设备树——dtb格式到struct device node结构体的转换
Posted 正在起飞的蜗牛
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了设备树——dtb格式到struct device node结构体的转换相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1、参考资料
2、struct device_node结构体
struct device_node
const char *name; //节点的名字
const char *type; //device_type属性的值
phandle phandle; //对应该节点的phandle属性
const char *full_name; //节点的名字, node-name[@unit-address]从“/”开始的,表示该node的full path
struct fwnode_handle fwnode;
struct property *properties; // 节点的属性
struct property *deadprops; /* removed properties 如果需要删除某些属性,kernel并非真的删除,而是挂入到deadprops的列表 */
struct device_node *parent; // 节点的父亲
struct device_node *child; // 节点的孩子(子节点)
struct device_node *sibling; // 节点的兄弟(同级节点)
#if defined(CONFIG_OF_KOBJ) // 在sys文件系统表示
struct kobject kobj;
#endif
unsigned long _flags;
void *data;
#if defined(CONFIG_SPARC)
const char *path_component_name;
unsigned int unique_id;
struct of_irq_controller *irq_trans;
#endif
;
3、struct property结构体
struct property
char *name; //属性名字
int length; //value的长度
void *value; //属性值
struct property *next; //指向统一节点的下一个属性
#if defined(CONFIG_OF_DYNAMIC) || defined(CONFIG_SPARC)
unsigned long _flags;
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_OF_PROMTREE)
unsigned int unique_id;
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_OF_KOBJ)
struct bin_attribute attr;
#endif
;
4、转换过程的函数调用关系
unflatten_device_tree() //解析dtb格式成struct device node结构体
__unflatten_device_tree()
unflatten_dt_nodes() //计算解析出的struct device node结构体所需要的内存大小
dt_alloc() //申请上面计算出来的需要的内存
unflatten_dt_nodes() //将dtb数据解析成device node结构体,保存在上面申请的内存中
of_alias_scan() //处理aliases节点,根据节点的别名找到对应节点并保存到aliases_lookup链表中
5、__unflatten_device_tree()函数
5.1、函数调用
__unflatten_device_tree(initial_boot_params, NULL, &of_root,early_init_dt_alloc_memory_arch, false);
| 传参 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| initial_boot_params | dtb数据的所在地址 |
| of_root | 保存将来解析的struct device_node结构体的根节点 |
| early_init_dt_alloc_memory_arch | 用于申请内存的函数 |
| false | 觉得是否设置根节点的OF_DETACHED标志 |
5.2、函数源码
__unflatten_device_tree(initial_boot_params, NULL, &of_root,
early_init_dt_alloc_memory_arch, false);
static void *__unflatten_device_tree(const void *blob,
struct device_node *dad,
struct device_node **mynodes,
void *(*dt_alloc)(u64 size, u64 align),
bool detached)
int size;
void *mem;
pr_debug(" -> unflatten_device_tree()\\n");
if (!blob)
pr_debug("No device tree pointer\\n");
return NULL;
//打印dtb的相关信息
pr_debug("Unflattening device tree:\\n");
pr_debug("magic: %08x\\n", fdt_magic(blob));
pr_debug("size: %08x\\n", fdt_totalsize(blob));
pr_debug("version: %08x\\n", fdt_version(blob));
//校验dtb的数据头
if (fdt_check_header(blob))
pr_err("Invalid device tree blob header\\n");
return NULL;
/* 第一次调用:计算解析出的struct device_node结构体所占内存大小 */
size = unflatten_dt_nodes(blob, NULL, dad, NULL);
if (size < 0)
return NULL;
//将内存大小4字节对齐
size = ALIGN(size, 4);
pr_debug(" size is %d, allocating...\\n", size);
/* 申请解析设备树dtb数据需要的内存 */
mem = dt_alloc(size + 4, __alignof__(struct device_node));
if (!mem)
return NULL;
memset(mem, 0, size);
//将申请内存空间的下一个地址处赋值为0xdeadbeef
*(__be32 *)(mem + size) = cpu_to_be32(0xdeadbeef);
pr_debug(" unflattening %p...\\n", mem);
/* 第二次调用:解析dtb数据成device node结构体,保存在上面申请的内存中*/
unflatten_dt_nodes(blob, mem, dad, mynodes);
//检查解析的device_node结构体所占内存是否越界
if (be32_to_cpup(mem + size) != 0xdeadbeef)
pr_warning("End of tree marker overwritten: %08x\\n",
be32_to_cpup(mem + size));
if (detached && mynodes)
of_node_set_flag(*mynodes, OF_DETACHED);
pr_debug("unflattened tree is detached\\n");
pr_debug(" <- unflatten_device_tree()\\n");
return mem;
(1)unflatten_dt_nodes()会被调用两次,传参不同该函数会有不同的功能;第一次是计算所需内存大小,第二次是真正解析dtb数据成device_node格式;
(2)of_root变量保存的是根节点对应的struct device_node结构体;
6、struct device_node *of_root变量
(1)无论是dtb格式还是struct device_node格式,里面表达的数据是没变的,只是组织形式不同,解析的方法就不同。dtb格式和struct device_node格式都有专门的解析函数,dtb格式下是需要知道dtb数据所在内存地址,struct device_node格式是需要知道根节点的struct device_node结构体;
(2)of_root就是保存的根节点的struct device_node结构体,后续解析设备树的信息就是利用of_root根节点和专门的解析函数即可;
7、struct device_node格式下如何解析出信息
7.1、相关文件和操作函数
(1)在struct device_node格式下内核提供相关的操作函数,具体查看"drivers/of/base.c"文件;
(2)我们调用相关的函数,可以通过节点路径、节点名字、父节点等方式去查找需要的device_node结构体;
7.2、of_alias_scan()函数
void of_alias_scan(void * (*dt_alloc)(u64 size, u64 align))
struct property *pp;
//通过节点的路径查看aliases节点
of_aliases = of_find_node_by_path("/aliases");
//通过节点的路径查看chosen节点
of_chosen = of_find_node_by_path("/chosen");
if (of_chosen == NULL)
of_chosen = of_find_node_by_path("/chosen@0");
if (of_chosen)
/* linux,stdout-path and /aliases/stdout are for legacy compatibility */
const char *name = of_get_property(of_chosen, "stdout-path", NULL);
if (!name)
name = of_get_property(of_chosen, "linux,stdout-path", NULL);
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_PPC) && !name)
name = of_get_property(of_aliases, "stdout", NULL);
if (name)
of_stdout = of_find_node_opts_by_path(name, &of_stdout_options);
if (!of_aliases)
return;
for_each_property_of_node(of_aliases, pp)
const char *start = pp->name;
const char *end = start + strlen(start);
struct device_node *np;
struct alias_prop *ap;
int id, len;
/* Skip those we do not want to proceed */
if (!strcmp(pp->name, "name") ||
!strcmp(pp->name, "phandle") ||
!strcmp(pp->name, "linux,phandle"))
continue;
np = of_find_node_by_path(pp->value);
if (!np)
continue;
······
(1)of_alias_scan()函数主要是处理aliases节点,处理节点的别名,方便后续访问;
(2)查找aliases节点对应的device_node结构体就是通过绝对路径进行查找;
(3)of_find_node_by_path( )函数内部会根据of_root节点进行查找,of_root节点就是根节点;
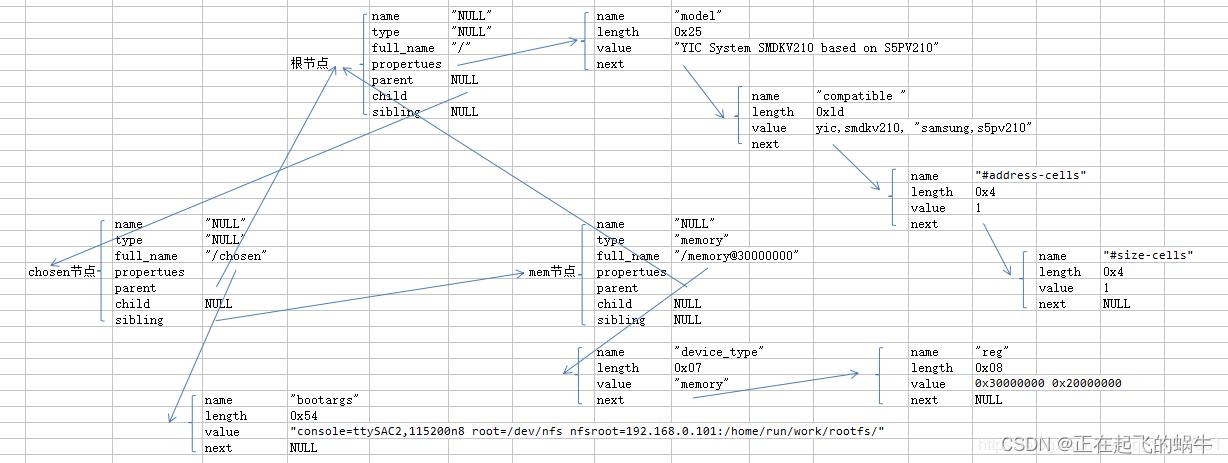
8、dts示例源码
/dts-v1/;
/memreserve/ 0x4ff00000 0x100000;
/
model = "YIC System SMDKV210 based on S5PV210";
compatible = "yic,smdkv210", "samsung,s5pv210";
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <1>;
chosen
bootargs = "console=ttySAC2,115200n8 root=/dev/nfs nfsroot=192.168.0.101:/home/run/work/rootfs/";
;
memory@30000000
device_type = "memory";
reg = <0x30000000 0x20000000>;
;
;
9、dts文件和struct device_node的转换图
以上是关于设备树——dtb格式到struct device node结构体的转换的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
设备树(dtb数据)匹配struct machine_desc结构体
RK3399平台开发系列讲解(内核设备树篇)4.22设备树dtb信息转化为device_node结构
Linux DTS (Device Tree Source)设备树源码