C++ new/delete与 malloc/free
Posted Overboom
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C++ new/delete与 malloc/free相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
malloc free / new delete区别
1. malloc free / new delete作用于基本数据类型
针对基本数据类型,new出来的内存可以用delete释放,也可以用free释放,同样malloc出来的内存,可以用free释放也可以用用delete释放。
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
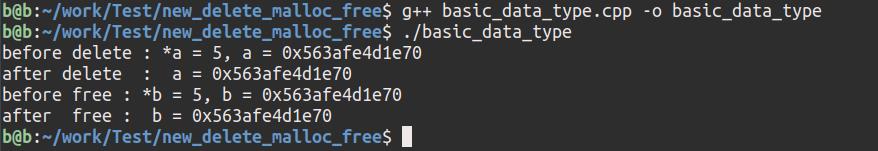
int *a (new int(5));
printf("before delete : *a = %d, a = %p\\n", *a, a);
delete(a);
printf("after delete : a = %p\\n", a);
int *b (new int(5));
printf("before free : *b = %d, b = %p\\n", *b, b);
free(a);
printf("after free : b = %p\\n", b);
return 0;
编译输出:
2. malloc free / new delete作用于结构体/类
针对结构体/类,new做两件事,一是分配内存,二是调用类的构造函数;同样,delete会调用类的析构函数和释放内存。而malloc和free只是分配和释放内存。
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class CTest
public:
CTest();
~CTest();
public:
void print_test();
;
CTest::CTest()
printf("CTest 构造函数\\n");
CTest::~CTest()
printf("CTest 析构函数调用\\n");
void CTest::print_test()
printf("do nothing, just printf\\n");
int main(void)
CTest *test_ (new CTest);
test_->print_test();
delete test_;
CTest *test2_ = (CTest*)malloc(sizeof(CTest));
test2_->print_test();
free(test2_);
return 0;
编译输出:

3. delete p 与 delete [] p
基本类型数组,delete p与delete [] p是一样的
针对结构体/类,单个堆上的对象,不可以delete []p
4. new在栈区、静态区分配内存
new分配的内存默认是在堆区分配内存的,new也可以在栈区、静态区分配内存,但是在栈区、静态区都不可以delete
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
static int g_array[100] = 0;
// 栈上分配内存示例
void mem_in_stack()
char str[1024] = 'M';
char *p_str1 = new(str)char[10]'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e';
char *p_str2 = new(str+40)char[20]'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e';
//检验分配的内存可以访问
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
cout << p_str1[i] << " ";
cout << endl << "************************" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
cout << p_str2[i] << " ";
cout << endl << "************************" << endl;
// 打印str的地址和p_str1, p_str2的地址
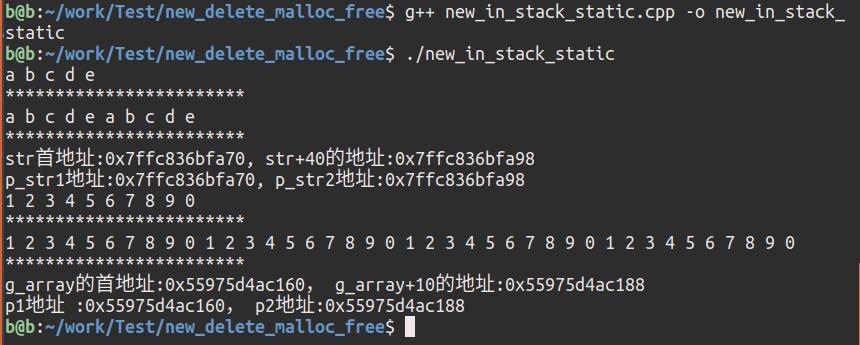
printf("str首地址:%p, str+40的地址:%p\\n", str, str+40);
printf("p_str1地址:%p, p_str2地址:%p\\n", p_str1, p_str2);
// 静态区分配内存示例
void mem_in_static()
int *p1 = new(g_array)int[10]1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0;
int *p2 = new(g_array+10)int[40]1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
cout << p1[i] << " ";
cout << endl << "************************" << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < 40; i++)
cout << p1[i] << " ";
cout << endl << "************************" << endl;
// 打印g_array的地址和p1,p2的地址
printf("g_array的首地址:%p, g_array+10的地址:%p\\n", g_array, g_array+10);
printf("p1地址 :%p, p2地址:%p\\n", p1, p2);
int main(void)
mem_in_stack();
mem_in_static();
return 0;
编译输出:
以上是关于C++ new/delete与 malloc/free的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章