mybatis源码配置文件解析之五:解析mappers标签
Posted 迷茫中守候
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了mybatis源码配置文件解析之五:解析mappers标签相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
在上篇博客中分析了plugins标签,《mybatis源码配置文件解析之四:解析plugins标签 》,了解了其使用方式及背后的原理。现在来分析<mappers>标签。
一、概述
在mybatis的核心配置文件(mybatis-config.xml)中,有关mappers的配置如下,
<mappers> <!-- <mapper resource="cn/com/mybatis/dao/UserMapper.xml"/> <mapper resource="cn/com/mybatis/dao/MenuMapper.xml"/> --> <!--第二种做法 --> <package name="cn.com.mybatis.dao" /> </mappers>
从上面的配置文件,可以看到配置mappers文件有两种方式,一种是配置mapper标签,另一种是配置package标签。从配置的内容上来看,其配置的方式也是存在差别,配置mapper标签配置的是一个xml文件,该文件中存在相关的sql语句;配置package标签配置的是一个包的权限路径(在spring和mybatis结合的时候使用了此种方式),该包表示的是mapper的接口文件。
最终上面的两种方式都会被解析到mybatis的configuration类中,供用户使用。如果存在重复配置mybatis会如何处理,下面在分析过程中会解答该问题。
二、详述
上面了解了<mappers>标签的使用方式,下面看mybatis是如何解析该标签的。
在XMLConfigBuilder类中的parseConfiguration方法
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) { try { //issue #117 read properties first //解析properties标签 propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties")); //解析settings标签,1、把<setting>标签解析为Properties对象 Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings")); /*2、对<settings>标签中的<setting>标签中的内容进行解析,这里解析的是<setting name="vfsImpl" value=","> * VFS是mybatis中用来表示虚拟文件系统的一个抽象类,用来查找指定路径下的资源。上面的key为vfsImpl的value可以是VFS的具体实现,必须 * 是权限类名,多个使用逗号隔开,如果存在则设置到configuration中的vfsImpl属性中,如果存在多个,则设置到configuration中的仅是最后一个 * */ loadCustomVfs(settings); //解析别名标签,例<typeAlias alias="user" type="cn.com.bean.User"/> typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases")); //解析插件标签 pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins")); //解析objectFactory标签,此标签的作用是mybatis每次创建结果对象的新实例时都会使用ObjectFactory,如果不设置 //则默认使用DefaultObjectFactory来创建,设置之后使用设置的 objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory")); //解析objectWrapperFactory标签 objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory")); //解析reflectorFactory标签 reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory")); settingsElement(settings); // read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631 //解析environments标签 environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments")); databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider")); typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers")); //解析<mappers>标签 mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers")); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e); } }
在该方法的最下方,看下面这行代码
//解析<mappers>标签 mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
上面这行代码便是解析mappers标签的方法的调用。看其方法定义,
/** * 解析<mappers>标签,在此标签中可以配置<mapper>和<package>两种标签,其中<mapper>标签可以配置resource、url、class三种属性, * 这里的三种属性,仅可以同时出现一个;<package>标签只需要配置包名即可。 * @param parent * @throws Exception */ private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception { if (parent != null) { for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) { //1、解析package标签,获得name属性即包名 if ("package".equals(child.getName())) { String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name"); //扫描包名,把 configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage); } else {//2、解析<mapper>标签,标签中可以配置resource、url、class三个属性,但只能配置其中一个。 String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource"); String url = child.getStringAttribute("url"); String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class"); if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) { ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource); InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments()); /** * 处理mapper文件和对应的接口 */ mapperParser.parse(); } else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) { ErrorContext.instance().resource(url); InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url); XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments()); mapperParser.parse(); } else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) { Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass); configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface); } else { throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one."); } } } } }
通过上面代码的分析及在配置文件中的配置,解析<mappers>标签分为两部分,分别解析package和mapper子标签。且是循环解析,也就是在含义多个包的时候需要配置多个package子标签。
1、解析package子标签
从上面的方法也就是mapperElement方法中,可以知道在解析<mappers>标签时首先解析的是package子标签,也就是说在同时配置package和mapper子标签时,先解析的是package子标签,解析标签是有顺序的。下面解析package子标签的过程,仅给出和解析package有关的代码,
//1、解析package标签,获得name属性即包名 if ("package".equals(child.getName())) { String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name"); //扫描包名,把 configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage); }
上面的代码,解析出package子标签中的包名,调用了configuration.addMappers方法,
public void addMappers(String packageName) { mapperRegistry.addMappers(packageName); }
调用了mapperRegistry.addMappers方法,
/** * @since 3.2.2 */ public void addMappers(String packageName) { addMappers(packageName, Object.class); }
下面看addMappers方法,
public void addMappers(String packageName, Class<?> superType) { //解析packageName下的class文件 ResolverUtil<Class<?>> resolverUtil = new ResolverUtil<Class<?>>(); resolverUtil.find(new ResolverUtil.IsA(superType), packageName); Set<Class<? extends Class<?>>> mapperSet = resolverUtil.getClasses(); //处理解析好的mapper接口文件 for (Class<?> mapperClass : mapperSet) { addMapper(mapperClass); } }
上面的方法首先会解析指定包下的class文件,看下面的解析过程,
resolverUtil.find(new ResolverUtil.IsA(superType), packageName);
看find方法,
public ResolverUtil<T> find(Test test, String packageName) { //把包名中的“.”替换成“/” String path = getPackagePath(packageName); try { //获得包路径下的所有文件名称 List<String> children = VFS.getInstance().list(path); for (String child : children) { if (child.endsWith(".class")) { addIfMatching(test, child); } } } catch (IOException ioe) { log.error("Could not read package: " + packageName, ioe); } return this; }
遍历包下的所有class文件,调用addIfMatching方法,
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected void addIfMatching(Test test, String fqn) {
try {
String externalName = fqn.substring(0, fqn.indexOf(\'.\')).replace(\'/\', \'.\');
ClassLoader loader = getClassLoader();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Checking to see if class " + externalName + " matches criteria [" + test + "]");
}
Class<?> type = loader.loadClass(externalName);
if (test.matches(type)) {
matches.add((Class<T>) type);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.warn("Could not examine class \'" + fqn + "\'" + " due to a " +
t.getClass().getName() + " with message: " + t.getMessage());
}
}
加载class文件,判断是否符合test.matches,该方法如下,
/** Returns true if type is assignable to the parent type supplied in the constructor. */ @Override public boolean matches(Class<?> type) { return type != null && parent.isAssignableFrom(type); }
如果符合条件则放入matches中,matches定义在ResolverUtil中。回到addMappers方法中,find方法结束后调用下面的方法,获取matches中的值,
Set<Class<? extends Class<?>>> mapperSet = resolverUtil.getClasses();
然后循环解析mapperSet,
//处理解析好的mapper接口文件 for (Class<?> mapperClass : mapperSet) { addMapper(mapperClass); }
解析过程如下,
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) { if (type.isInterface()) {//判断是否为接口 if (hasMapper(type)) {//如果knownMappers中已经存在该type,则抛出异常 throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry."); } boolean loadCompleted = false; try { //把type放入knownMappers中,其value为一个MapperProxyFactory对象 knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<T>(type)); // It\'s important that the type is added before the parser is run // otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the // mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won\'t try. //对mapper文件进行解析, MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type); //具体的解析过程,1、先解析对应的XML映射文件,2、再解析接口方法中的注解信息 parser.parse(); loadCompleted = true; } finally { if (!loadCompleted) {//如果解析失败,则删除knowMapper中的信息 knownMappers.remove(type); } } } }
把mapper接口类封装为MapperProxyFactory对象,并放入knownMappers中,接着对接口类进行解析,如果解析失败会把刚才放入knownMappers中的值从knownMappers中移除。下面看如何解析接口类(解析对应的XML文件),
public void parse() { String resource = type.toString(); if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) { //解析和接口同名的xml文件,前提是存在该文件,如果不存在该文件要怎么解析那?答案是解析接口中方法上的注解 /** * 解析和接口同名的xml配置文件,最终要做的是把xml文件中的标签,转化为mapperStatement, * 并放入mappedStatements中 * */ loadXmlResource(); configuration.addLoadedResource(resource); assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName()); //解析接口上的@CacheNamespace注解 parseCache(); parseCacheRef(); //获得接口中的所有方法,并解析方法上的注解 Method[] methods = type.getMethods(); for (Method method : methods) { try { // issue #237 if (!method.isBridge()) { //解析方法上的注解 parseStatement(method); } } catch (IncompleteElementException e) { configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method)); } } } parsePendingMethods(); }
上面的解析分为两个过程,首先解析对应的XML映射文件,再解析方法上的注解。
1.1、解析xml文件
下面看如何继续对应的XML文件,
loadXmlResource();
看如何解析xml文件,
private void loadXmlResource() { // Spring may not know the real resource name so we check a flag // to prevent loading again a resource twice // this flag is set at XMLMapperBuilder#bindMapperForNamespace if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded("namespace:" + type.getName())) { //解析对应的XML映射文件,其名称为接口类+"."+xml,即和接口类同名且在同一个包下。 String xmlResource = type.getName().replace(\'.\', \'/\') + ".xml"; InputStream inputStream = null; try { inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(type.getClassLoader(), xmlResource); } catch (IOException e) { // ignore, resource is not required } if (inputStream != null) { XMLMapperBuilder xmlParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, assistant.getConfiguration(), xmlResource, configuration.getSqlFragments(), type.getName()); //解析xml映射文件 xmlParser.parse(); } } }
首先确定XML映射文件的位置,和接口类同名且在同一个包下。如下的例子,
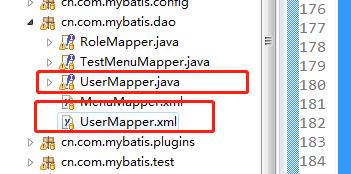
确定好对应的映射文件位置,接着便是解析该xml文件,
if (inputStream != null) { XMLMapperBuilder xmlParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, assistant.getConfiguration(), xmlResource, configuration.getSqlFragments(), type.getName()); //解析xml映射文件 xmlParser.parse(); }
解析过程如下,
public void parse() { if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) { //解析mapper文件中的<mapper>标签及其子标签 configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper")); configuration.addLoadedResource(resource); bindMapperForNamespace(); } parsePendingResultMaps(); parsePendingCacheRefs(); parsePendingStatements(); }
解析的过程在解析<mapper>标签的时候再详细分析。解析的最终结果是把XML中的select|update|delete|insert标签转化为MappedStatement对象,放入configuration中。
1.2、解析接口中方法上的注解
上面解析了接口对于的XML文件,下面看如何解析接口中的方法,
//获得接口中的所有方法,并解析方法上的注解 Method[] methods = type.getMethods(); for (Method method : methods) { try { // issue #237 if (!method.isBridge()) { //解析方法上的注解 parseStatement(method); } } catch (IncompleteElementException e) { configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method)); }
看parseStatement方法,
void parseStatement(Method method) { Class<?> parameterTypeClass = getParameterType(method); LanguageDriver languageDriver = getLanguageDriver(method); //获得方法上的注解,并生成SqlSource SqlSource sqlSource = getSqlSourceFromAnnotations(method, parameterTypeClass, languageDriver); if (sqlSource != null) { Options options = method.getAnnotation(Options.class); //生成mappedStatementId,为接口的权限类名+方法名。从这里可以得出同一个接口或namespace中不允许有同名的方法名或id final String mappedStatementId = type.getName() + "." + method.getName(); Integer fetchSize = null; Integer timeout = null; StatementType statementType = StatementType.PREPARED; ResultSetType resultSetType = ResultSetType.FORWARD_ONLY; SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = getSqlCommandType(method); boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT; boolean flushCache = !isSelect; boolean useCache = isSelect; KeyGenerator keyGenerator; String keyProperty = "id"; String keyColumn = null; if (SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType) || SqlCommandType.UPDATE.equals(sqlCommandType)) { // first check for SelectKey annotation - that overrides everything else SelectKey selectKey = method.getAnnotation(SelectKey.class); if (selectKey != null) { keyGenerator = handleSelectKeyAnnotation(selectKey, mappedStatementId, getParameterType(method), languageDriver); keyProperty = selectKey.keyProperty(); } else if (options == null) { keyGenerator = configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() ? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE; } else { keyGenerator = options.useGeneratedKeys() ? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE; keyProperty = options.keyProperty(); keyColumn = options.keyColumn(); } } else { keyGenerator = NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE; } if (options != null) { if (FlushCachePolicy.TRUE.equals(options.flushCache())) { flushCache = true; } else if (FlushCachePolicy.FALSE.equals(options.flushCache())) { flushCache = false; } useCache = options.useCache(); fetchSize = options.fetchSize() > -1 || options.fetchSize() == Integer.MIN_VALUE ? options.fetchSize() : null; //issue #348 timeout = options.timeout() > -1 ? options.timeout() : null; statementType = options.statementType(); resultSetType = options.resultSetType(); } String resultMapId = null; ResultMap resultMapAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(ResultMap.class); if (resultMapAnnotation != null) { String[] resultMaps = resultMapAnnotation.value(); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); for (String resultMap : resultMaps) { if (sb.length() > 0) { sb.append(","); } sb.append(resultMap); } resultMapId = sb.toString(); } else if (isSelect) { resultMapId = parseResultMap(method); } assistant.addMappedStatement( mappedStatementId, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType, fetchSize, timeout, // ParameterMapID null, parameterTypeClass, resultMapId, getReturnType(method), resultSetType, flushCache, useCache, // TODO gcode issue #577 false, keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, // DatabaseID null, languageDriver, // ResultSets options != null ? nullOrEmpty(options.resultSets()) : null); } }
从上面的代码,可以看出最终调用了assistant.addMappedStatement方法,该方法会把注解信息封装为MappedStatement对象,放入configuration中。详细过程,后面分析。
2、解析mapper子标签
上面分析了mybatis解析<package>标签的过程,下面看直接解析<mapper>子标签。代码为部分代码
else {//2、解析<mapper>标签,标签中可以配置resource、url、class三个属性,但只能配置其中一个。 String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource"); String url = child.getStringAttribute("url"); String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class"); if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) { ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource); InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments()); /** * 处理mapper文件和对应的接口 */ mapperParser.parse(); } else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) { ErrorContext.instance().resource(url); InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url); XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments()); mapperParser.parse(); } else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) { Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass); configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface); } else { throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one."); } }
前边说过,在<mapper>子标签中可以配置resource、url、class三个属性,但是只能配置其中一个,上面分别对其进行了解析,其解析过程和上面解析<packge>中的过程类似,解析resource和url属性的时候都是把XML映射文件解析为inputSream,然后对文件进行解析;解析class属性的时候和解析<package>的过程一样。
三、总结
本文分析了mybatis解析<mappers>标签的过程,分为解析<package>、<mapper>子标签,其解析过程主要为解析Mapper接口和XML映射文件,其详细过程后面详细分析。
有不当之处,欢迎指正,感谢!
以上是关于mybatis源码配置文件解析之五:解析mappers标签的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
mybatis源码-解析配置文件(四-1)之配置文件Mapper解析(cache)