段[in]:用来指定设置给lpstrFile字段对应的buffer长度的。
- lpstrInitialDir字段[in]:用来指定打开文件对话框时的初始显示路径。
- Flags字段[in]:用来设定文件对话框支持的属性,比如支持多选的OFN_ALLOWMULTISELECT、选择的文件必须存在OFN_FILEMUSTEXIST等。
1.2、设置支持文件多选,控制选择文件的个数上限
要支持文件多选,需要给OPENFILENAME结构体的Flags字段添加OFN_ALLOWMULTISELECT选项。如果要控制选择文件的个数上限,比如我们在IM聊天框中限制用户插入图片的个数(比如我们此处限制为5个图片文件):
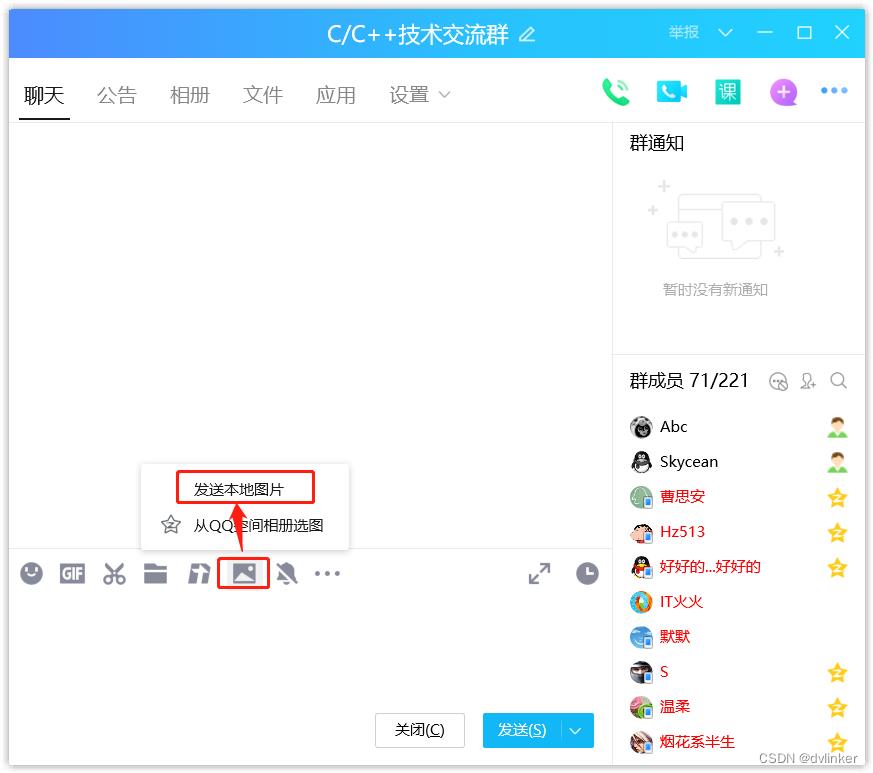
我可以在给OPENFILENAME结构体参数设置lpstrFilter字段指定接收用户选择信息时指定buffer的长度最多存放5张图片的路径。
如果选择多个文件时的文件信息超过buffer的长度,则GetOpenFileName会返回失败,此时可以调用CommDlgExtendedError获取错误码,如果错误码是FNERR_BUFFERTOOSMALL,则表示buffer太小存不下选择的多个图片文件信息,此时可以弹出提示框,相关代码如下:
// 设置最多选择5个文件的buffer长度
int nBufLen = 5*(MAX_PATH+1) + 1;
TCHAR* pBuf = new TCHAR[nBufLen];
memset( pBuf, 0, nBufLen*sizeof(TCHAR) );
OPENFILENAME ofn;
memset( &ofn, 0 ,sizeof(ofn) );
ofn.lStructSize = sizeof(ofn);
ofn.hwndOwner = m_hParentWnd;
ofn.lpstrFile = pBuf;
ofn.nMaxFile = nBufLen;
ofn.lpstrFilter = _T("All Files(*.*)\\0*.*\\0\\0");
ofn.lpstrFileTitle = NULL;
ofn.nMaxFileTitle = 0;
ofn.lpstrInitialDir = NULL;
ofn.Flags = OFN_EXPLORER|OFN_ALLOWMULTISELECT|OFN_FILEMUSTEXIST|OFN_HIDEREADONLY;
// 打开文件打开对话框
BOOL bRet = ::GetOpenFileName( &ofn );
if ( !bRet )
// 上面的ofn.lpstrFile buffer的长度设置存放3个图片路径,选择较多文件时
// 会超出给定的buffer长度,所以此处要判断一下这样的情况,并给出提示5
DWORD dwErr = CommDlgExtendedError();
if ( dwErr == FNERR_BUFFERTOOSMALL )
// FNERR_BUFFERTOOSMALL - The buffer pointed to by the lpstrFile member
// of the OPENFILENAME structure is too small
::MessageBox( NULL, _T("最多只允许选择5个文件,请重新选择"), _T("提示"), MB_OK );
delete []pBuf;
return;
// 再检查一下用户选择的文件个数,检测是否达到上限
int nPicTotal = 0;
UIPOSITION pos = (UIPOSITION)ofn.lpstrFile;
while ( pos != NULL )
// 获取用户选择的每个文件的路径,此处可以将文件的路径保存下来
strPicPath = GetNextPathName( pos, ofn );
++nPicTotal;
if ( nPicTotal > 5 )
::MessageBox( NULL, _T("最多只允许选择5个文件,请重新选择"), _T("提示"), MB_OK );
delete []pBuf;
return;
当然,我们仅仅通过FNERR_BUFFERTOOSMALL错误判断文件个数超限了,是不够的。可能用户选择了6个文件时,总的buffer不会超限,所以还要在解析出来用户选择的每个文件后计算一下选择的文件个数。
1.3、从OPENFILENAME结构体的lpstrFile字段解析出用户选择的文件的完整路径
上面我们讲了,用户在选择完多个文件后,点击确定,API函数GetOpenFileName返回,传给该API函数的OPENFILENAME结构体对象参数的lpstrFile字段中存放这用户选择的文件信息,比如我选择了3个文件(docker.png、linux.png、running.png),lpstrFile中存放的数据格式会是:
C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\CSDN文章图集\\docker.png\\0linux.png\\0running.png
因为这段字串中包含\\0,所以我们不能把lpstrFile当成字符串来处理。我们专门封装了接口GetNextPathName,该接口负责将每个文件的完整路径解析:
// 主要用于文件打开对话框选中多个文件时,解析出多个文件名(绝对路径),从MFC库中的CFileDialog类的GetNextPathName函数中剥离出来的
CUIString GetNextPathName( UIPOSITION& pos, OPENFILENAME& ofn )
BOOL bExplorer = ofn.Flags & OFN_EXPLORER;
TCHAR chDelimiter;
if ( bExplorer )
chDelimiter = '\\0';
else
// For old-style dialog boxes, the strings are space separated and the function uses
// short file names for file names with spaces.
chDelimiter = ' ';
LPTSTR lpsz = (LPTSTR)pos;
if ( lpsz == ofn.lpstrFile ) // first time
if ( (ofn.Flags & OFN_ALLOWMULTISELECT) == 0 )
pos = NULL;
return ofn.lpstrFile;
// find char pos after first Delimiter
while( *lpsz != chDelimiter && *lpsz != '\\0' )
lpsz = _tcsinc( lpsz );
lpsz = _tcsinc( lpsz );
// if single selection then return only selection
if ( *lpsz == 0 )
pos = NULL;
return ofn.lpstrFile;
CString strPath = ofn.lpstrFile;
if ( !bExplorer )
LPTSTR lpszPath = ofn.lpstrFile;
while( *lpszPath != chDelimiter )
lpszPath = _tcsinc(lpszPath);
strPath = strPath.Left( lpszPath - ofn.lpstrFile );
LPTSTR lpszFileName = lpsz;
CString strFileName = lpsz;
// find char pos at next Delimiter
while( *lpsz != chDelimiter && *lpsz != '\\0' )
lpsz = _tcsinc(lpsz);
if ( !bExplorer && *lpsz == '\\0' )
pos = NULL;
else
if ( !bExplorer )
strFileName = strFileName.Left( lpsz - lpszFileName );
lpsz = _tcsinc( lpsz );
if ( *lpsz == '\\0' ) // if double terminated then done
pos = NULL;
else
pos = (UIPOSITION)lpsz;
// only add '\\\\' if it is needed
if ( !strPath.IsEmpty() )
// check for last back-slash or forward slash (handles DBCS)
LPCTSTR lpsz = _tcsrchr( strPath, '\\\\' );
if ( lpsz == NULL )
lpsz = _tcsrchr( strPath, '/' );
// if it is also the last character, then we don't need an extra
if ( lpsz != NULL &&
(lpsz - (LPCTSTR)strPath) == strPath.GetLength()-1 )
ASSERT( *lpsz == '\\\\' || *lpsz == '/' );
return strPath + strFileName;
return strPath + '\\\\' + strFileName;
我们在外部循环调用GetNextPathName函数即可:
UIPOSITION pos = (UIPOSITION)ofn.lpstrFile;
while ( pos != NULL )
// 获取用户选择的每个文件的路径,此处可以将文件的路径保存下来
strPicPath = GetNextPathName( pos, ofn );
++nPicTotal;
2、调用GetSaveFileName接口启动保存文件对话框
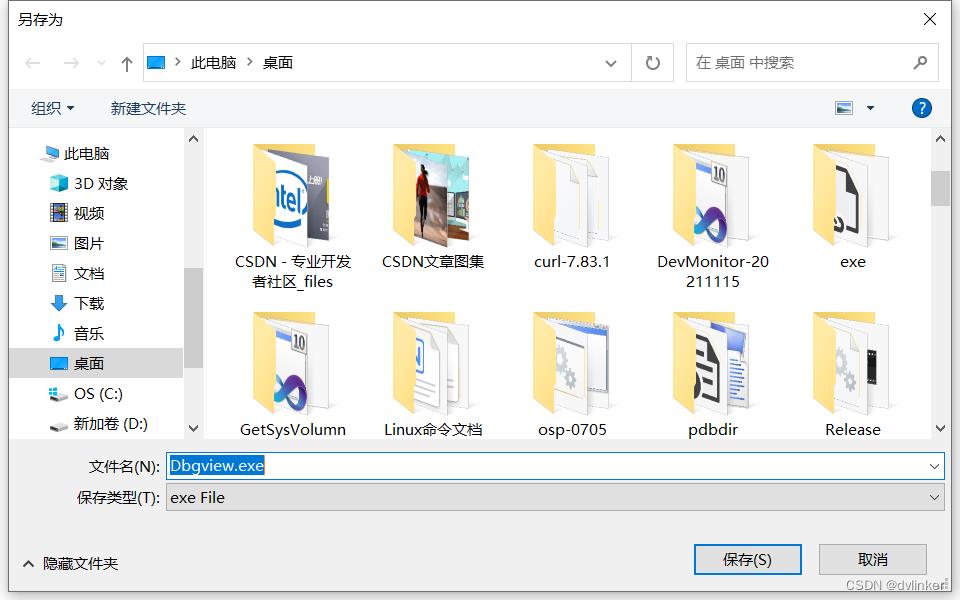
当我们需要使用保存文件对话框保存一个文件时,我们可以调用系统API函数GetSaveFileName来启动系统的保存文件对话框。调用该函数时也是传入OPENFILENAME结构体对象的,通过该结构体给打开文件对话框设置一些属性参数。
对于GetSaveFileName接口,OPENFILENAME结构体中的lpstrFile字段的含义是不同的,此处用来设置保存文件的默认名字的。调用函数的示例代码如下:
TCHAR szFile[3*MAX_PATH] = 0 ;
_tcscpy( szFile, strFileName );
OPENFILENAME ofn;
memset( &ofn, 0 ,sizeof(ofn) );
ofn.lStructSize = sizeof(OPENFILENAME);
ofn.hwndOwner = NULL;
ofn.lpstrFilter = _T("All Files(*.*)|0*.*||");
ofn.lpstrFile = szFile;
ofn.nMaxFile = sizeof(szFile)/sizeof(TCHAR);
ofn.lpstrDefExt = (LPCTSTR)strExt;
ofn.lpstrInitialDir = NULL;
ofn.Flags = OFN_EXPLORER|OFN_PATHMUSTEXIST|OFN_HIDEREADONLY|OFN_NOCHANGEDIR|OFN_OVERWRITEPROMPT|OFN_ENABLEHOOK;
ofn.lpfnHook = FileSaveAs_OFNHookProc; // 设置回调函数,添加额外的处理机制if ( ::GetSaveFileName( &ofn ) )
// 用户最终输入的文件名的完整路径
CString strPathName = ofn.lpstrFile;
在上述代码中,我们添加了OFN_OVERWRITEPROMPT属性,用来指定覆盖同名文件时给出提示;我们还添加了OFN_ENABLEHOOK属性,用来指定设置回调函数,在函数中添加额外的处理机制。在本例中,我们的HOOK回调函数如下:
// 文件对话框回调函数
UINT_PTR CALLBACK FileSaveAs_OFNHookProc(
HWND hdlg, // handle to child dialog box
UINT uiMsg, // message identifier
WPARAM wParam, // message parameter
LPARAM lParam // message parameter
)
if( uiMsg == WM_NOTIFY)
LPOFNOTIFY pofn = (LPOFNOTIFY)lParam;
if( pofn->hdr.code == CDN_FILEOK )
HWND hFileDlg = ::GetParent( hdlg );
// 获取用户选择保存路径
TCHAR achCurPath[MAX_PATH*3] = 0 ;
int nRet = ::SendMessage( hFileDlg, CDM_GETFOLDERPATH, sizeof(achCurPath)/sizeof(TCHAR),
(LPARAM)achCurPath );
if ( nRet < 0 )
return 0;
// 判断当前程序对选择的目录是否有写权限
BOOL bCanWrite = CanAccessFile( achCurPath, GENERIC_WRITE );
if ( !bCanWrite )
::MessageBox( hFileDlg, STRING_HAVE_NO_RIGHT_SAVE_FILE, STRING_TIP, MB_OK|MB_ICONWARNING );
::SetWindowLong( hdlg, DWL_MSGRESULT, 1 );
return 1;
return 0;
在HOOK回调函数中我们拦截了点击确定的消息,判断一下用户当前选择的路径有没有权限保存文件。因为在Win7及以上系统中,如果程序没有管理员权限,是没有权利向C:\\Windows、C:\\Program Files等系统关键路径中写入文件的。
判断程序是否对某个路径有写权限,我们封装了专门的判断函数,如下所示:
// 将要检测的权限GENERIC_XXXXXX传递给dwGenericAccessMask,可检测对
// 文件或者文件夹的权限
BOOL CanAccessFile( CString strPath, DWORD dwGenericAccessMask )
CString strLog;
strLog.Format( _T("[CanAccessFile] strPath: %s, dwGenericAccessMask: %d"), strPath, dwGenericAccessMask );
WriteUpdateLog( strLog );
DWORD dwSize = 0;
PSECURITY_DESCRIPTOR psd = NULL;
SECURITY_INFORMATION si = OWNER_SECURITY_INFORMATION |
GROUP_SECURITY_INFORMATION | DACL_SECURITY_INFORMATION;
WriteLog( _T("[CanAccessFile] GetFileSecurity - NULL") );
// 获取文件权限信息结构体大小
BOOL bRet = GetFileSecurity( strPath, si, psd, 0, &dwSize );
if ( bRet || GetLastError() != ERROR_INSUFFICIENT_BUFFER )
strLog.Format( _T("[CanAccessFile] GetFileSecurity - NULL failed, GetLastError: %d"), GetLastError() );
WriteLog( strLog );
return FALSE;
char* pBuf = new char[dwSize];
ZeroMemory( pBuf, dwSize );
psd = (PSECURITY_DESCRIPTOR)pBuf;
strLog.Format( _T("[CanAccessFile] GetFileSecurity - dwSize: %d"), dwSize );
WriteLog( strLog );
// 获取文件权限信息结构体大小
bRet = GetFileSecurity( strPath, si, psd, dwSize, &dwSize );
if ( !bRet )
strLog.Format( _T("[CanAccessFile] GetFileSecurity - dwSize failed, GetLastError: %d"), GetLastError() );
WriteLog( strLog );
delete []pBuf;
return FALSE;
WriteLog( _T("[CanAccessFile] OpenProcessToken") );
HANDLE hToken = NULL;
if ( !OpenProcessToken( GetCurrentProcess(), TOKEN_ALL_ACCESS, &hToken ) )
strLog.Format( _T("[CanAccessFile] OpenProcessToken failed, GetLastError: %d"), GetLastError() );
WriteLog( strLog );
delete []pBuf;
return FALSE;
WriteLog( _T("[CanAccessFile] DuplicateToken") );
// 模拟令牌
HANDLE hImpersonatedToken = NULL;
if( !DuplicateToken( hToken, SecurityImpersonation, &hImpersonatedToken ) )
strLog.Format( _T("[CanAccessFile] DuplicateToken failed, GetLastError: %d"), GetLastError() );
WriteLog( strLog );
delete []pBuf;
CloseHandle( hToken );
return FALSE;
WriteLog( _T("[CanAccessFile] MapGenericMask") );
// 在检测是否有某个权限时,将GENERIC_WRITE等值传给本函数的第二个参数dwGenericAccessMask
// GENERIC_WRITE等参数在调用CreateFile创建文件时会使用到,下面调用MapGenericMask将
// GENERIC_WRITE等转换成FILE_GENERIC_WRITE等
// 将GENERIC_XXXXXX转换成FILE_GENERIC_XXXXXX
GENERIC_MAPPING genMap;
genMap.GenericRead = FILE_GENERIC_READ;
genMap.GenericWrite = FILE_GENERIC_WRITE;
genMap.GenericExecute = FILE_GENERIC_EXECUTE;
genMap.GenericAll = FILE_ALL_ACCESS;
MapGenericMask( &dwGenericAccessMask, &genMap );
WriteLog( _T("[CanAccessFile] AccessCheck") );
// 调用AccessCheck来检测是否有指定的权限
PRIVILEGE_SET privileges = 0 ;
DWORD dwGrantedAccess = 0;
DWORD privLength = sizeof(privileges);
BOOL bGrantedAccess = FALSE;
if( AccessCheck( psd, hImpersonatedToken, dwGenericAccessMask,
&genMap, &privileges, &privLength, &dwGrantedAccess, &bGrantedAccess ) )
strLog.Format( _T("[CanAccessFile] AccessCheck succeed, dwGenericAccessMask: %d, dwGrantedAccess: %d, bGrantedAccess: %d, "),
dwGenericAccessMask, dwGrantedAccess, bGrantedAccess );
WriteLog( strLog );
if ( bGrantedAccess )
if ( dwGenericAccessMask == dwGrantedAccess )
bGrantedAccess = TRUE;
else
bGrantedAccess = FALSE;
else
bGrantedAccess = FALSE;
else
strLog.Format( _T("[CanAccessFile] AccessCheck failed, GetLastError: %d"), GetLastError() );
WriteLog( strLog );
bGrantedAccess = FALSE;
strLog.Format( _T("[CanAccessFile] bGrantedAccess: %d"), bGrantedAccess );
WriteLog( strLog );
delete []pBuf;
CloseHandle( hImpersonatedToken );
CloseHandle( hToken );
return bGrantedAccess;
另外,我们可以在HOOK回调函数中调整文件对话框相对于父窗口的弹出位置,拦截WM_INITDIALOG消息,代码如下:
// 通过该回调函数移动文件保存对话框的位置,解决win32 文件对话框默认显示在屏幕左上方的问题
UINT_PTR CALLBACK OFNHookProc(
HWND hdlg, // handle to child dialog box
UINT uiMsg, // message identifier
WPARAM wParam, // message parameter
LPARAM lParam // message parameter
)
if ( uiMsg == WM_INITDIALOG )
HWND hFileDlg = ::GetParent( hdlg );
HWND hParent = ::GetParent( hFileDlg );
RECT rcParent;
::GetWindowRect( hParent, &rcParent );
RECT rcFileDlg;
::GetWindowRect( hFileDlg, &rcFileDlg );
int nFileDlgWdith = rcFileDlg.right - rcFileDlg.left;
int nFileDlgHeight = rcFileDlg.bottom - rcFileDlg.top;
RECT rcDst;
rcDst.left = rcParent.left + ( (rcParent.right - rcParent.left) - nFileDlgWdith )/2;
rcDst.right = rcDst.left + nFileDlgWdith;
rcDst.bottom = rcParent.bottom + 1;
rcDst.top = rcDst.bottom - nFileDlgHeight;
// 下面保证文件对话框处于屏幕可视区域内
if ( rcDst.left < 0 )
rcDst.left = 0;
rcDst.right = rcDst.left + nFileDlgWdith;
if ( rcDst.top < 0 )
rcDst.top = 0;
rcDst.bottom = rcDst.top + nFileDlgHeight;
int nXScreen = ::GetSystemMetrics( SM_CXSCREEN );
int nYScreen = ::GetSystemMetrics( SM_CYSCREEN );
if ( rcDst.right > nXScreen )
rcDst.right = nXScreen;
rcDst.left = rcDst.right - nFileDlgWdith;
if ( rcDst.bottom > nYScreen )
rcDst.bottom = nYScreen;
rcDst.top = rcDst.bottom - nFileDlgHeight;
// 重新设置文件对话框位置
::SetWindowPos( hFileDlg, NULL, rcDst.left, rcDst.top, 0, 0, SWP_NOSIZE | SWP_NOZORDER );
return 1;
return 0;
3、调用SHBrowseForFolder接口打开浏览文件夹对话框
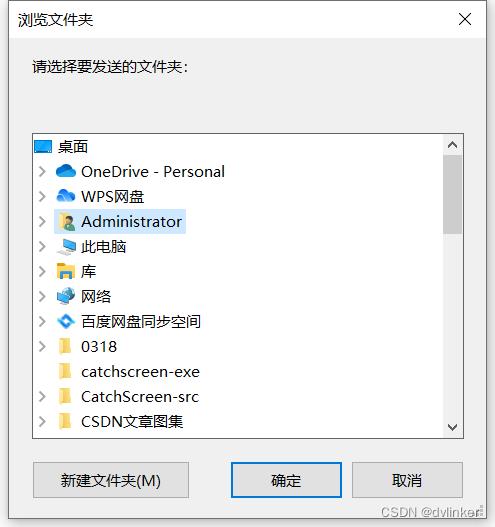
当我们在IM聊天框中发起文件传输时,我们要发送的是一个文件夹,可能就需要使用到系统的浏览文件夹对话框来选择要发送的文件夹。当我们在接收到多个文件时,可以选择全部另存为,此时也需要使用系统的浏览文件夹对话框来选择要另存为的路径。
我们调用SHBrowseForFolder接口即可打开浏览文件夹对话框,相关代码如下所示:
// 打开目录选择对话框
::CoInitialize( NULL );
LPMALLOC lpMalloc = NULL;
TCHAR pchSelDir[MAX_PATH] = 0;
pchSelDir[0] = _T('\\0');
if( E_FAIL == ::SHGetMalloc(&lpMalloc) )
::CoUninitialize();
return;
BROWSEINFO browseInfo;
browseInfo.hwndOwner = m_hParentWnd;
browseInfo.pidlRoot = NULL;
browseInfo.pszDisplayName = NULL;
browseInfo.lpszTitle = STRING_SEL_FOLDER_TO_SEND;
browseInfo.ulFlags= BIF_RETURNONLYFSDIRS;
browseInfo.lpfn = NULL;
browseInfo.lParam = 0;
// 打开浏览文件夹对话框
LPITEMIDLIST lpItemIDList = NULL;
if ( ( lpItemIDList = ::SHBrowseForFolder(&browseInfo) ) != NULL )
// 获取用户选择的文件夹
::SHGetPathFromIDList( lpItemIDList, pchSelDir );
lpMalloc->Free( lpItemIDList );
lpMalloc->Release();
else
lpMalloc->Free( lpItemIDList );
lpMalloc->Release();
::CoUninitialize();
return;
::CoUninitialize();4、最后
在此将C++处理打开文件对话框、保存文件对话框、浏览文件夹对话框的细节分享出来,希望大家可以直接参考,不要再走弯路了。
以上是关于一文带你搞懂C++如何操作文件对话框(附源码)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章