dup/dup2
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了dup/dup2相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
dup函数复制oldfd描述符给一个新的描述符,即这个新的文件描述符指向oldfd所拥有的文件表项。这个新的描述符是未被使用的最小的描述符,dup函数返回这个描述符
dup2函数和dup函数类似,它们的区别就是dup2可以用newfd参数指定新的描述符,如果newfd描述符已经打开,则覆盖;如果newfd等于oldfd,则dup2直接返回newfd.
这两个函数返回的新文件描述符和参数oldfd描述符共享同一文件表项
函数原型:
#include<unistd.h>
int dup(int oldfd);
int dup2(int oldfd, int newfd);
可以这么简单的记忆,这两个函数都使newfd(dup中是返回值)所指向的文件和oldfd所指向的文件一样
下面两个程序都使输出重定向到log文件中
dup
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main()
{
umask(0);
ssize_t fd=open("./log",O_CREAT|O_WRONLY,0644);
//关闭标准输出
close(1);
ssize_t newfd=dup(fd);
close(fd);
int count=0;
while(count++<10){
printf("hello\n");
}
fflush(stdout);
close(1);
return 0;
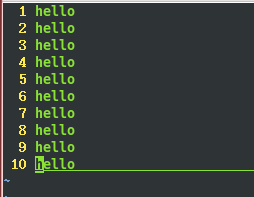
}运行结果会在当前目录下生成一个log文件,并在log文件里写入10条hello
如下图:
dup2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main()
{
umask(0);
ssize_t fd=open("./log",O_CREAT|O_WRONLY,0644);
//关闭标准输出
close(1);
//把标准输出重定向到fd所表示的文件中
dup2(fd,1);
close(fd);
int count=0;
while(count++<10){
printf("hello\n");
}
fflush(stdout);
close(1);
return 0;
}运行结果和上个程序结果相同
《完》
本文出自 “零蛋蛋” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://lingdandan.blog.51cto.com/10697032/1783266
以上是关于dup/dup2的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章