Windows无法启动 Diagnostic policy service服务(位于本地计算机上)错误1069:由于登录失败而无法启动服务
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Windows无法启动 Diagnostic policy service服务(位于本地计算机上)错误1069:由于登录失败而无法启动服务相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
电脑显示连接不可用,诊断后结果为:诊断策略服务未运行,百度后按照网上的方法,找到服务里面的选项,更改后启动服务,却被告知提问中的错误,求解答!!上不了网啊
参考技术A 系统有问题,还是用个验证过的系统盘重装系统吧。用u盘或者硬盘这些都是可以的,且安装速度非常快。但关键是:要有经过验证的(兼容ide、achi、Raid模式的安装)并能够自动永久激活、可以自动安装机器硬件的驱动程序的系统盘,这样就可以全程自动顺利重装系统了。…………si xin xiang li mian…………望采纳!本回答被提问者和网友采纳PoEdu - Windows阶段班 Po学校Lesson006_线程_线程的启动到消亡 &线程状态 & 线程安全 & CONTEXT结构体 & 令牌锁
-
011_线程启动到死亡的详细讲解
- 1. 线程内核对象
- 使用计数 2 ##决定当前线程何时销毁
- 暂停计数 1 ##UINT类型初始为1,可以暂停多次,如置为0则取消暂停。
- 退出代码 STILL_ACTIVE
- Signaled FALSE
- CONTEXT 为空
- 2. 栈
##在隶属于当前进程的空间中,分配一块“栈”空间,以供线程使用- 参数 lpParam
- 入口地址 lpfnAddr
- 3. CONTEXT
##线程上一次运行时的寄存器- IP(指令寄存器) void RtlUserThreadStart(未公开的函数)(lpParam,lpFnAddr)
- SP(栈寄存器) lpFnAddr
- 4. 交给CPU调度
- 5. RtlUserThreadStart
- SEH ##设置结构化异常
- 调用线程函数,传递lpParam
- 等待线程函数的返回
- ExitThread ## 使用计数递减
- 1. 线程内核对象
-
012_beginthreadex和CreateThread
- 多线程运行库的设置
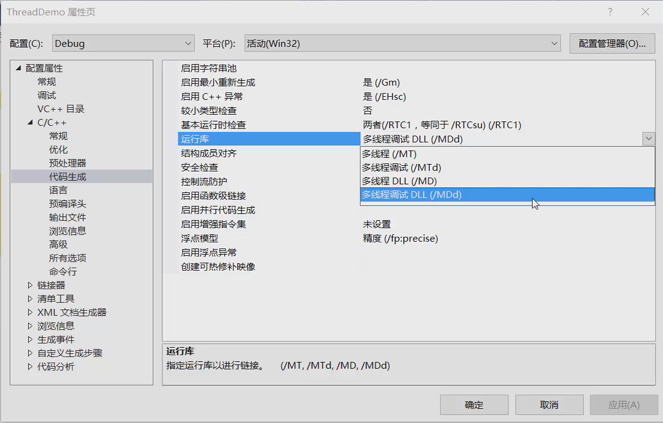
- _beginthreadex() 函数隶属于C标准的运行库,要包含头文件: process.h
- 非线程安全:
- 多线程访问全局变量时,会有出错的机率。
- 举例C语言的错误处理机制:errno 非线程安全
- C语言的设计者,为了解决线程的安全问题,给出了_beginthreadex()函数。
- _beginthreadex()函数的区别:
- 1 参数与 CreateThread()函数的参数意义相同,但其类型已经不同。
- 2 beginthreadex()比CreateThread()函数,多开辟了一段空间,分配在堆上面,存储一些全局的变量。以期线程安全。多分配了堆空间后,才来调用CreateThread();
- 3 使用beginthreadex()要配套_endthreadex()使用.
- 建议使用_beginthreadex(),有多分配一段堆空间。
- _beginthread()函数不建议使用,因为其并没有多分配一段堆空间。这里要注意使用EX版本的函数。
- 多线程运行库的设置
-
013_线程状态
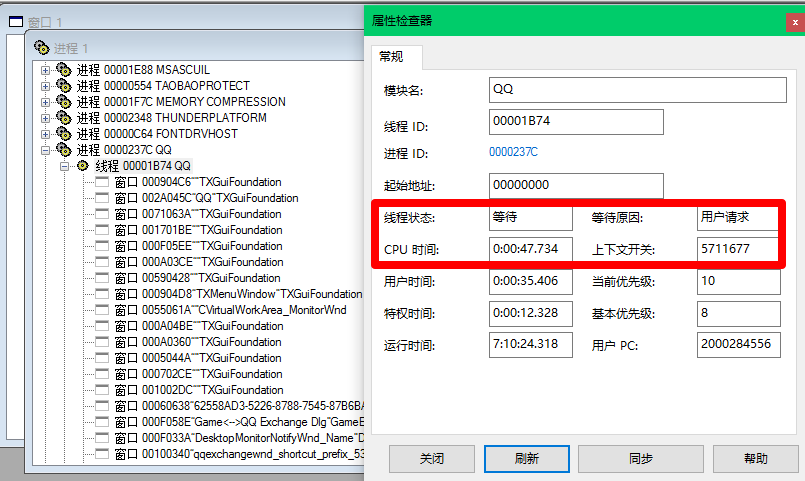
-
014_线程的挂起转态
-
启动
- CONTEXT 初始
- 使用计数 置为2
- 暂停计数 置为1
- 在后续CreateThread完成后,减1得出0,为0则进入CPU的调度。当前线程是可执行的状态。
-
运行
- 执行我们的函数
- 时不时的切换线程,将CPU寄存器的状态写入CONTEXT
- 切换到当前时,先读取CONTEXT
- 执行我们的函数
-
挂起
- SuspendThread() 32位 Wow64SuspendThread() 64位
- 调用暂停线程函数SuspendThread(),函数会把暂停计数+1
- SuspendThread函数会返回0,第一次调用结束时返回1;第二次调用时返回1,第二次结束时返回2. 此函数有调用时的返回,与结束时的返回。
- ResumeThread() 恢复挂起线程
- 调用此函数,会把当前线程的暂停计数-1
- 有几次挂起,就要有几次恢复调用,不然线程仍然不会进入运行。
- 不建议使用线程的挂起:
- 如果线程入口函数里面,有new新的堆空间,而操作系统切换线程时,有可能会使得这块堆空间,在被占用的情况下,却没有占用的标记。此时当此堆空间被访问时,就出了非常隐蔽的BUG。
- 要区分2种挂起:
- 1 操作系统切换线程时的“挂起”——在“池”中
- 准确来说是“切换”线程。按操作系统的算法,线程在进行CPU调度时,所产生的暂停。
- 2 SuspendThread()函数产生的挂起 ——不在“池”中
- 挂起的线程被拿出CPU的线程运行调度池
- SuspendThread() 32位 Wow64SuspendThread() 64位
-
-
015_线程 等待、休眠、及饥饿线程
-
等待休眠 Sleep()
- Sleep(100); 表示休眠100毫秒后,CPU再来运行;
- 这里100毫秒并不能准确不差,因为windows操作系统非实时的,CPU的运行时调度也是非实时的;所以在时间方面有一点误差,只能说是无限接近100毫秒。
- 放弃当前的时间片,在一段时间之内,CPU不会调度此线程
- Sleep(INFINITE) 永远等待
- INFINITE 其值为-1;
- 一直等待到进程结束
- Sleep(0) 放弃线程执行时间片
- SwitchToThread() 把CPU剩余的时间片,分配给"饥饿度"较高的线程.
- 调度另外一个线程,也就是把CPU的执行周期给另外一个线程身上。
- CPU时间片“饥饿度”:如果一此线程相对时间片很少,或者一直没有得到执行,我们就称其为“饥饿”线程。饥饿度相对较高。
-
-
016_CONTEXT结构体
- 源码
typedef struct _CONTEXT { // // The flags values within this flag control the contents of // a CONTEXT record. // // If the context record is used as an input parameter, then // for each portion of the context record controlled by a flag // whose value is set, it is assumed that that portion of the // context record contains valid context. If the context record // is being used to modify a threads context, then only that // portion of the threads context will be modified. // // If the context record is used as an IN OUT parameter to capture // the context of a thread, then only those portions of the thread‘s // context corresponding to set flags will be returned. // // The context record is never used as an OUT only parameter. // DWORD ContextFlags; // // This section is specified/returned if CONTEXT_DEBUG_REGISTERS is // set in ContextFlags. Note that CONTEXT_DEBUG_REGISTERS is NOT // included in CONTEXT_FULL. // DWORD Dr0; DWORD Dr1; DWORD Dr2; DWORD Dr3; DWORD Dr6; DWORD Dr7; // // This section is specified/returned if the // ContextFlags word contians the flag CONTEXT_FLOATING_POINT. // FLOATING_SAVE_AREA FloatSave; // // This section is specified/returned if the // ContextFlags word contians the flag CONTEXT_SEGMENTS. // DWORD SegGs; DWORD SegFs; DWORD SegEs; DWORD SegDs; // // This section is specified/returned if the // ContextFlags word contians the flag CONTEXT_INTEGER. // DWORD Edi; DWORD Esi; DWORD Ebx; DWORD Edx; DWORD Ecx; DWORD Eax; // // This section is specified/returned if the // ContextFlags word contians the flag CONTEXT_CONTROL. // DWORD Ebp; DWORD Eip; DWORD SegCs; // MUST BE SANITIZED DWORD EFlags; // MUST BE SANITIZED DWORD Esp; DWORD SegSs; // // This section is specified/returned if the ContextFlags word // contains the flag CONTEXT_EXTENDED_REGISTERS. // The format and contexts are processor specific // BYTE ExtendedRegisters[MAXIMUM_SUPPORTED_EXTENSION]; } CONTEXT;
- 源码
-
017_线程安全及上锁
- 示例
-
// ContextDemo.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 // #include "stdafx.h" #include <windows.h> #include <process.h> BOOL bUseing = FALSE; unsigned int __stdcall ThreadRun(void* lParam) { int nNum = 0; while (true) { if (!bUseing) { bUseing = TRUE; _tprintf(TEXT("ThreadRun:%d\r\n"), nNum++); bUseing = FALSE; } } } unsigned int __stdcall ThreadMonitor(void* lParam) { HANDLE hThread = (HANDLE)(lParam); while (true) { CONTEXT context; context.ContextFlags = CONTEXT_ALL; SuspendThread(hThread); GetThreadContext(hThread, &context); if (!bUseing) { bUseing = TRUE; _tprintf(TEXT("EAX:0x%x ESP:0x%x EIP:0x%x\r\n"), context.Eax, context.Esp, context.Eip); bUseing = FALSE; } ResumeThread(hThread); } } int main() { HANDLE hThreads[2]; hThreads[0] = (HANDLE)_beginthreadex(nullptr, 0, ThreadRun,nullptr, 0, nullptr); hThreads[1] = (HANDLE)_beginthreadex(nullptr, 0, ThreadMonitor,hThreads[0], 0, nullptr); WaitForMultipleObjects(sizeof(hThreads)/sizeof(HANDLE),hThreads,true,INFINITE); for (int i = 0; i<sizeof(hThreads)/sizeof(HANDLE);++i) { CloseHandle(hThreads[i]); } return 0; }
以上是关于Windows无法启动 Diagnostic policy service服务(位于本地计算机上)错误1069:由于登录失败而无法启动服务的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
win7 windows 无法启动diagnostic policy service服务(位于 本地计算机上)。错误5:拒绝访问?
Windows无法启动 Diagnostic policy service服务(位于本地计算机上)错误1069:由于登录失败而无法启动服务
WIN7系统 ,诊断策略服务未运行 无法启动 Diagnostic Policy Service
System.Diagnostic.Process.Start vs System.Windows.Forms.Help.ShowHelp 打开CHM文件
PoEdu - Windows阶段班 Po学校Lesson006_线程_线程的启动到消亡 &线程状态 & 线程安全 & CONTEXT结构体 & 令牌锁