Android DataStore 使用详解
Posted 赵彦军
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android DataStore 使用详解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/zhaoyanjun6/article/details/127358235
本文出自【赵彦军的博客】
文章目录
概述
官方文档:https://developer.android.com/topic/libraries/architecture/datastore
Jetpack DataStore 是一种数据存储解决方案,允许您使用协议缓冲区存储键值对或类型化对象。DataStore 使用 Kotlin 协程和 Flow 以异步、一致的事务方式存储数据。
使用
添加依赖:
implementation "androidx.datastore:datastore-preferences:1.0.0"
定义dataStore
//定义DataStore
val Context.dataStore: DataStore<Preferences> by preferencesDataStore(name = "user_info")
//定义key
val keyName = stringPreferencesKey("name")
val keyAge = intPreferencesKey("age")
保存数据:
import android.os.Bundle
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import androidx.datastore.preferences.core.edit
import androidx.lifecycle.lifecycleScope
import kotlinx.coroutines.launch
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity()
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?)
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
lifecycleScope.launch
saveData("zhaoyanjun", 18)
//dataStore保存数据
suspend fun saveData(name: String, age: Int)
dataStore.edit
it[keyName] = name //保存字符串
it[keyAge] = age //保存int
获取数据
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity()
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?)
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
lifecycleScope.launch
getData()
//dataStore获取数据,collect 是一个挂起函数,所以会一直挂起,只要name的值发起变更,collect 就会回调
suspend fun getData()
val nameFlow = dataStore.data.map
it[keyName]
nameFlow.collect name ->
Log.d("getData ", "name $name")
dataStore.data 是一个 Flow 对象,使用一个 collect 操作符 可以接受 值的变化,一旦值发生变化,collect 就会回调,可以实现数据驱动 UI 的效果。
DataStore 本地数据
DataStore 文件在 files/datastore/ 目录,完整路径是
/data/data/com.zyj.exoplayerdemo/files/datastore/user_info.preferences_pb
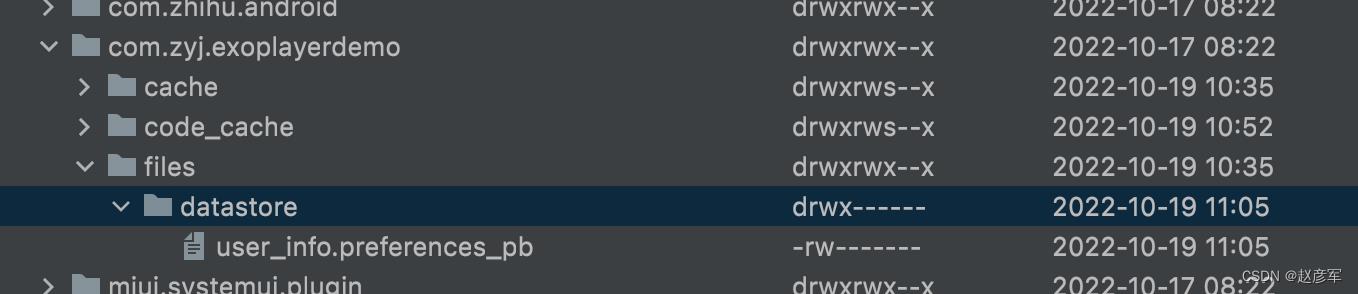
查看DataStore 文件
双击 user_info.preferences_pb 在 AS 里打开
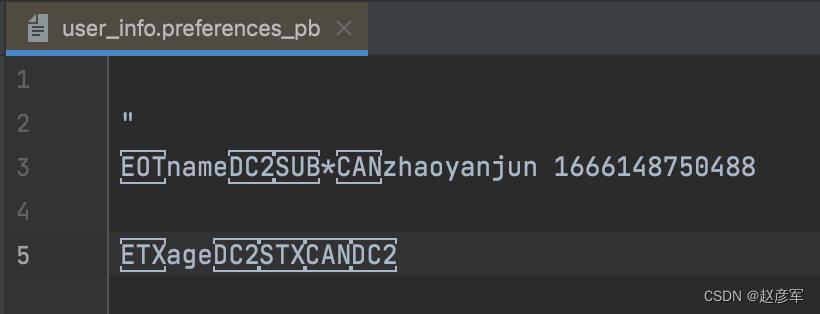
发现是乱码。
点击右键把 user_info.preferences_pb 导出到桌面
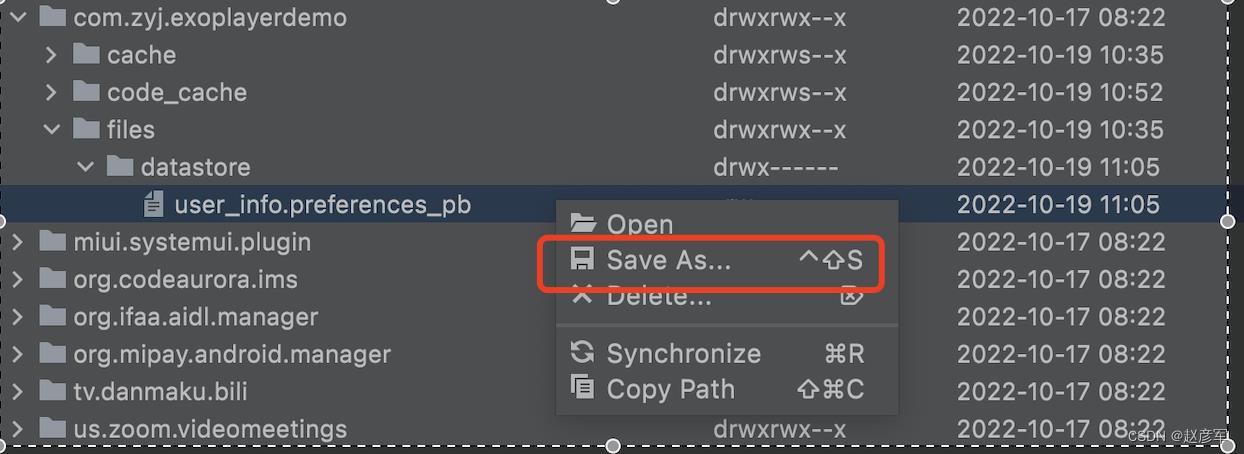
在 mac appStore 下载安装 Protobuf Viewer
用 Protobuf Viewer 打开我们导出的 pb 文件
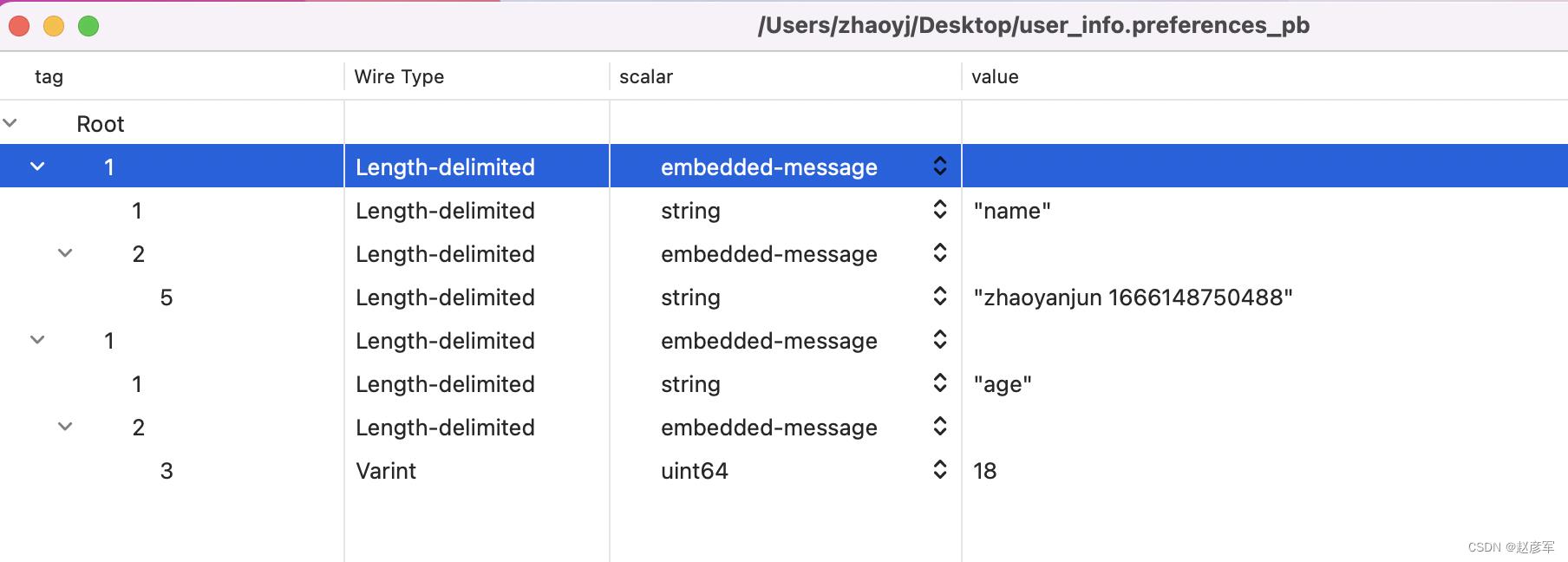
Key 的枚举
在文中我们用到了
stringPreferencesKey("name")
intPreferencesKey("age")
除此之外,DataStore 还提供了其他类型的 Key
@JvmName("intKey")
public fun intPreferencesKey(name: String): Preferences.Key<Int> = Preferences.Key(name)
@JvmName("doubleKey")
public fun doublePreferencesKey(name: String): Preferences.Key<Double> = Preferences.Key(name)
@JvmName("stringKey")
public fun stringPreferencesKey(name: String): Preferences.Key<String> = Preferences.Key(name)
@JvmName("booleanKey")
public fun booleanPreferencesKey(name: String): Preferences.Key<Boolean> = Preferences.Key(name)
@JvmName("floatKey")
public fun floatPreferencesKey(name: String): Preferences.Key<Float> = Preferences.Key(name)
@JvmName("longKey")
public fun longPreferencesKey(name: String): Preferences.Key<Long> = Preferences.Key(name)
@JvmName("stringSetKey")
public fun stringSetPreferencesKey(name: String): Preferences.Key<Set<String>> =
Preferences.Key(name)
同步API
在上面的演示过程中,我们使用 Flow 的 collect 操作符 , 但是 collect 会一直处于挂起状态,只要值发生变化,我们就会收到通知,符合数据驱动 UI 的设计模式。
但是在现实开发中,我们往往需要一个同步 api , 仅仅获取当前一次值,我们只关注本次的值是什么,至于以后得值变化,我们不关心。DataStore 提供了 同步api 来供我们使用 。
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?)
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
lifecycleScope.launch
//同步api
val first = dataStore.data.first()
val name = first[keyName]
val age = first[keyAge]
Log.d("getData ", "name $name")
Log.d("getData ", "age $age")
如果是 pb 文件里面没有值,那么就会返回 null
com.zyj.exoplayerdemo D/getData: name null
com.zyj.exoplayerdemo D/getData: age null
所以我们可以把获取名字,封装成一个同步方法
suspend fun getNameData(): String?
val nameFlow = dataStore.data.map
it[keyName]
return nameFlow.first()
清除内容
清除某个key
val keyName = stringPreferencesKey("name")
suspend fun clear()
dataStore.edit
it.remove(keyName)
清除所有值
suspend fun clear()
dataStore.edit
it.clear()
包含key
suspend fun contains()
dataStore.edit
//是否包含某个key
var result = it.contains(keyName)
SharedPreferences 数据迁移
如果你原来是用 SharedPreferences , 想换到 DataStore 上,DataStore 提供了一键迁移,就一行代码就搞定了。
val Context.dataStore: DataStore<Preferences> by preferencesDataStore(
name = "user_info",
produceMigrations = context ->
listOf(SharedPreferencesMigration(context, "sp_file_name"))
)
DataStore 源码
DataStore 是一个接口
public interface DataStore<T>
/**
* Provides efficient, cached (when possible) access to the latest durably persisted state.
* The flow will always either emit a value or throw an exception encountered when attempting
* to read from disk. If an exception is encountered, collecting again will attempt to read the
* data again.
*
* Do not layer a cache on top of this API: it will be be impossible to guarantee consistency.
* Instead, use data.first() to access a single snapshot.
*
* @return a flow representing the current state of the data
* @throws IOException when an exception is encountered when reading data
*/
public val data: Flow<T>
/**
* Updates the data transactionally in an atomic read-modify-write operation. All operations
* are serialized, and the transform itself is a coroutine so it can perform heavy work
* such as RPCs.
*
* The coroutine completes when the data has been persisted durably to disk (after which
* [data] will reflect the update). If the transform or write to disk fails, the
* transaction is aborted and an exception is thrown.
*
* @return the snapshot returned by the transform
* @throws IOException when an exception is encountered when writing data to disk
* @throws Exception when thrown by the transform function
*/
public suspend fun updateData(transform: suspend (t: T) -> T): T
以上是关于Android DataStore 使用详解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Android Jetpack组件 DataStore的使用和简单封装
Android Jetpack组件 DataStore的使用和简单封装
社区说|DataStore:Android K-V 存储的后浪