Day600&601.马踏棋盘算法 -数据结构和算法Java
Posted 阿昌喜欢吃黄桃
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Day600&601.马踏棋盘算法 -数据结构和算法Java相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
马踏棋盘算法
- 图的深度优先DFS
- 回溯
- 八皇后问题、小老鼠找迷宫问题
一、介绍


二、思路分析

三、代码实现
package com.achang.algorithm;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 马踏棋盘问题&骑士周游问题
*/
class HorseChessBoard
public static void main(String[] args)
x = 6;
y = 6;
int row = 2;//马儿走的行初始化位置
int column = 4;//马儿走的列初始化位置
int[][] chessboard = new int[x][y];//创建棋盘
visited = new boolean[x * y];//初始化值都是false
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
traversalChessboard(chessboard, row - 1, column - 1, 1);
System.out.println(("程序运行了:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms"));
//输出结果
for (int[] ints : chessboard)
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints));
//标记棋盘的各个位置是否被访问过
private static boolean[] visited;
//标记是否棋盘的所有位置都被访问
private static boolean finished;
private static int x;//棋盘的列数
private static int y;//棋盘的行数
/**
* 马踏棋盘算法
*
* @param chessBoard 棋盘
* @param row 马儿当前的行位置
* @param column 马儿当前的列位置
* @param step 马儿走的第几步,初始位置为第一步
*/
public static void traversalChessboard(int[][] chessBoard, int row, int column, int step)
chessBoard[row][column] = step;
visited[row * x + column] = true;
//获取当前位置可以走的下一个位置的集合
ArrayList<Point> ps = next(new Point(column, row));
while (!ps.isEmpty())
Point p = ps.remove(0);
//判断是否被访问过
if (!visited[p.y * x + p.x])
traversalChessboard(chessBoard, p.y, p.x, step + 1);
//判断马儿是否完成任务,使用step和应该走的步数比较 x*y=棋盘的大小
//如果没有达到数量,则表示任务没有完成,将整个棋盘置0
//1、棋盘到目前位置,仍然没有走完
//2、棋盘处于应该回溯过程
if (step < (x * y) && !finished)
chessBoard[row][column] = 0;
visited[row * x + column] = false;
else
finished = true;
/**
* 获取当前节点接下来能走哪个点
*
* @param curPoint 当前点
* @return 接下来可以走的点
*/
public static ArrayList<Point> next(Point curPoint)
ArrayList<Point> points = new ArrayList<>();
Point point = new Point();
//表示马可以走5这个位置
if ((point.x = curPoint.x - 2) >= 0 && (point.y = curPoint.y - 1) >= 0)
points.add(new Point(point));
//表示马可以走6这个位置
if ((point.x = curPoint.x - 1) >= 0 && (point.y = curPoint.y - 2) >= 0)
points.add(new Point(point));
//表示马可以走7这个位置
if ((point.x = curPoint.x + 1) < x && (point.y = curPoint.y - 2) >= 0)
points.add(new Point(point));
//表示马可以走0这个位置
if ((point.x = curPoint.x + 2) < x && (point.y = curPoint.y - 1) >= 0)
points.add(new Point(point));
//表示马可以走1这个位置
if ((point.x = curPoint.x + 2) < x && (point.y = curPoint.y + 1) < y)
points.add(new Point(point));
//表示马可以走2这个位置
if ((point.x = curPoint.x + 1) < x && (point.y = curPoint.y + 2) < y)
points.add(new Point(point));
//表示马可以走3这个位置
if ((point.x = curPoint.x - 1) >= 0 && (point.y = curPoint.y + 2) < y)
points.add(new Point(point));
//表示马可以走4这个位置
if ((point.x = curPoint.x - 2) >= 0 && (point.y = curPoint.y + 1) < y)
points.add(new Point(point));
return points;
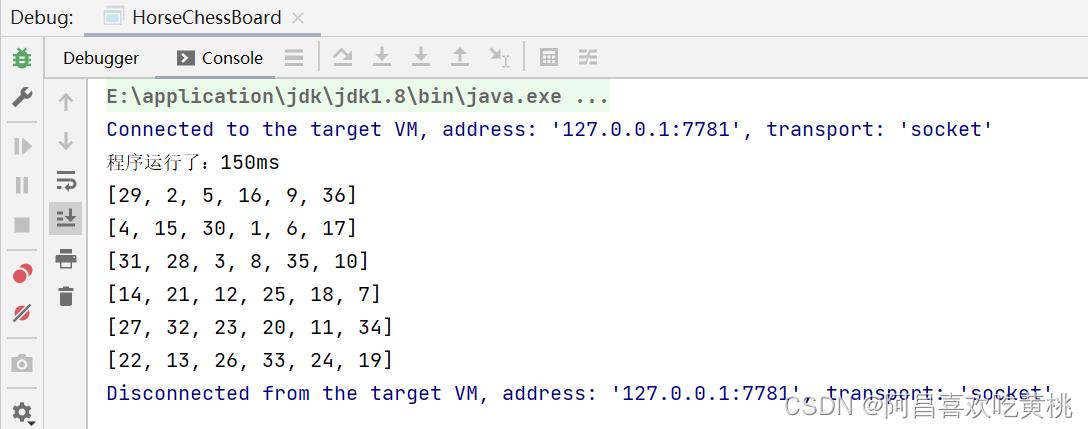
当我们将棋盘设置为8*8以后,会发现这个算法会大幅度降低速度!!!
四、贪心算法优化方案

package com.achang.algorithm;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
/**
* 马踏棋盘问题&骑士周游问题
*/
class HorseChessBoard
public static void main(String[] args)
x = 6;
y = 6;
int row = 2;//马儿走的行初始化位置
int column = 4;//马儿走的列初始化位置
int[][] chessboard = new int[x][y];//创建棋盘
visited = new boolean[x * y];//初始化值都是false
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
traversalChessboard(chessboard, row - 1, column - 1, 1);
System.out.println(("程序运行了:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + "ms"));
//输出结果
for (int[] ints : chessboard)
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints));
//标记棋盘的各个位置是否被访问过
private static boolean[] visited;
//标记是否棋盘的所有位置都被访问
private static boolean finished;
private static int x;//棋盘的列数
private static int y;//棋盘的行数
/**
* 马踏棋盘算法
*
* @param chessBoard 棋盘
* @param row 马儿当前的行位置
* @param column 马儿当前的列位置
* @param step 马儿走的第几步,初始位置为第一步
*/
public static void traversalChessboard(int[][] chessBoard, int row, int column, int step)
chessBoard[row][column] = step;
visited[row * x + column] = true;
//获取当前位置可以走的下一个位置的集合
ArrayList<Point> ps = next(new Point(column, row));
sort(ps);
while (!ps.isEmpty())
Point p = ps.remove(0);
//判断是否被访问过
if (!visited[p.y * x + p.x])
traversalChessboard(chessBoard, p.y, p.x, step + 1);
//判断马儿是否完成任务,使用step和应该走的步数比较 x*y=棋盘的大小
//如果没有达到数量,则表示任务没有完成,将整个棋盘置0
//1、棋盘到目前位置,仍然没有走完
//2、棋盘处于应该回溯过程
if (step < (x * y) && !finished)
chessBoard[row][column] = 0;
visited[row * x + column] = false;
else
finished = true;
/**
* 获取当前节点接下来能走哪个点
*
* @param curPoint 当前点
* @return 接下来可以走的点
*/
public static ArrayList<Point> next(Point curPoint)
ArrayList<Point> points = new ArrayList<>();
Point point = new Point();
//表示马可以走5这个位置
if ((point.x = curPoint.x - 2) >= 0 && (point.y = curPoint.y - 1) >= 0)
points.add(new Point(point));
//表示马可以走6这个位置
if ((point.x = curPoint.x - 1) >= 0 && (point.y = curPoint.y - 2) >= 0)
points.add(new Point(point));
//表示马可以走7这个位置
if ((point.x = curPoint.x + 1) < x && (point.y = curPoint.y - 2) >= 0)
points.add(new Point(point));
//表示马可以走0这个位置
if ((point.x = curPoint.x + 2) < x && (point.y = curPoint.y - 1) >= 0)
points.add(new Point(point));
//表示马可以走1这个位置
if ((point.x = curPoint.x + 2) < x && (point.y = curPoint.y + 1) < y)
points.add(new Point(point));
//表示马可以走2这个位置
if ((point.x = curPoint.x + 1) < x && (point.y = curPoint.y + 2) < y)
points.add(new Point(point));
//表示马可以走3这个位置
if ((point.x = curPoint.x - 1) >= 0 && (point.y = curPoint.y + 2) < y)
points.add(new Point(point));
//表示马可以走4这个位置
if ((point.x = curPoint.x - 2) >= 0 && (point.y = curPoint.y + 1) < y)
points.add(new Point(point));
return points;
//贪心算法优化,根据当前这一步的所有的下一步的选择的位置,进行非递降排序(递增排序,1122344456789)
public static void sort(ArrayList<Point> ps)
ps.sort(new Comparator<Point>()
@Override
public int compare(Point o1, Point o2)
ArrayList<Point> next = next(o1);
ArrayList<Point> next1 = next(o1);
if (next.size() < next1.size())
return -1;
else if (next.size() == next1.size())
return 0;
else
return 1;
);


以上是关于Day600&601.马踏棋盘算法 -数据结构和算法Java的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章