Linux 内核 内存管理munmap 系统调用源码分析 ② ( do_munmap 函数执行流程 | do_munmap 函数源码 )
Posted 韩曙亮
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Linux 内核 内存管理munmap 系统调用源码分析 ② ( do_munmap 函数执行流程 | do_munmap 函数源码 )相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
munmap 系统调用函数 调用了 vm_munmap 函数 , 在 vm_munmap 函数 中 , 又调用了 do_munmap 函数 , do_munmap 函数 是 删除 内存映射 的 核心函数 ;
一、do_munmap 函数执行流程
do_munmap 函数执行流程 :
根据 unsigned long start 参数的起始地址 , 找到要删除的 第一个 虚拟内存区域 vm_area_struct 结构体实例 ,
int do_munmap(struct mm_struct *mm, unsigned long start, size_t len,
struct list_head *uf)
...
struct vm_area_struct *vma, *prev, *last;
...
/* Find the first overlapping VMA */
vma = find_vma(mm, start);
if (!vma)
return 0;
...
如果不是删除整个 vam 内存区域 , 而只是删除部分内存 , 那么需要分裂 vm_area_struct *vma 指向的内存区域 ;
error = __split_vma(mm, vma, start, 0);
根据 end 结束地址 , 找到 需要删除的 虚拟内存区域 的 最后一个 vm_area_struct *last 实例 ;
/* Does it split the last one? */
last = find_vma(mm, end);
如果不是删除整个 vam 内存区域 , 而只是删除部分内存 , 那么需要分裂 vm_area_struct *last 指向的内存区域 ;
if (last && end > last->vm_start)
int error = __split_vma(mm, last, end, 1);
if (error)
return error;
如果 被删除的 内存区域 被锁定在 内存中 , 即 不允许换出到交换区 , 则调用 munlock_vma_pages_all 函数 解除 内存锁定 ;
/*
* unlock any mlock()ed ranges before detaching vmas
*/
if (mm->locked_vm)
struct vm_area_struct *tmp = vma;
while (tmp && tmp->vm_start < end)
if (tmp->vm_flags & VM_LOCKED)
mm->locked_vm -= vma_pages(tmp);
munlock_vma_pages_all(tmp);
tmp = tmp->vm_next;
调用 detach_vmas_to_be_unmapped 函数 , 将要删除的 " 虚拟内存区域 " 从 进程的 虚拟内存区域 链表 和 红黑树 数据结构中删除 ,
这些内存区域 单独放在一个临时链表中 ;
/*
* Remove the vma's, and unmap the actual pages
*/
detach_vmas_to_be_unmapped(mm, vma, prev, end);
调用 unmap_region 函数 , 将 进程 的 页表中 的 " 被删除内存区域 对应的 映射 " 删除 , 从 处理器 页表缓存 中 也 删除对应 映射 ;
unmap_region(mm, vma, prev, start, end);
调用 arch_unmap 函数 , 执行 该处理器架构 对应的 删除内存映射 的 处理操作 ;
arch_unmap(mm, vma, start, end);
调用 remove_vma_list 函数 , 删除所有的虚拟内存区域 ;
/* Fix up all other VM information */
remove_vma_list(mm, vma);
二、do_munmap 函数源码
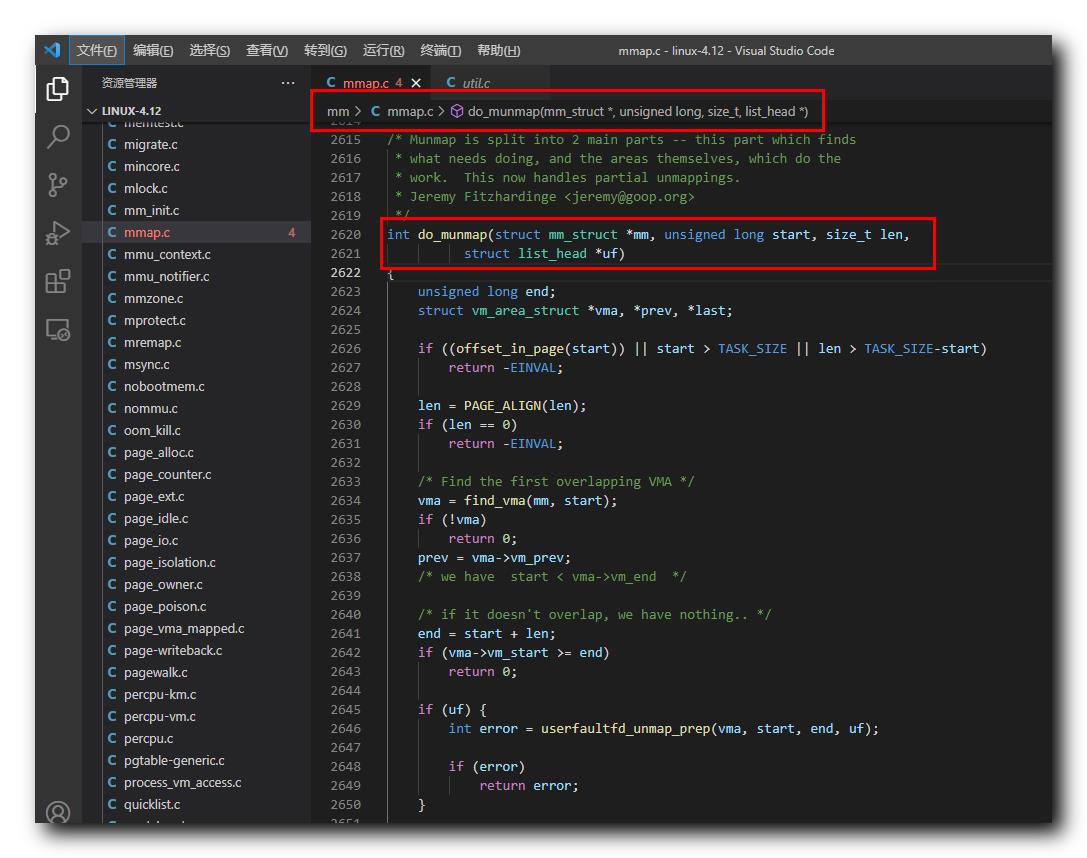
do_munmap 函数 , 定义在 Linux 内核源码 linux-4.12\\mm\\mmap.c#2620 位置 ;
do_munmap 函数源码如下 :
/* Munmap is split into 2 main parts -- this part which finds
* what needs doing, and the areas themselves, which do the
* work. This now handles partial unmappings.
* Jeremy Fitzhardinge <jeremy@goop.org>
*/
int do_munmap(struct mm_struct *mm, unsigned long start, size_t len,
struct list_head *uf)
unsigned long end;
struct vm_area_struct *vma, *prev, *last;
if ((offset_in_page(start)) || start > TASK_SIZE || len > TASK_SIZE-start)
return -EINVAL;
len = PAGE_ALIGN(len);
if (len == 0)
return -EINVAL;
/* Find the first overlapping VMA */
vma = find_vma(mm, start);
if (!vma)
return 0;
prev = vma->vm_prev;
/* we have start < vma->vm_end */
/* if it doesn't overlap, we have nothing.. */
end = start + len;
if (vma->vm_start >= end)
return 0;
if (uf)
int error = userfaultfd_unmap_prep(vma, start, end, uf);
if (error)
return error;
源码路径 : linux-4.12\\mm\\mmap.c#2620
以上是关于Linux 内核 内存管理munmap 系统调用源码分析 ② ( do_munmap 函数执行流程 | do_munmap 函数源码 )的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Linux 内核 内存管理内存管理系统调用 ① ( mmap 创建内存映射 | munmap 删除内存映射 | mprotect 设置虚拟内存区域访问权限 )
Linux 内核 内存管理内存管理系统调用 ④ ( 代码示例 | mmap 创建内存映射 | munmap 删除内存映射 )
Linux 内核 内存管理内存管理架构 ② ( 用户空间内存管理 | malloc | ptmalloc | 内核空间内存管理 | sys_brk | sys_mmap | sys_munmap)