Educational Codeforces Round 41 (Rated for Div. 2) G. Partitions
Posted hit_yjl
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Educational Codeforces Round 41 (Rated for Div. 2) G. Partitions相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
You are given a set of n elements indexed from 1 to n. The weight of i-th element is wi. The weight of some subset of a given set is denoted as 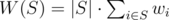 . The weight of some partition R of a given set into k subsets is
. The weight of some partition R of a given set into k subsets is 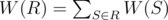 (recall that a partition of a given set is a set of its subsets such that every element of the given set belongs to exactly one subset in partition).
(recall that a partition of a given set is a set of its subsets such that every element of the given set belongs to exactly one subset in partition).
Calculate the sum of weights of all partitions of a given set into exactly k non-empty subsets, and print it modulo 109?+?7. Two partitions are considered different iff there exist two elements x and y such that they belong to the same set in one of the partitions, and to different sets in another partition.
The first line contains two integers n and k (1?≤?k?≤?n?≤?2·105) — the number of elements and the number of subsets in each partition, respectively.
The second line contains n integers wi (1?≤?wi?≤?109)— weights of elements of the set.
Print one integer — the sum of weights of all partitions of a given set into k non-empty subsets, taken modulo 109?+?7.
4 2
2 3 2 3
160
5 2
1 2 3 4 5
645
Possible partitions in the first sample:
- {{1,?2,?3},?{4}}, W(R)?=?3·(w1?+?w2?+?w3)?+?1·w4?=?24;
- {{1,?2,?4},?{3}}, W(R)?=?26;
- {{1,?3,?4},?{2}}, W(R)?=?24;
- {{1,?2},?{3,?4}}, W(R)?=?2·(w1?+?w2)?+?2·(w3?+?w4)?=?20;
- {{1,?3},?{2,?4}}, W(R)?=?20;
- {{1,?4},?{2,?3}}, W(R)?=?20;
- {{1},?{2,?3,?4}}, W(R)?=?26;
Possible partitions in the second sample:
- {{1,?2,?3,?4},?{5}}, W(R)?=?45;
- {{1,?2,?3,?5},?{4}}, W(R)?=?48;
- {{1,?2,?4,?5},?{3}}, W(R)?=?51;
- {{1,?3,?4,?5},?{2}}, W(R)?=?54;
- {{2,?3,?4,?5},?{1}}, W(R)?=?57;
- {{1,?2,?3},?{4,?5}}, W(R)?=?36;
- {{1,?2,?4},?{3,?5}}, W(R)?=?37;
- {{1,?2,?5},?{3,?4}}, W(R)?=?38;
- {{1,?3,?4},?{2,?5}}, W(R)?=?38;
- {{1,?3,?5},?{2,?4}}, W(R)?=?39;
- {{1,?4,?5},?{2,?3}}, W(R)?=?40;
- {{2,?3,?4},?{1,?5}}, W(R)?=?39;
- {{2,?3,?5},?{1,?4}}, W(R)?=?40;
- {{2,?4,?5},?{1,?3}}, W(R)?=?41;
- {{3,?4,?5},?{1,?2}}, W(R)?=?42.
思路一:考虑每个点对整体的贡献。也就是SUM (size * S(n - size, k - 1) )* wi, S(n, k)为第二类斯特林数。但这样需求出所有的S(i, k - 1),暂时不会nlogn求法。复杂度O(n*k)。
思路二:定义g(n, k, i, j)表示n个数分成k个非空集合且i与j在一个集合中的方案数。单独对一个点ai考虑,对于每一个合法的划分,它的贡献要有size次,size为ai所在集合的大小。那么对于SUM(g(n, k, i, j)),其中j从1遍历到n,在这些所有的方案中,我们之前考虑的特定的那个划分也正好出现了size次,两个数刚好等价了。所以答案就是g(n, k, i, i) + SUM(g(n, k, i, j) (j != i)) = S(n, k) + (n - 1) * S(n - 1, k)。对于单点斯特林数,可以通过容斥加快速幂nlogn求出。
S(n, k) = SUM((-1) ^ i * C(k, i) * (k - i) ^ n) / k!。复杂度nlogn。

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <fstream> 3 #include <sstream> 4 #include <cstdlib> 5 #include <cstdio> 6 #include <cmath> 7 #include <string> 8 #include <cstring> 9 #include <algorithm> 10 #include <queue> 11 #include <stack> 12 #include <vector> 13 #include <set> 14 #include <map> 15 #include <list> 16 #include <iomanip> 17 #include <cctype> 18 #include <cassert> 19 #include <bitset> 20 #include <ctime> 21 22 using namespace std; 23 24 #define pau system("pause") 25 #define ll long long 26 #define pii pair<int, int> 27 #define pb push_back 28 #define mp make_pair 29 #define clr(a, x) memset(a, x, sizeof(a)) 30 31 const double pi = acos(-1.0); 32 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 33 const int MOD = 1e9 + 7; 34 const double EPS = 1e-9; 35 36 /* 37 #include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp> 38 #include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp> 39 40 using namespace __gnu_pbds; 41 tree<pli, null_type, greater<pli>, rb_tree_tag, tree_order_statistics_node_update> T; 42 */ 43 44 int n, k; 45 ll W, N[400015]; 46 ll mpow(ll x, ll y) { 47 if (!y) return 1; 48 ll res = mpow(x, y >> 1); 49 if (y & 1) return res * res % MOD * x % MOD; 50 return res * res % MOD; 51 } 52 void pre() { 53 N[0] = 1; 54 for (int i = 1; i <= 400000; ++i) { 55 N[i] = N[i - 1] * i % MOD; 56 } 57 } 58 ll inv(ll x) { 59 return mpow(x, MOD - 2); 60 } 61 ll C(int n, int k) { 62 return N[n] * inv(N[n - k]) % MOD * inv(N[k]) % MOD; 63 } 64 ll stirling(ll x, ll y) { 65 ll res = 0; 66 for (int i = 0; i < y; ++i) { 67 if (i & 1) res -= C(y, i) * mpow(y - i, x) % MOD; 68 else res += C(y, i) * mpow(y - i, x) % MOD; 69 } 70 res = (res % MOD + MOD) % MOD; 71 return res * inv(N[y]) % MOD; 72 } 73 int main() { 74 pre(); 75 scanf("%d%d", &n, &k); 76 for (int i = 1, w; i <= n; ++i) { 77 scanf("%d", &w); 78 W += w; 79 } 80 printf("%lld\n", W % MOD * (stirling(n, k) + (n - 1) * stirling(n - 1, k) % MOD) % MOD); 81 return 0; 82 }
以上是关于Educational Codeforces Round 41 (Rated for Div. 2) G. Partitions的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Educational Codeforces Round 7 A
Educational Codeforces Round 7
Educational Codeforces Round 90
Educational Codeforces Round 33
