Zipkin简介
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Zipkin简介相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A Zipkin是一个分布式跟踪系统。它有助于收集解决服务架构中延迟问题所需的计时数据。特性包括此数据的收集和查找。如果日志文件中有跟踪ID,则可以直接跳转到它。也可以根据服务、操作名称、标签、持续时间等属性进行查询。将为您总结一些有趣的数据,例如花费在服务上的时间百分比,以及操作是否失败。
Zipkin UI还提供了一个依赖关系图,显示通过每个应用程序的跟踪请求的数量。这有助于识别聚合行为,包括错误路径或对弃用服务的调用。
应用程序需要被“检测”,以向Zipkin报告跟踪数据。这通常意味着跟踪程序或检测库的配置。最流行的向Zipkin报告数据的方式是通过HTTP或Kafka,尽管还有很多其他的选择,如Apache ActiveMQ, gRPC和RabbitMQ。提供给UI的数据存储在内存中,或者通过Apache Cassandra或Elasticsearch等后端持久存储。
微服务之分布式跟踪系统(springboot+zipkin+mysql)
通过上一节《微服务之分布式跟踪系统(springboot+zipkin)》我们简单熟悉了zipkin的使用,但是收集的数据都保存在内存中重启后数据丢失,不过zipkin的Storage除了内存,还有Cassandra、MYSQL、ElasticSearch。
二、zipkin的各种Storage配置简介
zipkin存在一些公用的配置,同时存在一些私有的配置(详细信息地址为:https://github.com/openzipkin/zipkin/tree/master/zipkin-server#configuration-for-the-ui),此处不做配置说明的翻译(因为都比较简单易懂),其公用的配置如下所示:
-
*`QUERY_PORT`: Listen port for the http api and web ui; Defaults to 9411
-
*`QUERY_LOG_LEVEL`: Log level written to the console; Defaults to INFO
-
*`QUERY_LOOKBACK`: How many milliseconds queries can look back from endTs;Defaults to 7 days
-
*`STORAGE_TYPE`: SpanStore implementation: one of `mem`, `mysql`, `cassandra`,`elasticsearch`
-
*`COLLECTOR_PORT`: Listen port for the scribe thrift api; Defaults to 9410
-
*`COLLECTOR_SAMPLE_RATE`: Percentage of traces to retain, defaults to alwayssample (1.0).
(1)Cassandra Storage配置
-
* `CASSANDRA_KEYSPACE`: The keyspace to use. Defaults to "zipkin".
-
* `CASSANDRA_CONTACT_POINTS`: Comma separated list of hosts / ip addresses part of Cassandra cluster. Defaults to localhost
-
* `CASSANDRA_LOCAL_DC`: Name of the datacenter that will be considered "local" for latency load balancing. When unset, load-balancing is round-robin.
-
* `CASSANDRA_ENSURE_SCHEMA`: Ensuring cassandra has the latest schema. If enabled tries to execute scripts in the classpath prefixed with `cassandra-schema-cql3`. Defaults to true
-
* `CASSANDRA_USERNAME` and `CASSANDRA_PASSWORD`: Cassandra authentication. Will throw an exception on startup if authentication fails. No default
-
* `CASSANDRA_USE_SSL`: Requires `javax.net.ssl.trustStore` and `javax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword`, defaults to false.
(2)MySQL Storage配置
-
* `MYSQL_DB`: The database to use. Defaults to "zipkin".
-
* `MYSQL_USER` and `MYSQL_PASS`: MySQL authentication, which defaults to empty string.
-
* `MYSQL_HOST`: Defaults to localhost
-
* `MYSQL_TCP_PORT`: Defaults to 3306
-
* `MYSQL_MAX_CONNECTIONS`: Maximum concurrent connections, defaults to 10
-
* `MYSQL_USE_SSL`: Requires `javax.net.ssl.trustStore` and `javax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword`, defaults to false.
(3)Elasticsearch Storage配置
-
* `ES_CLUSTER`: The name of the elasticsearch cluster to connect to. Defaults to "elasticsearch".
-
* `ES_HOSTS`: A comma separated list of elasticsearch hostnodes to connect to. When in host:port
-
format, they should use the transport port, not the http port. To use http, specify
-
base urls, ex. http://host:9200. Defaults to "localhost:9300". When not using http,
-
Only one of the hosts needs to be available to fetch the remaining nodes in the
-
cluster. It is recommended to set this to all the master nodes of the cluster.
-
-
If the http URL is an AWS-hosted elasticsearch installation (e.g.
-
https://search-domain-xyzzy.us-west-2.es.amazonaws.com) then Zipkin will attempt to
-
use the default AWS credential provider (env variables, system properties, config
-
files, or ec2 profiles) to sign outbound requests to the cluster.
-
* `ES_PIPELINE`: Only valid when the destination is Elasticsearch 5.x. Indicates the ingest
-
pipeline used before spans are indexed. No default.
-
* `ES_MAX_REQUESTS`: Only valid when the transport is http. Sets maximum in-flight requests from
-
this process to any Elasticsearch host. Defaults to 64.
-
* `ES_AWS_DOMAIN`: The name of the AWS-hosted elasticsearch domain to use. Supercedes any set
-
`ES_HOSTS`. Triggers the same request signing behavior as with `ES_HOSTS`, but
-
requires the additional IAM permission to describe the given domain.
-
* `ES_AWS_REGION`: An optional override to the default region lookup to search for the domain
-
given in `ES_AWS_DOMAIN`. Ignored if only `ES_HOSTS` is present.
-
* `ES_INDEX`: The index prefix to use when generating daily index names. Defaults to zipkin.
-
* `ES_DATE_SEPARATOR`: The date separator to use when generating daily index names. Defaults to ‘-‘.
-
* `ES_INDEX_SHARDS`: The number of shards to split the index into. Each shard and its replicas
-
are assigned to a machine in the cluster. Increasing the number of shards
-
and machines in the cluster will improve read and write performance. Number
-
of shards cannot be changed for existing indices, but new daily indices
-
will pick up changes to the setting. Defaults to 5.
三、zipkin环境准备与启动
在本节中,以MySQL为例进行说明,由于目前只是Mysql5.6和5.7进行测试过,所以本次我选择Mysql5.7版本。
(1) 初始化数据库
安装好Mysql5.7后新建zipkin的数据库,然后执行下面的SQL语句新建表:
-
CREATETABLE IF NOT EXISTS zipkin_spans (
-
`trace_id_high` BIGINT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0COMMENT ‘If non zero, this means the trace uses 128 bit traceIds instead of 64bit‘,
-
`trace_id` BIGINT NOT NULL,
-
`id` BIGINT NOT NULL,
-
`name` VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
-
`parent_id` BIGINT,
-
`debug` BIT(1),
-
`start_ts` BIGINT COMMENT ‘Span.timestamp():epoch micros used for endTs query and to implement TTL‘,
-
`duration` BIGINT COMMENT ‘Span.duration():micros used for minDuration and maxDuration query‘
-
)ENGINE=InnoDB ROW_FORMAT=COMPRESSED CHARACTER SET=utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
-
-
ALTERTABLE zipkin_spans ADD UNIQUE KEY(`trace_id_high`, `trace_id`, `id`) COMMENT‘ignore insert on duplicate‘;
-
ALTERTABLE zipkin_spans ADD INDEX(`trace_id_high`, `trace_id`, `id`) COMMENT ‘forjoining with zipkin_annotations‘;
-
ALTERTABLE zipkin_spans ADD INDEX(`trace_id_high`, `trace_id`) COMMENT ‘forgetTracesByIds‘;
-
ALTERTABLE zipkin_spans ADD INDEX(`name`) COMMENT ‘for getTraces and getSpanNames‘;
-
ALTERTABLE zipkin_spans ADD INDEX(`start_ts`) COMMENT ‘for getTraces ordering andrange‘;
-
-
CREATETABLE IF NOT EXISTS zipkin_annotations (
-
`trace_id_high` BIGINT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0COMMENT ‘If non zero, this means the trace uses 128 bit traceIds instead of 64bit‘,
-
`trace_id` BIGINT NOT NULL COMMENT ‘coincideswith zipkin_spans.trace_id‘,
-
`span_id` BIGINT NOT NULL COMMENT ‘coincideswith zipkin_spans.id‘,
-
`a_key` VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL COMMENT‘BinaryAnnotation.key or Annotation.value if type == -1‘,
-
`a_value` BLOB COMMENT‘BinaryAnnotation.value(), which must be smaller than 64KB‘,
-
`a_type` INT NOT NULL COMMENT‘BinaryAnnotation.type() or -1 if Annotation‘,
-
`a_timestamp` BIGINT COMMENT ‘Used toimplement TTL; Annotation.timestamp or zipkin_spans.timestamp‘,
-
`endpoint_ipv4` INT COMMENT ‘Null whenBinary/Annotation.endpoint is null‘,
-
`endpoint_ipv6` BINARY(16) COMMENT ‘Null whenBinary/Annotation.endpoint is null, or no IPv6 address‘,
-
`endpoint_port` SMALLINT COMMENT ‘Null whenBinary/Annotation.endpoint is null‘,
-
`endpoint_service_name` VARCHAR(255) COMMENT‘Null when Binary/Annotation.endpoint is null‘
-
)ENGINE=InnoDB ROW_FORMAT=COMPRESSED CHARACTER SET=utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
-
-
ALTERTABLE zipkin_annotations ADD UNIQUE KEY(`trace_id_high`, `trace_id`, `span_id`,`a_key`, `a_timestamp`) COMMENT ‘Ignore insert on duplicate‘;
-
ALTERTABLE zipkin_annotations ADD INDEX(`trace_id_high`, `trace_id`, `span_id`)COMMENT ‘for joining with zipkin_spans‘;
-
ALTERTABLE zipkin_annotations ADD INDEX(`trace_id_high`, `trace_id`) COMMENT ‘forgetTraces/ByIds‘;
-
ALTERTABLE zipkin_annotations ADD INDEX(`endpoint_service_name`) COMMENT ‘forgetTraces and getServiceNames‘;
-
ALTERTABLE zipkin_annotations ADD INDEX(`a_type`) COMMENT ‘for getTraces‘;
-
ALTERTABLE zipkin_annotations ADD INDEX(`a_key`) COMMENT ‘for getTraces‘;
-
ALTERTABLE zipkin_annotations ADD INDEX(`trace_id`, `span_id`, `a_key`) COMMENT ‘fordependencies job‘;
-
-
CREATETABLE IF NOT EXISTS zipkin_dependencies (
-
`day` DATE NOT NULL,
-
`parent` VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
-
`child` VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
-
`call_count` BIGINT
-
)ENGINE=InnoDB ROW_FORMAT=COMPRESSED CHARACTER SET=utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
-
-
ALTERTABLE zipkin_dependencies ADD UNIQUE KEY(`day`, `parent`, `child`);
(2) 启动实例
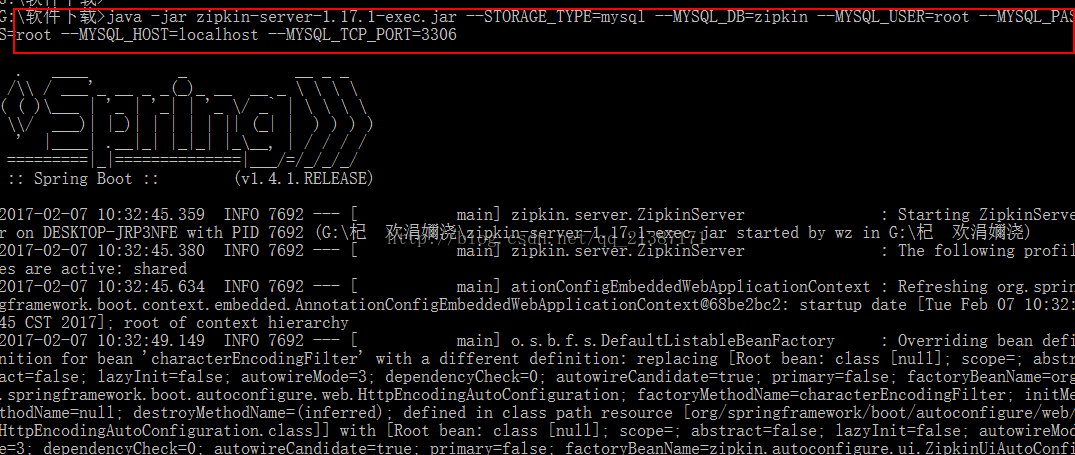
执行命令:java -jar zipkin-server-1.17.1-exec.jar --STORAGE_TYPE=mysql--MYSQL_DB=zipkin --MYSQL_USER=root --MYSQL_PASS=root --MYSQL_HOST=localhost--MYSQL_TCP_PORT=3306,启动成功如下图所示:
(3) 查看运行效果
通过上图,我们发现zipkin使用springboot,并且启动的端口为9411,然后我们通过浏览器访问,效果如下:
四、分布式跟踪系统实践(springboot+zipkin+mysql)
4.1场景设置与分析
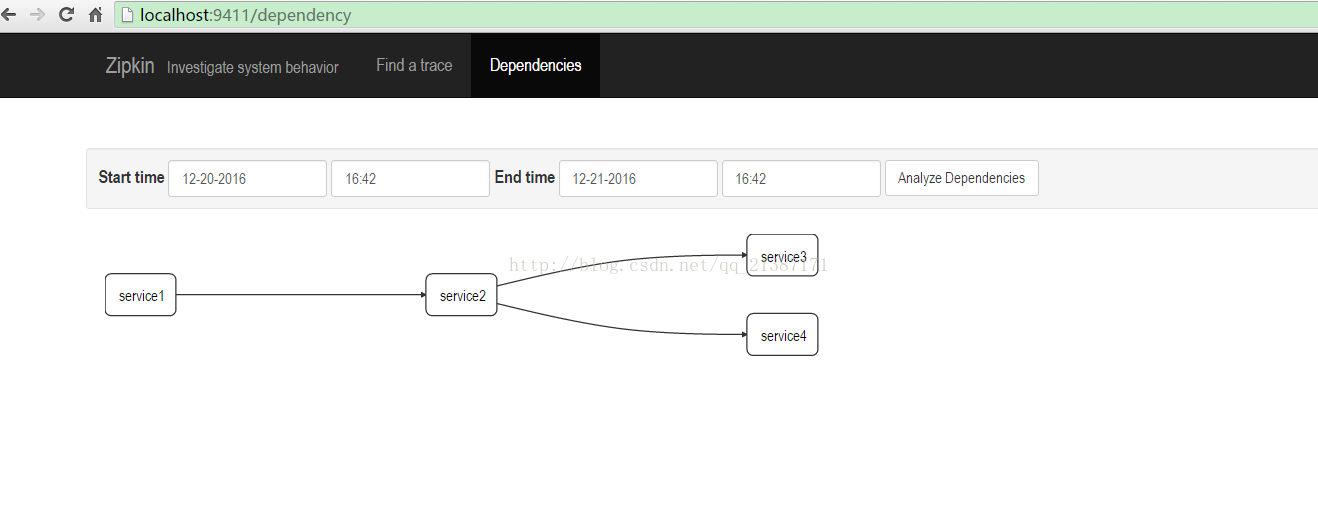
现在有一个服务A调用服务B,服务B又分别调用服务C和D,整个链路过程的关系图如下所示:
4.2 代码编写
具体代码和上一节代码相同,源代码下载地址:https://github.com/dreamerkr/mircoservice.git文件夹springboot+zipkin下面。
4.3运行效果
(1)分别启动每个服务,然后访问服务1,浏览器访问(http://localhost:8081/service1/test)
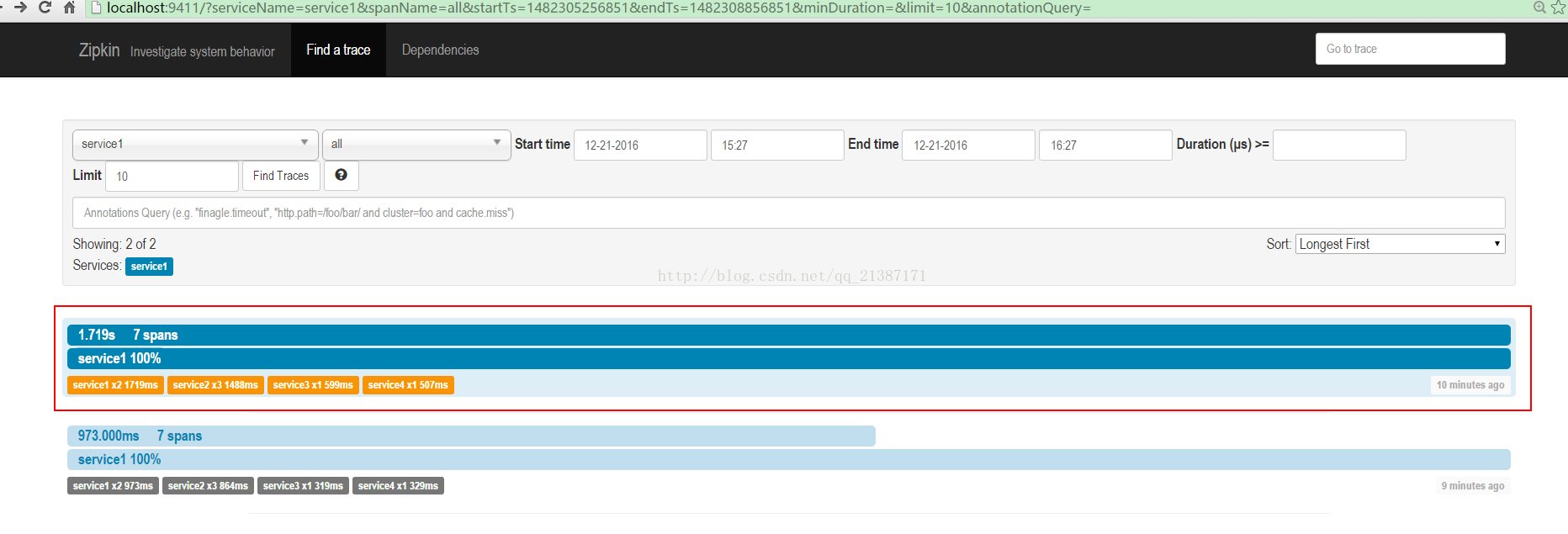
(2)输入zipkin地址,每次trace的列表
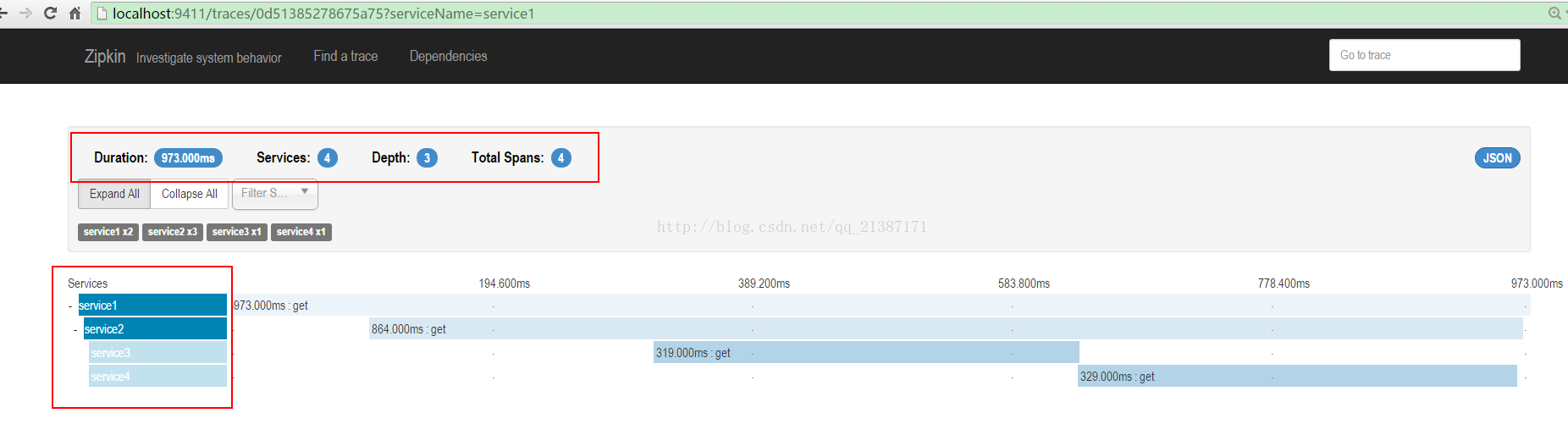
点击其中的trace,可以看trace的树形结构,包括每个服务所消耗的时间:
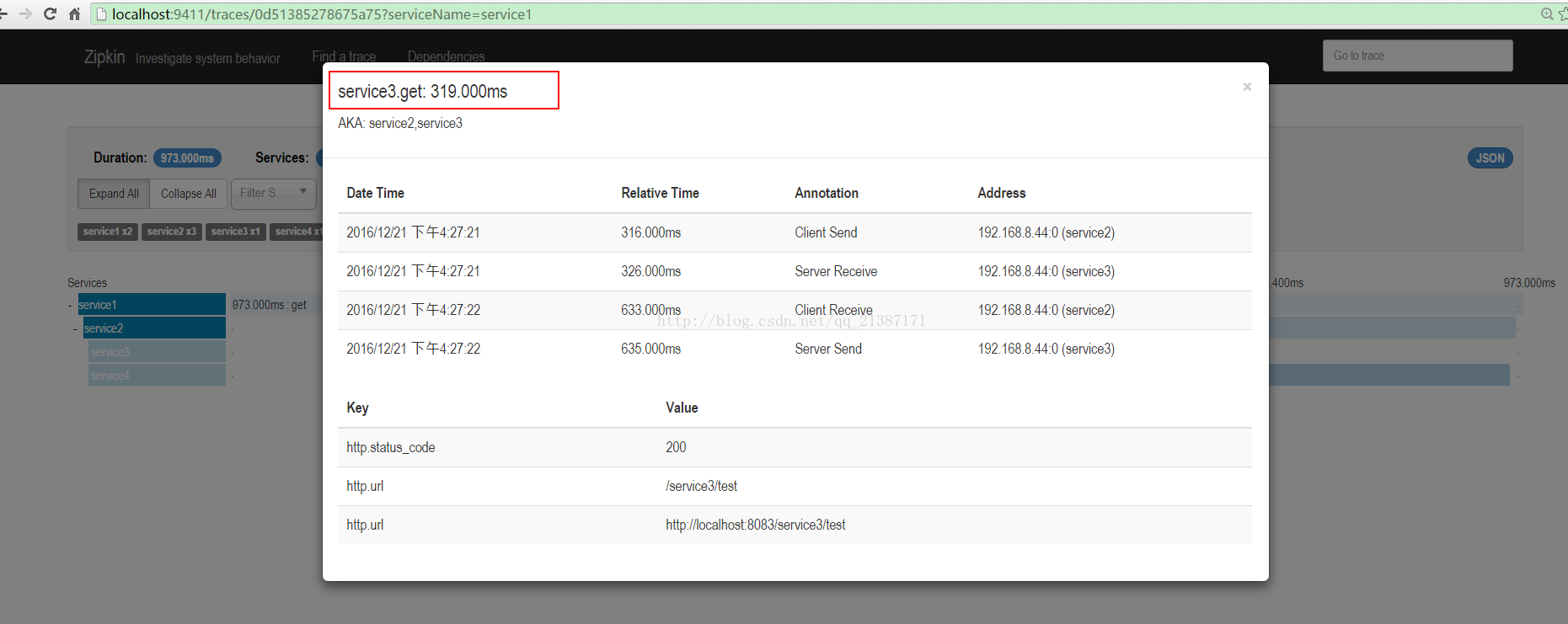
点击每个span可以获取延迟信息:
同时可以查看服务之间的依赖关系:
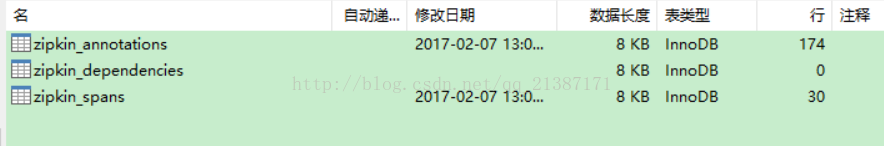
同时查看zipkin数据库表已经存在数据:
以上是关于Zipkin简介的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章