二叉树的前序中序后序遍历迭代实现
Posted 奇迹迪
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了二叉树的前序中序后序遍历迭代实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
二叉树的前序、中序、后序遍历迭代实现
二叉树的前序遍历,迭代实现 根-左-右
思路:
1、 借用栈的结构
2、 先push(root)
3、 node = pop()
3.1、list.add( node.val )
3.1、push( node.right )
3.3、push( node.left )
4、循环步骤3直到栈空
肯定很难理解,我们一步步执行下,请看图
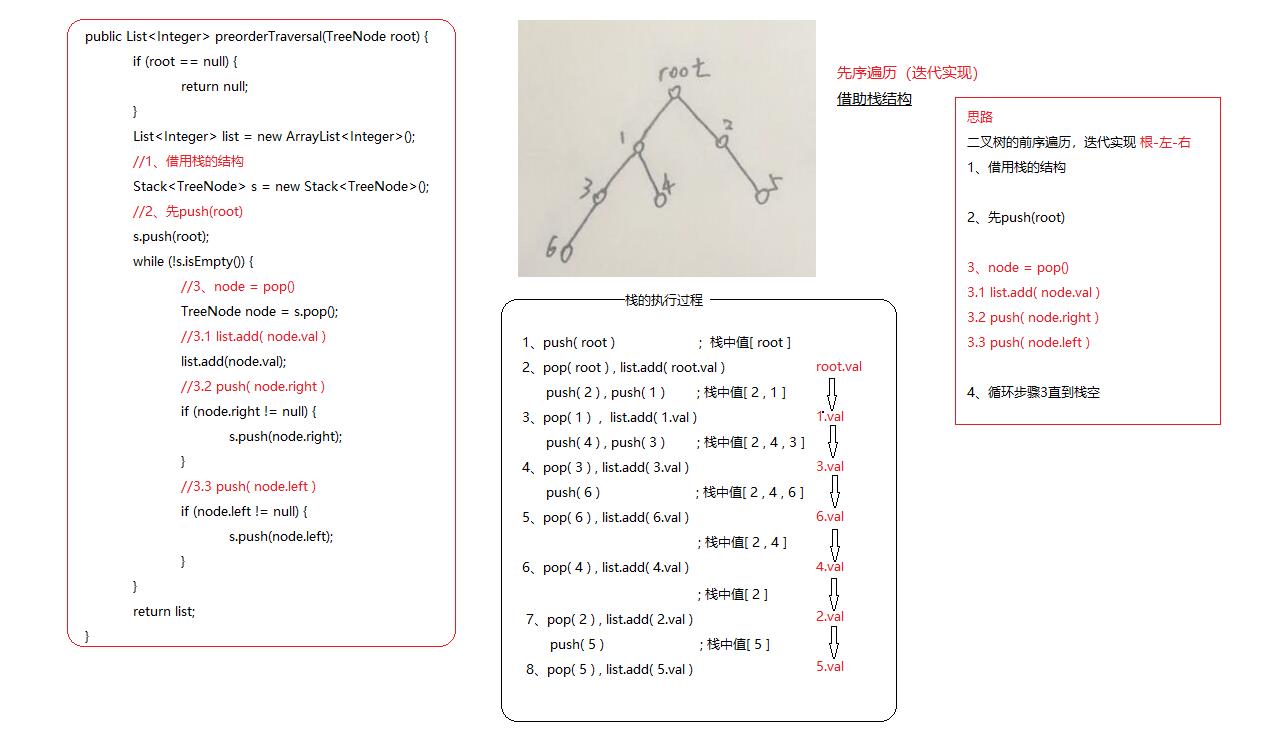
我们来实现一下代码
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Stack<TreeNode> s = new Stack<TreeNode>();
s.push(root);
while (!s.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = s.pop();
list.add(node.val);
if (node.right != null) {
s.push(node.right);
}
if (node.left != null) {
s.push(node.left);
}
}
return list;
}
中序遍历 左-根-右
思路:
1、 借用栈的结构
2、 把root、以及root左孩子都压入栈中
2.1、node = pop()
2.2、list.add( node.val )
2.3、root = node.right
3、循环步骤2直到栈为空且root为null
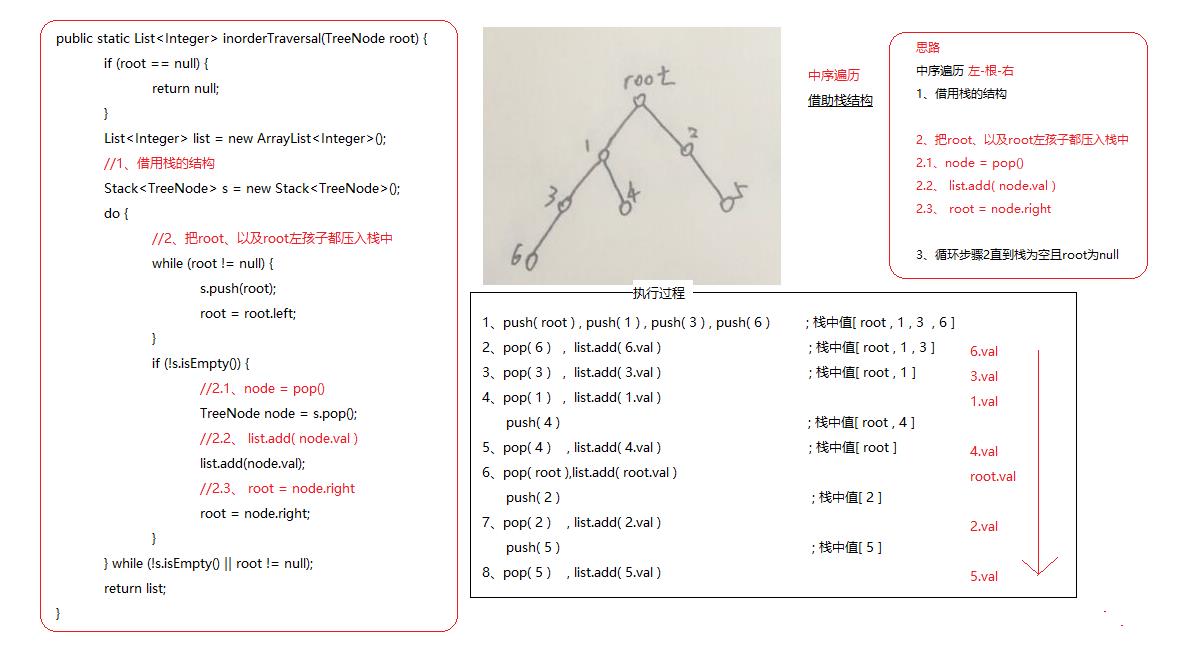
我们实现一下代码
public static List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Stack<TreeNode> s = new Stack<TreeNode>();
do {
while (root != null) {
s.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
if (!s.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = s.pop();
list.add(node.val);
root = node.right;
}
} while (!s.isEmpty() || root != null);
return list;
}
后序遍历 左-右-根
思路:
1、 借用栈的结构
2、 先push(root)
3、 node = pop()
3.1、list.add( 0 , node.val )
3.2、push( node.left )
3.3、push( node.right )
4、循环步骤3直到栈空
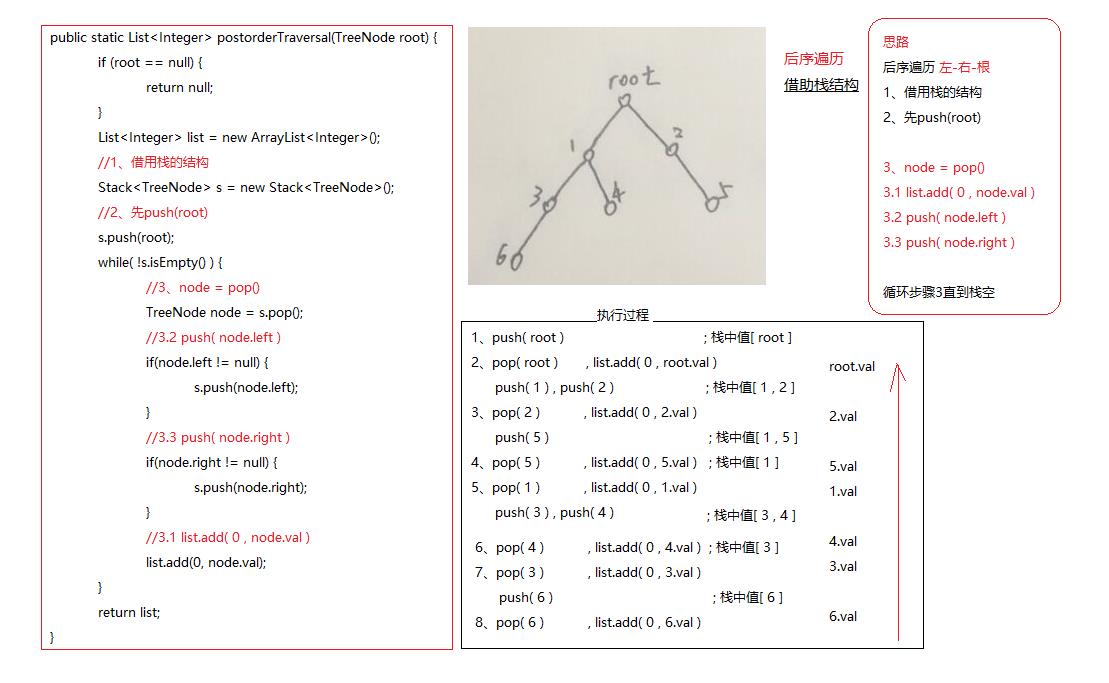
我们实现一下代码
public static List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Stack<TreeNode> s = new Stack<TreeNode>();
s.push(root);
while( !s.isEmpty() ) {
TreeNode node = s.pop();
if(node.left != null) {
s.push(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null) {
s.push(node.right);
}
list.add(0, node.val);
}
return list;
}
补充:
TreeNode类
class TreeNode {
public int val;
public TreeNode left, right;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.left = this.right = null;
}
}
前序遍历,递归实现
public void preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if(root != null) {
System.out.print( root.val + " " );
preorderTraversal( root.left );
preorderTraversal( root.right );
}
}
中序遍历,递归实现
public void inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if(root != null) {
inorderTraversal( root.left );
System.out.print( root.val + " " );
inorderTraversal( root.right );
}
}
后序遍历,递归实现
public void postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if(root != null) {
postorderTraversal( root.left );
postorderTraversal( root.right );
System.out.print( root.val + " " );
}
}
递归的实现还是比较简单的,也容易理解;
以上是关于二叉树的前序中序后序遍历迭代实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章