Android——自定义View(学习Android开发与艺术探索)
Posted LCY天上殿
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android——自定义View(学习Android开发与艺术探索)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
ViewRoot和DecorView
ViewRoot对应于ViewRootImpl类,是连接WindowManager和DecorView的纽带,View的三大流程均是通过ViewRoot来完成的。在ActivityThread中,当Activity对象被创建完毕后,会将DecorView添加到Window中,同时会创建ViewRootImpl对象,并将ViewRootImpl对象和DecorView建立关联。
View的绘制流程从ViewRoot的performTraversals开始,经过measure、layout和draw三个过程才可以把一个View绘制出来,其中measure用来测量View的宽高,layout用来确定View在父容器中的放置位置,而draw则负责将View绘制到屏幕上。
performTraversals会依次调用performMeasure、performLayout和performDraw三个方法,这三个方法分别完成顶级View的measure、layout和draw这三大流程。其中performMeasure中会调用measure方法,在measure方法中又会调用onMeasure方法,在onMeasure方法中则会对所有子元素进行measure过程,这样就完成了一次measure过程;子元素会重复父容器的measure过程,如此反复完成了整个View数的遍历。另外两个过程类似,大致调用流程如下图:
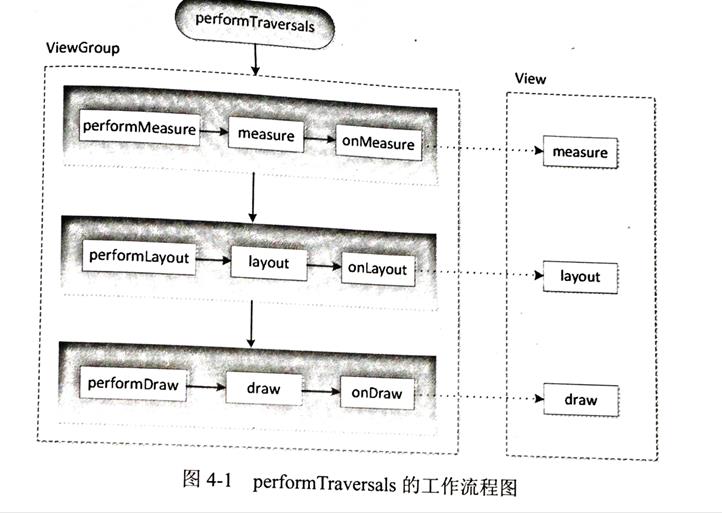
measure过程决定了View的宽/高,完成后可通过getMeasuredWidth/getMeasureHeight方法来获取View测量后的宽/高。Layout过程决定了View的四个顶点的坐标和实际View的宽高,完成后可通过getTop、getBotton、getLeft和getRight拿到View的四个定点坐标。Draw过程决定了View的显示,完成后View的内容才能呈现到屏幕上。
如下图,DecorView作为顶级View,一般情况下它内部包含了一个竖直方向的LinearLayout,里面分为两个部分(具体情况和android版本和主题有关),上面是标题栏,下面是内容栏。在Activity通过setContextView所设置的布局文件其实就是被加载到内容栏之中的。
DecorView其实是一个FrameLayout,View层的事件都先经过DecorView,然后才传给我们的View。

理解MeasureSpec
MeasureSpec很大程度上决定一个View的尺寸规格,测量过程中,系统会将View的layoutParams根据父容器所施加的规则转换成对应的MeasureSpec,再根据这个measureSpec来测量出View的宽/高。
MeasureSpec代表一个32位的int值,高2位为SpecMode,低30位为SpecSize,SpecMode是指测量模式,SpecSize是指在某种测量模式下的规格大小。
MpecMode有三类;
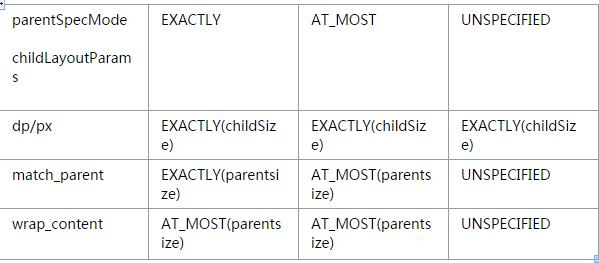
1.UNSPECIFIED 父容器不对View进行任何限制,要多大给多大,一般用于系统内部
2.EXACTLY 父容器检测到View所需要的精确大小,这时候View的最终大小就是SpecSize所指定的值,对应LayoutParams中的match_parent和具体数值这两种模式。
3.AT_MOST 父容器指定了一个可用大小即SpecSize,View的大小不能大于这个值,不同View实现不同,对应LayoutParams中的wrap_content。
当View采用固定宽/高的时候,不管父容器的MeasureSpec的是什么,View的MeasureSpec都是精确模式兵其大小遵循Layoutparams的大小。 当View的宽/高是match_parent时,如果他的父容器的模式是精确模式,那View也是精确模式并且大小是父容器的剩余空间;如果父容器是最大模式,那么View也是最大模式并且起大小不会超过父容器的剩余空间。 当View的宽/高是wrap_content时,不管父容器的模式是精确还是最大化,View的模式总是最大化并且不能超过父容器的剩余空间。
MeasureSpec和LayoutParams的关系
在View测量的时候,系统会将LayoutParams在父容器的约束下转化成对应的MeasureSpec,然后根据这个MeasureSpec来确定View测量后的高/宽
子元素的MeasureSpec主要是根据父容器的MeasureSpec和自身的LayoutParams确定
View的工作流程
1. View的measure过程
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));}setMeasuredDimension方法会设置View的宽/高的测量值
getDefaultSize方法返回的大小就是measureSpec中的specSize,也就是View测量后的大小,绝大部分情况和View的最终大小(layout阶段确定)相同。
getSuggestedMinimumWidth方法,作为getDefaultSize的第一个参数(建议宽度)
直接继承View的自定义控件,需要重写onMeasure方法并且设置
wrap_content时的自身大小,否则在布局中使用了wrap_content相当于使用了match_parent。解决方法:在onMeasure时,给View指定一个内部宽/高,并在wrap_content时设置即可,其他情况沿用系统的测量值即可。
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSpecMode=MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecMode=MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSpecSize=MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecSize=MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
if(widthSpecMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightSpecMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
setMeasuredDimension(mWidth,mHeight);
}else if(widthSpecMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
setMeasuredDimension(mWidth,widthSpecSize);
}else if(heightSpecMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
setMeasuredDimension(heightSpecSize,mHeight);
}
}ViewGroup的measure过程:
对于ViewGroup来说,除了完成自己的measure过程之外,还会遍历去调用所有子元素的measure方法,个个子元素再递归去执行这个过程,和View不同的是,ViewGroup是一个抽象类,没有重写View的onMeasure方法,提供了measureChildren方法。
measureChildren方法,遍历获取子元素,子元素调用measureChild方法
measureChild方法,取出子元素的LayoutParams,再通过getChildMeasureSpec方法来创建子元素的MeasureSpec,接着将MeasureSpec传递给View的measure方法进行测量。
ViewGroup没有定义其测量的具体过程,因为不同的ViewGroup子类有不同的布局特征,所以其测量过程的onMeasure方法需要各个子类去具体实现。
measure完成之后,通过getMeasureWidth/Height方法就可以获取View的测量宽/高,需要注意的是,在某些极端情况下,系统可能要多次measure才能确定最终的测量宽/高,比较好的习惯是在onLayout方法中去获取测量宽/高或者最终宽/高。
如何在Activity中获取View的宽/高信息
因为View的measure过程和Activity的生命周期不是同步进行,如果View还没有测量完毕,那么获取到的宽/高就是0;所以在Activity的onCreate、onStart、onResume中均无法正确的获取到View的宽/高信息。下面给出4种解决方法。
第一种:Activity/View#onWindowFocusChanged。
onWindowFocusChanged这个方法的含义是:VieW已经初始化完毕了,宽高已经准备好了,需要注意:它会被调用多次,当Activity的窗口得到焦点和失去焦点 均会被调用。
第二种:view.post(runnable)。
通过post将一个runnable投递到消息队列的尾部,当Looper调用此runnable的时候,View也初始化好了。
第三种:ViewTreeObserver。
使用ViewTreeObserver的众多回调可以完成这个功能,比如OnGlobalLayoutListener这个接口,当View树的状态发送改变或View树内部的View的可见性发生改变时,onGlobalLayout方法会被回调。需要注意的是,伴随着View树状态的改变,onGlobalLayout会被回调多次。
第四种:view.measure(int widthMeasureSpec,int heightMeasureSpec)。
(1). match_parent:
无法measure出具体的宽高,因为不知道父容器的剩余空间,无法测量出View的大小
(2). 具体的数值(dp/px):
int widthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(100,MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
int heightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(100,MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
view.measure(widthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec);
(3). wrap_content:
int widthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec((1<<30)-1,MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
int heightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec((1<<30)-1,MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
view.measure(widthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec);
2. View的layout过程
在View的默认实现中,View的测量宽/高和最终宽/高是相等的,测量宽/高形成于View的measure过程,而最终宽/高形成于View的layout过程。
3. View的draw过程
将View绘制到屏幕上,大概的几个步骤:
1.绘制背景background.draw(canvas)
2.绘制自己(onDraw)
3.绘制children(dispatchDraw)
4.绘制装饰(onDrawScrollBars)
View的绘制过程是通过dispatchDraw来实现的,它会遍历所有子元素的draw方法。
如果一个View不需要绘制任何内容,那么设置setWillNotDraw为true后,系统会进行相应的优化;ViewGroup默认为true,如果我们的自定义ViewGroup需要通过onDraw来绘制内容的时候,需要显示的关闭它。
自定义View
直接继承View或ViewGroup的控件, 需要在onMeasure中对wrap_content做特殊处理。
直接继承View的控件,如果不在draw方法中处理padding,那么padding属性就无法起作用。直接继承ViewGroup的控件也需要在onMeasure和onLayout中考虑padding和子元素margin的影响,不然padding和子元素的margin无效。
View内部提供了post系列的方法,完全可以替代Handler的作用。
View中有线程和动画,需要在View的onDetachedFromWindow中停止。
两个例子:
继承View重写onDraw方法:
public class CircleView extends View{
private int mColor=Color.RED;
private Paint paint=new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);//抗锯齿
public CircleView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public CircleView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public CircleView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
public CircleView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
TypedArray a=context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,R.styleable.CircleView);//获取自定义属性
mColor=a.getColor(R.styleable.CircleView_circle_color,Color.RED);
a.recycle();
init();
}
private void init(){
paint.setColor(mColor);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {//处理View使其支持wra_content
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSpecMode=MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecMode=MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSpecSize=MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecSize=MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
if(widthSpecMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightSpecMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
setMeasuredDimension(200,200);
}else if(widthSpecMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
setMeasuredDimension(200,widthSpecSize);
}else if(heightSpecMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
setMeasuredDimension(heightSpecSize,200);
}
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
final int paddingLeft=getPaddingLeft();
final int paddingRight=getPaddingRight();
final int paddingTop=getPaddingTop();
final int paddingBottom=getPaddingBottom();
int width=getWidth()-paddingLeft-paddingRight;
int height=getHeight()-paddingBottom-paddingTop;
int radius=Math.min(width,height)/2;
canvas.drawCircle(width/2+paddingLeft,height/2+paddingTop,radius,paint);
}
}继承ViewGroup派生出特殊的Layout
HorizontalScrollView:内部的子元素可以进行水平滑动,子元素中可竖直滑动。
public class HorizontalScrollView extends ViewGroup{
private int mChildrenSize;
private int mChildWidth;
private int mChildIndex;
//分别记录上次滑动的坐标
private int mLastX=0;
private int mLastY=0;
//分别记录上次滑动的坐标(onInterceptTouchEvent)
private int mLastXIntercept=0;
private int mLastYIntercept=0;
private Scroller mScroller;
private VelocityTracker mVelocityTracker;
public HorizontalScrollView(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
public HorizontalScrollView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
public HorizontalScrollView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init();
}
public HorizontalScrollView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
init();
}
private void init(){
if(mScroller==null){
mScroller=new Scroller(getContext());
mVelocityTracker=VelocityTracker.obtain();
}
}
@Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
boolean intercepted=false;
int x= (int) ev.getX();
int y= (int)ev.getY();
switch(ev.getAction()){
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:{
intercepted=false;
if(!mScroller.isFinished()){
mScroller.abortAnimation();
intercepted=true;
}
break;
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:{
int deltaX=x-mLastXIntercept;
int deltaY=y-mLastXIntercept;
if(Math.abs(deltaX)>Math.abs(deltaY)){
intercepted=true;
}else{
intercepted=false;
}
break;
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:{
intercepted=false;
break;
}
default:break;
}
mLastX=x;
mLastY=y;
mLastXIntercept=x;
mLastYIntercept=y;
return intercepted;
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
mVelocityTracker.addMovement(event);
int x= (int) event.getX();
int y= (int)event.getY();
switch(event.getAction()){
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:{
if(!mScroller.isFinished()){
mScroller.abortAnimation();
}
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:{
int deltaX=x-mLastX;
int deltaY=y-mLastY;
scrollBy(-deltaX,0);
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:{
int scrollX=getScrollX();
mVelocityTracker.computeCurrentVelocity(1000);
float xVelocity=mVelocityTracker.getXVelocity();
if(Math.abs(xVelocity)>50){
mChildIndex=xVelocity>0? mChildIndex-1:mChildIndex+1;
}else{
mChildIndex=(scrollX+mChildWidth/2)/mChildWidth;
}
mChildIndex=Math.max(0,Math.min(mChildIndex,mChildIndex-1));
int dx=mChildIndex*mChildWidth-scrollX;
smoothScrollBy(dx,0);
mVelocityTracker.clear();
break;
}
default:break;
}
mLastY=y;
mLastX=x;
return true;
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int measuredWidth=0;
int measuredHeight=0;
final int childCount=getChildCount();
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec,heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSpaceSize=MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSpecMode=MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecSize=MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecMode=MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
if(childCount==0){
setMeasuredDimension(0,0);
}else if(widthSpecMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightSpecMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
final View childView=getChildAt(0);
measuredWidth=childView.getMeasuredWidth()*childCount;
measuredHeight=childView.getMeasuredHeight();
setMeasuredDimension(measuredWidth,measuredHeight);
}else if(widthSpecMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
final View childView=getChildAt(0);
measuredWidth=childView.getMeasuredWidth()*childCount;
setMeasuredDimension(measuredWidth,heightSpecSize);
}else if(heightSpecMode==MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
final View childView=getChildAt(0);
measuredHeight=childView.getMeasuredHeight();
setMeasuredDimension(widthSpaceSize,measuredHeight);
}
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int childLeft=0;
final int childCount=getChildCount();
for(int i=0;i<childCount;i++){
final View view=getChildAt(i);
if(view.getVisibility()!=View.GONE){
final int childWidth=view.getMeasuredWidth();
mChildWidth=childWidth;
view.layout(childLeft,0,childLeft+mChildWidth,getMeasuredHeight());
childLeft+=childWidth;
}
}
}
private void smoothScrollBy(int dx,int dy){
mScroller.startScroll(getScrollX(),0,dx,0,500);
invalidate();
}
@Override
public void computeScroll() {
if(mScroller.computeScrollOffset()){
scrollTo(mScroller.getCurrX(),mScroller.getCurrY());
postInvalidate();
}
}
@Override
protected void onDetachedFromWindow() {
mVelocityTracker.recycle();
super.onDetachedFromWindow();
}
}以上是关于Android——自定义View(学习Android开发与艺术探索)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章