MSK基于FPGA的MSK调制系统开发
Posted fpga和matlab
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了MSK基于FPGA的MSK调制系统开发相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.软件版本
ISE14.7
2.本算法实现
研究内容:
1) 设计和验证适合FPGA实现的MSK调制和解调实现方案,
2) MSK系统的发端:含随机数字信息生成模块、MSK调制模块、数模(DA)模块。
3) MSK系统的收端:含MSK解调模块、模数(AD)模块、误码率计算模块。
4) 信道:含功率可控的高斯白噪声(AWGN)生成模块。
5)实现语言:Verilog语言。
需实现的具体内容:
1.用MATLAB进行方案的设计和验证仿真
2.编制基于Verilog的系统(含发端、信道和收端)软件程序;
3进行硬件平台的程序下载和软硬件联调;
4利用测试设备,完成MSK系统各关键模块的输入和输出波形、功率谱的测量;
5仿照FPGA平台的硬件结构和布局,设计FGPA最小开发平台,并绘制其PCB电路图。
调制端的结构如下所示:

仿真结果如下所示:
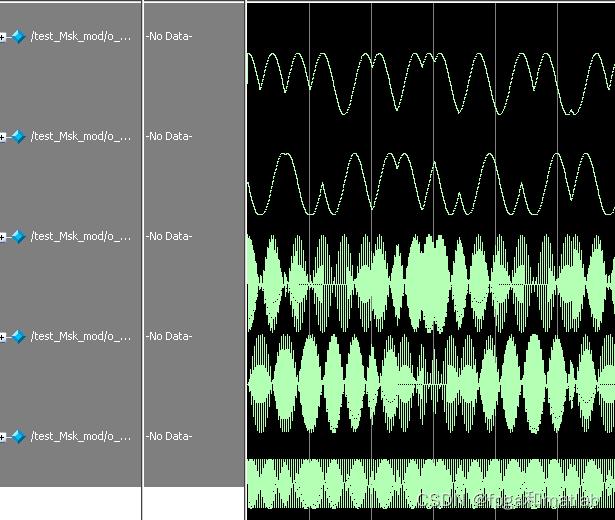
仿真结果可以看到,MSK调制端是完全正确的。
该部分程序如下:

程序中,顶层模块的调用,我们做了注释。
MSK解调部分按之前的系统框图进行设计。设计完的基本构架如下所示:
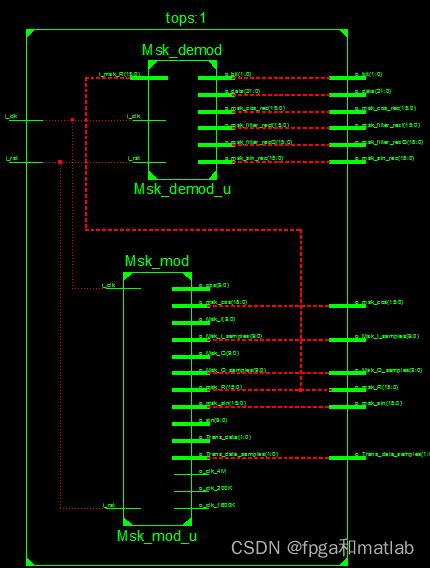
上述的构架就是整个系统的调制解调系统,其中解调端的仿真结果如下所示:

3.部分源码
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
//
// Company:
// Engineer:
//
// Create Date: 15:16:09 06/09/2013
// Design Name:
// Module Name: Msk_mod
// Project Name:
// Target Devices:
// Tool versions:
// Description:
//
// Dependencies:
//
// Revision:
// Revision 0.01 - File Created
// Additional Comments:
//
//
module Msk_mod(
i_clk, //40M
i_rst, //rst signal
o_clk_4M, //MSK rate
o_clk_1600K,//bit rate samples
o_clk_200K, //bit rate
o_Trans_data,//the binary data
o_Trans_data_samples,//the binary data samples
o_Msk_I, //MSK I
o_Msk_Q, //MSK Q samples
o_Msk_I_samples, //MSK I
o_Msk_Q_samples, //MSK Q samples
o_cos, //cos
o_sin, //sin
o_msk_cos, //MSK Cos
o_msk_sin, //MSK Sin
o_msk_R //MSK frequency
);
input i_clk;
input i_rst;
output o_clk_4M;
output o_clk_1600K;
output o_clk_200K;
output signed[1:0] o_Trans_data;
output signed[1:0] o_Trans_data_samples;
output signed[9:0] o_Msk_I;
output signed[9:0] o_Msk_Q;
output signed[9:0] o_Msk_I_samples;
output signed[9:0] o_Msk_Q_samples;
output signed[9:0] o_cos;
output signed[9:0] o_sin;
output signed[15:0]o_msk_cos;
output signed[15:0]o_msk_sin;
output signed[15:0]o_msk_R;
//generate the data rate clock and the fc clock
clk_gen clk_gen_u(
.i_clk (i_clk),
.i_rst (i_rst),
.o_clk_4M (o_clk_4M),
.o_clk_1600K(o_clk_1600K),
.o_clk_200K (o_clk_200K)
);
//generate the random data
binary_gen binary_gen_u(
.i_clk (o_clk_200K),
.i_rst (i_rst),
.o_dout(o_Trans_data)
);
//samples the data from low data to high data
samples samples_u(
.i_clk (o_clk_1600K),
.i_rst (i_rst),
.i_din (o_Trans_data),
.o_dout (o_Trans_data_samples)
);
//gen MSK I data and Q data
Msk_mod_sub1 Msk_mod_sub1_u(
.i_clk (o_clk_1600K),
.i_rst (i_rst),
.i_data (o_Trans_data_samples),
.o_mskI (o_Msk_I),
.o_mskQ (o_Msk_Q)
);
//samples the data from low data to high data
samples2 samples2_uI(
.i_clk (o_clk_4M),
.i_rst (i_rst),
.i_din (o_Msk_I),
.o_dout (o_Msk_I_samples)
);
//samples the data from low data to high data
samples2 samples2_uQ(
.i_clk (o_clk_4M),
.i_rst (i_rst),
.i_din (o_Msk_Q),
.o_dout (o_Msk_Q_samples)
);
//Mults
NCO_Trans NCO_Trans_u(
.i_clk (o_clk_4M),
.i_rst (i_rst),
.o_cos (o_cos),
.o_sin (o_sin)
);
//MSK Frequency data
reg signed[19:0]II;
reg signed[19:0]QQ;
always @(posedge o_clk_4M or posedge i_rst)
begin
if(i_rst)
begin
II <= 20'd0;
QQ <= 20'd0;
end
else begin
II <= o_cos*o_Msk_I_samples;
QQ <= o_sin*o_Msk_Q_samples;
end
end
assign o_msk_cos = II[19:4];
assign o_msk_sin = QQ[19:4];
assign o_msk_R = o_msk_cos[15],o_msk_cos[15:1]+o_msk_sin[15],o_msk_sin[15:1];
endmodule
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
//
// Company:
// Engineer:
//
// Create Date: 15:16:19 06/09/2013
// Design Name:
// Module Name: Msk_demod
// Project Name:
// Target Devices:
// Tool versions:
// Description:
//
// Dependencies:
//
// Revision:
// Revision 0.01 - File Created
// Additional Comments:
//
//
module Msk_demod(
i_clk,
i_rst,
i_msk_R,
o_msk_cos_rec,
o_msk_sin_rec,
o_msk_filter_recI,
o_msk_filter_recQ,
o_data,
o_bit
);
input i_clk;
input i_rst;
input signed[15:0]i_msk_R;
output signed[15:0]o_msk_cos_rec;
output signed[15:0]o_msk_sin_rec;
output signed[15:0]o_msk_filter_recI;
output signed[15:0]o_msk_filter_recQ;
output signed[31:0]o_data;
output signed[1:0] o_bit;
reg signed[31:0]err;
//generate the data rate clock and the fc clock
wire clk_4M; //10
wire clk_1600K; //25
wire clk_200K; //200
clk_gen clk_gen_u(
.i_clk (i_clk),
.i_rst (i_rst),
.o_clk_4M (clk_4M),
.o_clk_1600K(clk_1600K),
.o_clk_200K (clk_200K)
);
//Mults
wire signed[9:0]cos;
wire signed[9:0]sin;
NCO_Rec NCO_Rec_u(
.i_clk (clk_4M),
.i_rst (i_rst),
.i_phase (err[31:21]),
.o_cos (cos),
.o_sin (sin)
);
//MSK Frequency data
reg signed[19:0]II;
reg signed[19:0]QQ;
always @(posedge clk_4M or posedge i_rst)
begin
if(i_rst)
begin
II <= 20'd0;
QQ <= 20'd0;
end
else begin
II <= cos*i_msk_R;
QQ <= sin*i_msk_R;
end
end
assign o_msk_cos_rec = II[18:3];
assign o_msk_sin_rec = QQ[18:3];
Filter Filter_u1(
.i_clk(clk_4M),
.i_rst(i_rst),
.i_din(o_msk_cos_rec),
.o_dout(o_msk_filter_recI)
);
Filter Filter_u2(
.i_clk(clk_4M),
.i_rst(i_rst),
.i_din(o_msk_sin_rec),
.o_dout(o_msk_filter_recQ)
);
reg signed[31:0]err1;
reg signed[31:0]err2;
always @(posedge i_clk or posedge i_rst)
begin
if(i_rst)
begin
err1 <= 32'd0;
err2 <= 32'd0;
end
else begin
err1 <= o_msk_filter_recI*o_msk_filter_recQ;
err2 <= err1;
err <= 48*err1 + 128*(err1 - err2);
end
end
data_check data_check_u(
.i_clk_200K(clk_200K),
.i_rst(i_rst),
.i_filterI(o_msk_filter_recI),
.i_filterQ(o_msk_filter_recQ),
.o_dout(o_data),
.o_bit(o_bit)
);
endmodule
4.参考文献
[1]贾志强, 郭莉, 陈文志. 基于FPGA/DDS技术的MSK信号调制与解调[J]. 微计算机信息, 2009(29):3.A01-117
以上是关于MSK基于FPGA的MSK调制系统开发的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
通信算法之三十六:MSK/CPM+LDPC/Turbo软译码 仿真链路