技术实践丨体验量子神经网络在自然语言处理中的应用
Posted 华为云开发者社区
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了技术实践丨体验量子神经网络在自然语言处理中的应用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
本文分享自华为云社区《体验量子神经网络在自然语言处理中的应用》,原文作者:JeffDing。
本文从零带你体验量子神经网络在自然语言处理中的应用。
一、运行环境
CPU:Intel(R) Core(TM)i7-4712MQ CPU @ 2.30GHz
内存:4GB
操作系统:Ubuntu 20.10
MindSpore 版本:1.2
二、安装 Mindspore
参考官网安装文档:
www.mindspore.cn/install/
安装 MindQuantum 参照文档:
gitee.com/mindspore/m…
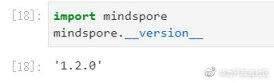
通过 Mindspore.__version__查看版本
三、体验量子神经网络在自然语言处理中的应用
1.环境准备
#引入包
import numpy as np
import time
from projectq.ops import QubitOperator
import mindspore.ops as ops
import mindspore.dataset as ds
from mindspore import nn
from mindspore.train.callback import LossMonitor
from mindspore import Model
from mindquantum.nn import MindQuantumLayer
from mindquantum import Hamiltonian, Circuit, RX, RY, X, H, UN
#数据预处理
def GenerateWordDictAndSample(corpus, window=2):
all_words = corpus.split()
word_set = list(set(all_words))
word_set.sort()
word_dict = {w: i for i,w in enumerate(word_set)}
sampling = []
for index, word in enumerate(all_words[window:-window]):
around = []
for i in range(index, index + 2*window + 1):
if i != index + window:
around.append(all_words)
sampling.append([around,all_words[index + window]])
return word_dict, sampling
word_dict, sample = GenerateWordDictAndSample("I love natural language processing")
print(word_dict)
print(\'word dict size: \', len(word_dict))
print(\'samples: \', sample)
print(\'number of samples: \', len(sample))运行结果:
[NOTE] Current simulator thread is 1. Ifyour simulation is slow, set OMP_NUM_THREADS to a appropriate number accrodingto your model.{\'I\': 0, \'language\': 1, \'love\': 2, \'natural\': 3, \'processing\': 4}word dict size: 5samples: [[[\'I\', \'love\', \'language\', \'processing\'], \'natural\']]number of samples: 1
根据如上信息,我们得到该句子的词典大小为 5,能够产生一个样本点。
2.编码线路
def Genera**coderCircuit(n_qubits, prefix=\'\'):
if len(prefix) != 0 and prefix[-1] != \'_\':
prefix += \'_\'
circ = Circuit()
for i in range(n_qubits):
circ += RX(prefix + str(i)).on(i)
return circ
Genera**coderCircuit(3,prefix=\'e\')运行结果:
RX(e_0|0)RX(e_1|1)RX(e_2|2)
我们通常用|0⟩">|0⟩|0⟩和|1⟩">|1⟩|1⟩来标记二能级量子比特的两个状态,由态叠加原理,量子比特还可以处于这两个状态的叠加态:
|ψ⟩=α|0⟩+β|1⟩">|ψ⟩=α|0⟩+β|1⟩|ψ⟩=α|0⟩+β|1⟩
对于 n">nn 比特的量子态,其将处于 2n">2n2n 维的希尔伯特空间中。对于上面由 5 个词构成的词典,我们只需要⌈log25⌉=3">⌈log25⌉=3⌈log25⌉=3 个量子比特即可完成编码,这也体现出量子计算的优越性。
例如对于上面词典中的“love”,其对应的标签为 2,2 的二进制表示为 010,我们只需将编码线路中的 e_0、e_1 和 e_2 分别设为 0">00、π">ππ和 0">00 即可。
#通过Evolution算子来验证
from mindquantum.nn import generate_evolution_operator
from mindspore import context
from mindspore import Tensor
n_qubits = 3 # number of qubits of this quantum circuit
label = 2 # label need to encode
label_bin = bin(label)[-1:1:-1].ljust(n_qubits,\'0\') # binary form of label
label_array = np.array([int(i)*np.pi for i in label_bin]).astype(np.float32) # parameter value of encoder
encoder = Genera**coderCircuit(n_qubits, prefix=\'e\') # encoder circuit
encoder_para_names = encoder.parameter_resolver().para_name # parameter names of encoder
print("Label is: ", label)
print("Binary label is: ", label_bin)
print("Parameters of encoder is: \\n", np.round(label_array, 5))
print("Encoder circuit is: \\n", encoder)
print("Encoder parameter names are: \\n", encoder_para_names)
context.set_context(mode=context.GRAPH_MODE, device_target="CPU")
# quantum state evolution operator
evol = generate_evolution_operator(param_names=encoder_para_names, circuit=encoder)
state = evol(Tensor(label_array))
state = state.asnumpy()
quantum_state = state[:, 0] + 1j * state[:, 1]
amp = np.round(np.abs(quantum_state)**2, 3)
print("Amplitude of quantum state is: \\n", amp)
print("Label in quantum state is: ", np.argmax(amp))运行结果:
Label is: 2Binary label is: 010Parameters of encoder is: [0. 3.14159 0. ]Encoder circuit is: RX(e_0|0)RX(e_1|1)RX(e_2|2)Encoder parameter names are: [\'e_0\', \'e_1\', \'e_2\']Amplitude of quantum state is: [0. 0. 1. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]Label in quantum state is: 2
通过上面的验证,我们发现,对于标签为 2 的数据,最后得到量子态的振幅最大的位置也是 2,因此得到的量子态正是对输入标签的编码。我们将对数据编码生成参数数值的过程总结成如下函数。
def GenerateTrainData(sample, word_dict):
n_qubits = np.int(np.ceil(np.log2(1 + max(word_dict.values()))))
data_x = []
data_y = []
for around, center in sample:
data_x.append([])
for word in around:
label = word_dict[word]
label_bin = bin(label)[-1:1:-1].ljust(n_qubits,\'0\')
label_array = [int(i)*np.pi for i in label_bin]
data_x[-1].extend(label_array)
data_y.append(word_dict[center])
return np.array(data_x).astype(np.float32), np.array(data_y).astype(np.int32)
GenerateTrainData(sample, word_dict)运行结果:
(array([[0. , 0. , 0. , 0. , 3.1415927, 0. , 3.1415927, 0. , 0. , 0. , 0. ,3.1415927]], dtype=float32), array([3], dtype=int32))
根据上面的结果,我们将 4 个输入的词编码的信息合并为一个更长向量,便于后续神经网络调用。
3.Ansatz 线路
#定义如下函数生成Ansatz线路
def GenerateAnsatzCircuit(n_qubits, layers, prefix=\'\'):
if len(prefix) != 0 and prefix[-1] != \'_\':
prefix += \'_\'
circ = Circuit()
for l in range(layers):
for i in range(n_qubits):
circ += RY(prefix + str(l) + \'_\' + str(i)).on(i)
for i in range(l % 2, n_qubits, 2):
if i < n_qubits and i + 1 < n_qubits:
circ += X.on(i + 1, i)
return circ
GenerateAnsatzCircuit(5, 2, \'a\')运行结果:
RY(a_0_0|0)RY(a_0_1|1)RY(a_0_2|2)RY(a_0_3|3)RY(a_0_4|4)X(1 <-: 0)X(3 <-: 2)RY(a_1_0|0)RY(a_1_1|1)RY(a_1_2|2)RY(a_1_3|3)RY(a_1_4|4)X(2 <-: 1)X(4 <-: 3)
4.测量
def GenerateEmbeddingHamiltonian(dims, n_qubits):
hams = []
for i in range(dims):
s = \'\'
for j, k in enumerate(bin(i + 1)[-1:1:-1]):
if k == \'1\':
s = s + \'Z\' + str(j) + \' \'
hams.append(Hamiltonian(QubitOperator(s)))
return hams
GenerateEmbeddingHamiltonian(5, 5)运行结果:
[1.0 Z0, 1.0 Z1,1.0 Z0 Z1, 1.0 Z2, 1.0 Z0 Z2]
5.量子版词向量嵌入层
运行之前请在终端运行 export OMP_NUM_THREADS=4
def QEmbedding(num_embedding, embedding_dim, window, layers, n_threads):
n_qubits = int(np.ceil(np.log2(num_embedding)))
hams = GenerateEmbeddingHamiltonian(embedding_dim, n_qubits)
circ = Circuit()
circ = UN(H, n_qubits)
encoder_param_name = []
ansatz_param_name = []
for w in range(2 * window):
encoder = Genera**coderCircuit(n_qubits, \'Encoder_\' + str(w))
ansatz = GenerateAnsatzCircuit(n_qubits, layers, \'Ansatz_\' + str(w))
encoder.no_grad()
circ += encoder
circ += ansatz
encoder_param_name.extend(list(encoder.parameter_resolver()))
ansatz_param_name.extend(list(ansatz.parameter_resolver()))
net = MindQuantumLayer(encoder_param_name,
ansatz_param_name,
circ,
hams,
n_threads=n_threads)
return net
class CBOW(nn.Cell):
def __init__(self, num_embedding, embedding_dim, window, layers, n_threads,
hidden_dim):
super(CBOW, self).__init__()
self.embedding = QEmbedding(num_embedding, embedding_dim, window,
layers, n_threads)
self.dense1 = nn.Dense(embedding_dim, hidden_dim)
self.dense2 = nn.Dense(hidden_dim, num_embedding)
self.relu = ops.ReLU()
def construct(self, x):
embed = self.embedding(x)
out = self.dense1(embed)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.dense2(out)
return out
class LossMonitorWithCollection(LossMonitor):
def __init__(self, per_print_times=1):
super(LossMonitorWithCollection, self).__init__(per_print_times)
self.loss = []
def begin(self, run_context):
self.begin_time = time.time()
def end(self, run_context):
self.end_time = time.time()
print(\'Total time used: {}\'.format(self.end_time - self.begin_time))
def epoch_begin(self, run_context):
self.epoch_begin_time = time.time()
def epoch_end(self, run_context):
cb_params = run_context.original_args()
self.epoch_end_time = time.time()
if self._per_print_times != 0 and cb_params.cur_step_num % self._per_print_times == 0:
print(\'\')
def step_end(self, run_context):
cb_params = run_context.original_args()
loss = cb_params.net_outputs
if isinstance(loss, (tuple, list)):
if isinstance(loss[0], Tensor) and isinstance(loss[0].asnumpy(), np.ndarray):
loss = loss[0]
if isinstance(loss, Tensor) and isinstance(loss.asnumpy(), np.ndarray):
loss = np.mean(loss.asnumpy())
cur_step_in_epoch = (cb_params.cur_step_num - 1) % cb_params.batch_num + 1
if isinstance(loss, float) and (np.isnan(loss) or np.isinf(loss)):
raise ValueError("epoch: {} step: {}. Invalid loss, terminating training.".format(
cb_params.cur_epoch_num, cur_step_in_epoch))
self.loss.append(loss)
if self._per_print_times != 0 and cb_params.cur_step_num % self._per_print_times == 0:
print("\\repoch: %+3s step: %+3s time: %5.5s, loss is %5.5s" % (cb_params.cur_epoch_num, cur_step_in_epoch, time.time() - self.epoch_begin_time, loss), flush=True, end=\'\')
import mindspore as ms
from mindspore import context
from mindspore import Tensor
context.set_context(mode=context.GRAPH_MODE, device_target="CPU")
corpus = """We are about to study the idea of a computational process.
Computational processes are abstract beings that inhabit computers.
As they evolve, processes manipulate other abstract things called data.
The evolution of a process is directed by a pattern of rules
called a program. People create programs to direct processes. In effect,
we conjure the spirits of the computer with our spells."""
ms.set_seed(42)
window_size = 2
embedding_dim = 10
hidden_dim = 128
word_dict, sample = GenerateWordDictAndSample(corpus, window=window_size)
train_x,train_y = GenerateTrainData(sample, word_dict)
train_loader = ds.NumpySlicesDataset({
"around": train_x,
"center": train_y
},shuffle=False).batch(3)
net = CBOW(len(word_dict), embedding_dim, window_size, 3, 4, hidden_dim)
net_loss = nn.SoftmaxCrossEntropyWithLogits(sparse=True, reduction=\'mean\')
net_opt = nn.Momentum(net.trainable_params(), 0.01, 0.9)
loss_monitor = LossMonitorWithCollection(500)
model = Model(net, net_loss, net_opt)
model.train(350, train_loader, callbacks=[loss_monitor], dataset_sink_mode=False)运行结果:
epoch: 25step: 20 time: 36.14, loss is 3.154epoch: 50 step: 20 time: 36.51, loss is 2.945epoch: 75 step: 20 time: 36.71, loss is 0.226epoch: 100 step: 20 time: 36.56, loss is 0.016Total time used: 3668.7517251968384
打印收敛过程中的损失函数值:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(loss_monitor.loss,\'.\')
plt.xlabel(\'Steps\')
plt.ylabel(\'Loss\')
plt.show()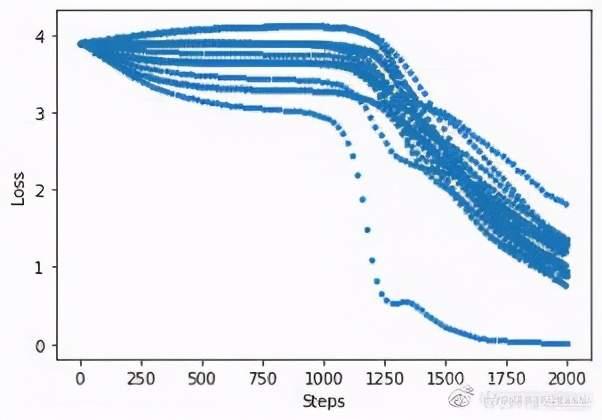
打印量子嵌入层的量子线路中的参数
net.embedding.weight.asnumpy()array([-6.4384632e-02,-1.2658586e-01, 1.0083634e-01, -1.3011757e-01, 1.4005195e-03, -1.9296107e-04, -7.9315618e-02,-2.9339856e-01, 7.6259784e-02, 2.9878360e-01, -1.3091319e-04, 6.8271365e-03, -8.5563213e-02, -2.4168481e-01, -8.2548901e-02, 3.0743122e-01, -7.8157615e-04, -3.2907310e-03, -1.4412615e-01,-1.9241245e-01, -7.5561814e-02, -3.1189525e-03, 3.8330450e-03,-1.4486053e-04, -4.8195502e-01, 5.3657538e-01, 3.8986996e-02, 1.7286544e-01, -3.4090234e-03, -9.5573599e-03, -4.8208281e-01, 5.9604627e-01, -9.7009525e-02, 1.8312852e-01, 9.5267012e-04, -1.2261710e-03, 3.4219343e-02, 8.0031365e-02, -4.5349425e-01, 3.7360430e-01, 8.9665735e-03, 2.1575980e-03, -2.3871836e-01,-2.4819574e-01, -6.2781256e-01, 4.3640310e-01, -9.7688911e-03,-3.9542126e-03, -2.4010721e-01, 4.8120108e-02, -5.6876510e-01, 4.3773583e-01, 4.7241263e-03, 1.4138421e-02, -1.2472854e-03, 1.1096644e-01, 7.1980711e-03, 7.3047012e-02, 2.0803964e-02, 1.1490706e-02, 8.6638138e-02, 2.0503466e-01, 4.7177267e-03, -1.8399477e-02, 1.1631225e-02, 2.0587114e-03, 7.6739892e-02, -6.3548386e-02, 1.7298019e-01, -1.9143591e-02, 4.1606693e-04,-9.2881303e-03], dtype=float32)
6.经典版词向量嵌入层
class CBOWClassical(nn.Cell):
def __init__(self, num_embedding, embedding_dim, window, hidden_dim):
super(CBOWClassical, self).__init__()
self.dim = 2 * window * embedding_dim
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(num_embedding, embedding_dim, True)
self.dense1 = nn.Dense(self.dim, hidden_dim)
self.dense2 = nn.Dense(hidden_dim, num_embedding)
self.relu = ops.ReLU()
self.reshape = ops.Reshape()
def construct(self, x):
embed = self.embedding(x)
embed = self.reshape(embed, (-1, self.dim))
out = self.dense1(embed)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.dense2(out)
return out
train_x = []
train_y = []
for i in sample:
around, center = i
train_y.append(word_dict[center])
train_x.append([])
for j in around:
train_x[-1].append(word_dict[j])
train_x = np.array(train_x).astype(np.int32)
train_y = np.array(train_y).astype(np.int32)
print("train_x shape: ", train_x.shape)
print("train_y shape: ", train_y.shape)
train_loader = ds.NumpySlicesDataset({
"around": train_x,
"center": train_y
},shuffle=False).batch(3)
net = CBOWClassical(len(word_dict), embedding_dim, window_size, hidden_dim)
net_loss = nn.SoftmaxCrossEntropyWithLogits(sparse=True, reduction=\'mean\')
net_opt = nn.Momentum(net.trainable_params(), 0.01, 0.9)
loss_monitor = LossMonitorWithCollection(500)
model = Model(net, net_loss, net_opt)
model.train(350, train_loader, callbacks=[loss_monitor], dataset_sink_mode=False)运行结果:
train_x shape: (58, 4)train_y shape: (58,)epoch: 25 step: 20 time: 0.077, loss is 3.156epoch: 50 step: 20 time: 0.095, loss is 3.025epoch: 75 step: 20 time: 0.115, loss is 2.996epoch: 100 step: 20 time: 0.088, loss is 1.773epoch: 125 step: 20 time: 0.083, loss is 0.172epoch: 150 step: 20 time: 0.110, loss is 0.008epoch: 175 step: 20 time: 0.086, loss is 0.003epoch: 200 step: 20 time: 0.081, loss is 0.001epoch: 225 step: 20 time: 0.081, loss is 0.000epoch: 250 step: 20 time: 0.078, loss is 0.000epoch: 275 step: 20 time: 0.079, loss is 0.000epoch: 300 step: 20 time: 0.080, loss is 0.000epoch: 325 step: 20 time: 0.078, loss is 0.000epoch: 350 step: 20 time: 0.081, loss is 0.000Total time used: 30.569124698638916
收敛图:
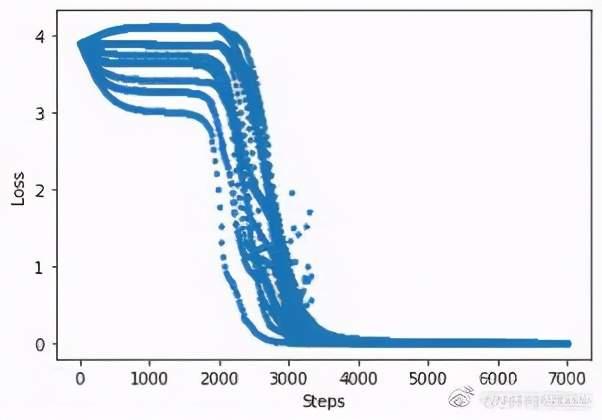
由上可知,通过量子模拟得到的量子版词嵌入模型也能很好的完成嵌入任务。当数据集大到经典计算机算力难以承受时,量子计算机将能够轻松处理这类问题。
以上是关于技术实践丨体验量子神经网络在自然语言处理中的应用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章