使用mysql-mmm实现MySQL高可用集群
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了使用mysql-mmm实现MySQL高可用集群相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
背景:之前实现的mysql同步复制功能(见笔者之前文章http://blog.csdn.net/kingofworld/article/details/39210937)仅仅是双机热备功能,还不能做到Mysql链接的自己主动切换。
本配置实现真正的mysql集群。使得在某台机子的mysql应用停止时,能让应用程序自己主动切换到另外一台机子的mysql连接,实现应用的高稳定性。而且使得扩展Mysql服务成为可能。
本配置使用mysql-mmm(master-master Replication Manager for MySQL)组件实现集群功能。
本次演示的配置使用三台机器,架构例如以下:
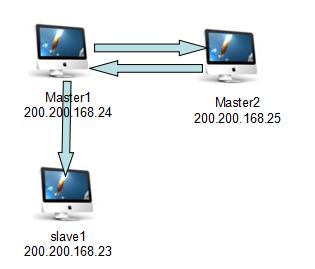
Master1 和Master2两台机器实现双机热备。当中一台机器的mysql服务停止或机器宕机。应用程序都会将数据库连接自己主动切换到另外一台机子。
另外用一台机子实时备份master1的数据。
1、安装mysql-mmm服务
在三台机器都安装
wget http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
rpm -ivh epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
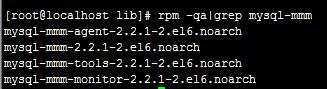
yum -y install mysql-mmm*
完毕后查看 rpm -qa|grep mysql-mmm
有下面组件表示成功安装
Rhel5或centos5,32位:http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/5/i386/epel-release-5-4.noarch.rpm
Rhel6或centos6,32位:http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/i386/epel-release-6-5.noarch.rpm
Rhel6或centos6,64位:http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
1、加入mysql的用户
在三台机器都加入mysql用户。分别用于复制、
进入mysql服务mysql -u root -p
use mysql;
grant REPLICATION slave,REPLICATION CLIENT on *.* to ‘repl‘@‘%‘ identified by ‘password‘; //建立复制用户
grant PROCESS,SUPER,REPLICATION CLIENT on *.* to ‘mmm_agent‘@‘%‘ identified by ‘password‘; //建立agent用户
grant REPLICATION CLIENT on *.* to ‘mmm_monitor‘@‘%‘ identified by ‘password‘; //建立用户
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
2、配置同步复制
配置复制的策略如架构图所看到的。
配置方法在我上一篇文章有介绍过,这里不再反复。见笔者之前文章http://blog.csdn.net/kingofworld/article/details/39210937
3、改动hosts
分别改动三台机器的hosts文件
vi /etc/hosts
加入
200.200.168.24 M1
200.200.168.25 M2
200.200.168.23 slave1
4、配置mysql-mmm
改动 /etc/mysql-mmm/mmm_common.conf 各台机子的配置都一样
active_master_role writer
<host default>
cluster_interface eth0
pid_path /var/run/mysql-mmm/mmm_agentd.pid
bin_path /usr/libexec/mysql-mmm/
replication_user repl
replication_password password
agent_user mmm_agent
agent_password <span style="font-size: 13.3333339691162px;">password</span>
</host>
<host M1>
ip 200.200.168.24
mode master
peer M2
</host>
<host M2>
ip 200.200.168.25
mode master
peer M1
</host>
<host slave1>
ip 200.200.168.23
mode slave
</host>
<role writer>
hosts M1,M2
ips 200.200.168.26
mode exclusive
</role>
<role reader>
hosts M1,M2,slave1
ips 200.200.168.27
mode balanced
</role>
注意:200.200.168.26和200.200.168.27是两个虚拟的IP地址,供应用程序调用,仅仅需用两个没人占用的IP就能够。分别用来提供写和读服务。为以后实现数据库的读写分离(但实现读写分离须要改动应用程序。mysql并不能自己主动识别并切换)。
改动/etc/mysql-mmm/mmm_agent.conf
三台机器分别设置为this M1、this M2、this slave1
改动/etc/mysql-mmm/mmm_mon.conf
仅仅是monitor(200.200.168.24)机子须要配置
include mmm_common.conf
<monitor>
ip 127.0.0.1
pid_path /var/run/mysql-mmm/mmm_mond.pid
bin_path /usr/libexec/mysql-mmm
status_path /var/lib/mysql-mmm/mmm_mond.status
ping_ips 200.200.168.24,200.200.168.25,200.200.168.23
auto_set_online 10
# The kill_host_bin does not exist by default, though the monitor will
# throw a warning about it missing. See the section 5.10 "Kill Host
# Functionality" in the PDF documentation.
#
# kill_host_bin /usr/libexec/mysql-mmm/monitor/kill_host
#
</monitor>
<host default>
monitor_user mmm_monitor
monitor_password password
</host>
debug 0
配置完毕后执行
三台机子都需执行:
/etc/init.d/mysql-mmm-agent start
Monitor机子执行
/etc/init.d/mysql-mmm-monitor start
5、查看服务状态及測试
在monitor机子执行mmm_control show
能够看到下面信息:

表示写server(200.200.168.26)使用的是200.200.168.24
读server(200.200.168.27)使用的是200.200.168.25
查看各个服务的状态:
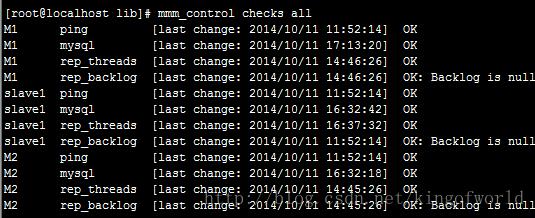
mmm_control checks all

6、測试:
将master1的mysql服务停止。然后mmm_control show查看状态
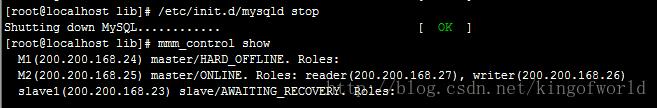
能够看到读写server都转移到了master2,这时servermaster1的流程应用还能够正常使用。能够进行申请流程測试
这时查看mmm_control checks all

将master1 的mysql服务启动,再查看状态:

读写server又分开了
以上是关于使用mysql-mmm实现MySQL高可用集群的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章