可视化n次贝塞尔曲线及过程动画演示--大宝剑
Posted 李可
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了可视化n次贝塞尔曲线及过程动画演示--大宝剑相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
起因
研究css中提供了2次、3次bezier,但是没有对n次bezier实现。对n次的实现有很大兴趣,所以就用js的canvas搞一下,顺便把过程动画模拟了一下。
投入真实生产之中,偏少。
n次bezier曲线,做前端实际生产中,并没有很大对帮助。仅仅学习研究之。
1,由于css样式中仅提供了2次/3次bezier曲线的形成,对n次bezier曲线的实现有很强的好奇心。
2,爱好数学之美和js动画,想实现bezier曲线的描绘过程,实现其过程演示动画。
故做此文。
先抛的两个例子,吊一吊Xing趣

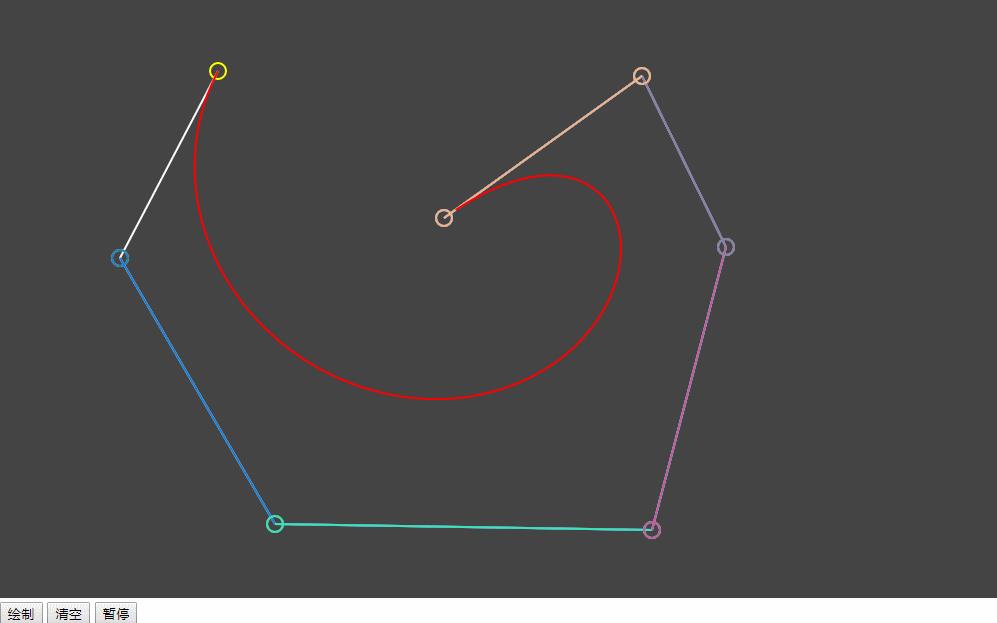
demo提供的api概述
- 我眼睛花,没看懂,能暂停不了?
- 可以控制动画暂停与继续。(供大家清楚地时刻看到每一帧)
- 我研究,先不追求性能,能控制播放时间不了?
- 可以是setInterval代替requestAnimationFrame控制每一帧的时间(已经注释,大家可以注释开控制时间)
1:只画一个bezier曲线,理解bezeir公式
好像很吊的样子,怎么实现的?我是这样最主要理解bezier曲线的公式,看我抄百度的贝塞尔公式图,看抄
![]()
- 线的个数 辅助线的个数
- n个节点(n>2),
- 总线数:(n-1)+(n-2)+...+1,公差为1等差数列求和,S=(1+n-1)(n-1)/2=n(n-1)/2
- 中间辅助线(包含最后一条):n*(n-1)/2-(n-1)
- 假如:2个节点,总1条 0辅助
- 假如:3个节点,总3条 1辅助
- 假如:4个节点,总6条 3辅助
- 假如:5个节点,总10条 6辅助
- 我是这样子理解 t的(自变量t的范围)
- 不论几次贝塞尔,t从0->1[0,1],这个过程:
- 假如:描了100个点,就是把范围1分成100份 ,每份0.01
- 假如:描了1000个点,就是把范围1分成100份 ,每份0.001
使用组合
数学偏low的人是组合哪个符号,表示不明白,举爪。
- 两个圆括号(n i)是什么?是组合吗,组合不C n i吗。我也是数学偏low的,别墨迹,直接上解释 知乎大法好,组合表示法
- 看我抄百度数学组合公式

- 阶乘是啥,我不知道~
//组合
function C(n, i) {
return f(n) / f(i) / f(n - i)
}
//阶乘公式 n!
//阶乘 factorial
function f(n) {
if (n < 0) {
return -1
} else if (n === 0 || n === 1) {
return 1
} else {
return (n * f(n - 1))
}
}
获取曲线的一个点的坐标
控制点固定,t为【0,1】的一个值的时候,获取bezier曲线的一个点的x y坐标
//曲线上的一个点,分别求出x,和y
//points确定系数
//t是自变量,这里获取一个点的时候,需要t固定,画线的时候再赋值[0,1],分100份的话,每次t差距0.01,循环t
//公式中需要组合
function getOnePointXY(points, t) {
return {
x: Sigmar(\'x\', points, t),
y: Sigmar(\'y\', points, t)
}
}
//x或者y方向上的坐标,bezier曲线求和
function sigmar(direction, points, t) {
var result = 0
//n+1个节点,是n次bezier曲线
let n = points.length - 1
for (let [i, { x, y }] of points.entries()) {
var A = C(n, i)
var P = direction === \'x\' ? x : direction === \'y\' ? y : x//不传\'x\' \'y\'默认x方向
var t1 = Math.pow(1 - t, n - i)
var t2 = Math.pow(t, i)
result += A * P * t1 * t2
}
return result
}
开始画一条曲线
点都确定了,开始画canvas
var controlPoints = [{ x: 100, y: 500 }, { x: 150, y: 400 }, { x: 600, y: 300 }, { x: 400, y: 150 }]
//一条bezier曲线上有多少个点,
//分100份的话,每次t差距0.01,循环。
//todo,用户配置--点--暂停--嵌入动画里面
var pointCount = 1000
var allBezeirPoints = nbezeirCurve(controlPoints, pointCount)
const pen = canvas.getContext(\'2d\')
pen.moveTo(allBezeirPoints[0].x, allBezeirPoints[0].y)
//pen.moveTo(0, allBezeirPoints[0].y)
for (let { x, y } of allBezeirPoints) {
pen.lineTo(x, y)
}
pen.stroke()
console.log(nbezeirCurve(controlPoints, pointCount))
//得到n次bezier曲线的pointCount个数个点数组
function nbezeirCurve(controlPoints, pointCount, t = 0) {
var step = 1 / pointCount//t->step++[0,1]
var pointArr = []
while (t < 1) {
pointArr.push(getOnePointXY(controlPoints, t))
t += step
}
return pointArr
}
一个贝塞尔曲线demo
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>bezeir by 李可</title>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="canvas" width="800" height="600"></canvas>
<script>
var controlPoints = [{ x: 100, y: 500 }, { x: 150, y: 400 }, { x: 600, y: 300 }, { x: 400, y: 150 }]
//一条bezier曲线上有多少个点,
//分100份的话,每次t差距0.01,循环。
//todo,用户配置--点--暂停--嵌入动画里面
var pointCount = 1000
var allBezeirPoints = nbezeirCurve(controlPoints, pointCount)
const pen = canvas.getContext(\'2d\')
pen.moveTo(allBezeirPoints[0].x, allBezeirPoints[0].y)
//pen.moveTo(0, allBezeirPoints[0].y)
for (let { x, y } of allBezeirPoints) {
pen.lineTo(x, y)
}
pen.stroke()
console.log(nbezeirCurve(controlPoints, pointCount))
//得到n次bezier曲线的pointCount个数个点数组
function nbezeirCurve(controlPoints, pointCount, t = 0) {
var step = 1 / pointCount//t->step++[0,1]
var pointArr = []
while (t < 1) {
pointArr.push(getOnePointXY(controlPoints, t))
t += step
}
return pointArr
}
//曲线上的一个点,分别求出x,和y
//points确定系数
//t是自变量,这里获取一个点的时候,需要t固定,画线的时候再赋值[0,1],分100份的话,每次t差距0.01,循环t
//公式中需要组合
function getOnePointXY(points, t) {
return {
x: Sigmar(\'x\', points, t),
y: Sigmar(\'y\', points, t)
}
}
//x或者y方向上的坐标,bezier曲线求和
function Sigmar(direction, points, t) {
var result = 0
//n+1个节点,是n次bezier曲线
let n = points.length - 1
for (let [i, { x, y }] of points.entries()) {
var A = C(n, i)
var P = direction === \'x\' ? x : direction === \'y\' ? y : x//不传\'x\' \'y\'默认x方向
var t1 = Math.pow(1 - t, n - i)
var t2 = Math.pow(t, i)
result += A * P * t1 * t2
}
return result
}
//组合
function C(n, i) {
return f(n) / f(i) / f(n - i)
}
//阶乘 factorial
function f(n) {
if (n < 0) {
return -1
} else if (n === 0 || n === 1) {
return 1
} else {
return (n * f(n - 1))
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
2:动画模拟bezier曲线过程
现在你明白了画一个bezier如此简单,是否特别想怎么用动画模仿出来这个贝塞尔的过程?继续看我BB
模拟动画的思路,那让我们继续想,怎么画这个动画呢?
....想来想去------>每一帧,把t的所有连线都画好。下一帧把上一帧的连线抹除后,再画t=t+0.01(这里分了100份,每份0.01)的的所有连线。
所有线,每一帧到底有多少线需要画?见下图。

针对每一帧:根据t
假使画5次贝赛尔曲线,先画4个线,(得到4个点,先画3个线),(得到3个点,再画2条)。
假使画4次贝赛尔曲线,先画3个线,(得到3个点,再画2条)。
假使画3次贝赛尔曲线,(画2条)。
画一条折线
function drawBrokenLine(points, t = 1, lineColor = \'white\', hasNode = true, nodeColor = \'white\') {
if (points.length >= 2) {
for (var i = 0; i < points.length - 1; i++) {
var current = points[i]
var next = points[i + 1]
drawLine(current, next, lineColor)
hasNode && drawNode(current, nodeColor)
}
hasNode && drawNode(points[points.length - 1], nodeColor)
}
return getPercentPoints(points, t)
}
动画每一帧中的2个技术点
t固定下,怎么得到上个折线中对应下次点坐标折线集合?看图说话。顺便看下代码
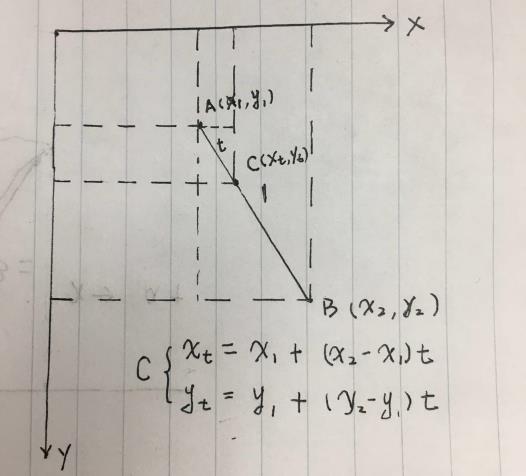
function getPercentPoints(points, t) {
if (points.length <= 1) {
return points
}
const perPoints = []
var inx = 0
while (inx < points.length - 1) {
const current = points[inx]
const next = points[inx + 1]
var perPoint = {
x: current.x + (next.x - current.x) * t,
y: current.y + (next.y - current.y) * t
}
perPoints.push(perPoint)
inx++
}
return perPoints
}
递归画折线
直到剩下 1个点时候,就是besier曲线上的值了
function drawframe(points, t) {
var lineColors = getColors(points)
canvas.width = canvas.width
init(pen)
//画第一折线
var percentPoints = drawBrokenLine(points, t, \'white\', true, \'yellow\')
var i = 0
//循环画中间折线
while (percentPoints.length > 1) {
const currentColor = lineColors[++i]
percentPoints = drawBrokenLine(percentPoints, t, currentColor, true, currentColor)
}
//循环画贝塞尔折(曲)线
const bezeirPoints = getBezierPoints(controlPoints, step, t)
drawBrokenLine(bezeirPoints, t, \'red\', false)
}
给折线上点颜色
给中间折线上上随机色啊,增加丢丢美感。
为显目,第一轮折线为白色,最后贝塞尔线确定为红色
一个贝塞尔曲线动画demo
最后的最后有完没完?还没BB完?完了..,不行,不要砍我........运行大宝剑
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>bezier by 李可</title>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="canvas" width="1000" height="600"></canvas>
<br>
<input type="button" id="btn1" value="绘制">
<input type="button" id="btn2" value="清空">
<input type="button" id="btn3" value="暂停">
<script>
function getPercentPoints(points, t) {
if (points.length <= 1) {
return points
}
const perPoints = []
var inx = 0
while (inx < points.length - 1) {
const current = points[inx]
const next = points[inx + 1]
var perPoint = {
x: current.x + (next.x - current.x) * t,
y: current.y + (next.y - current.y) * t
}
perPoints.push(perPoint)
inx++
}
return perPoints
}
function getBezierPoints(points, t, end = 1, start = 0) {
var pointArr = []
while (start <= end) {
var node = getOneBezierPoint(points, start)
pointArr.push(node)
start += t
}
return pointArr
}
//曲线上的一个点,分别求出x,和y
//points确定系数
//t是自变量,这里获取一个点的时候,需要t固定,画线的时候再赋值[0,1],分100份的话,每次t差距0.01,循环t
//公式中需要组合
function getOneBezierPoint(points, t) {
return {
x: sigmar(\'x\', points, t),
y: sigmar(\'y\', points, t)
}
}
//x或者y方向上的坐标,bezier曲线求和
function sigmar(direction, points, t) {
var result = 0
//n+1个节点,是n次bezier曲线
let n = points.length - 1
for (let [i, { x, y }] of points.entries()) {
var A = C(n, i)
var P = direction === \'x\' ? x : direction === \'y\' ? y : x//不传\'x\' \'y\'默认x方向
var t1 = Math.pow(1 - t, n - i)
var t2 = Math.pow(t, i)
result += A * P * t1 * t2
}
return result
}
//组合
function C(n, i) {
return f(n) / f(i) / f(n - i)
}
//阶乘 factorial
function f(n) {
if (n < 0) {
return -1
} else if (n === 0 || n === 1) {
return 1
} else {
return (n * f(n - 1))
}
}
</script>
<script>
const controlPoints = []//{ x: 100, y: 500 }, { x: 150, y: 400 }, { x: 600, y: 300 }, { x: 400, y: 150 }
const pen = canvas.getContext(\'2d\')
function init(pen) {
pen.fillStyle = "#444"
pen.fillRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height)
}
init(pen)
canvas.onmousedown = function (e) {
const point = { x: e.offsetX, y: e.offsetY }
controlPoints.push(point)
drawText(point, controlPoints.length)
drawNode(point)
drawLastLine(controlPoints)
}
//显示点击位置
function drawText(point, inx, y = 10, font = 16) {
pen.fillStyle = "#fff"
pen.textAlign = \'end\'
pen.textBaseline = \'hanging\'
pen.font = `${font}px`//times
pen.fillText(`${point.x}x${point.y}:${inx}`, 1000 - 20, inx === 1 ? y : (inx - 1) * font + y)
}
function drawLastLine(points) {
//画最后两点连线 -折线
var count = points.length
var current = points[count - 2]
var next = points[count - 1]
if (count >= 2) {
drawLine(current, next)
}
}
function drawNode(point, nodeColor = \'white\') {
//画节点
pen.beginPath()
pen.strokeStyle = nodeColor
pen.lineWidth = 2
pen.arc(point.x, point.y, 8, 0, 2 * Math.PI)
pen.stroke()
}
function drawLine(current, next, color = "white") {
//画最后两点连线 -折线
pen.beginPath()
pen.strokeStyle = color
pen.lineWidth = 2
pen.moveTo(current.x, current.y)
pen.lineTo(next.x, next.y)
pen.stroke()
}
const pointCount = 100
const step = 1 / pointCount//t->step++[0,1]
//绘bezier曲线
function drawBrokenLine(points, t = 1, lineColor = \'white\', hasNode = true, nodeColor = \'white\') {
if (points.length >= 2) {
for (var i = 0; i < points.length - 1; i++) {
var current = points[i]
var next = points[i + 1]
drawLine(current, next, lineColor)
hasNode && drawNode(current, nodeColor)
}
hasNode && drawNode(points[points.length - 1], nodeColor)
}
return getPercentPoints(points, t)
}
function getRandomColor() {
var color = "#"
for (let i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
color += Array.from(\'0123456789abcdef\')[Math.floor(16 * Math.random())]
}
return color
}
//n次,画n-1条折线
var lineColors = []
function getColors(points) {
const len = points.length
for (let i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {
lineColors.push(getRandomColor())
}
return lineColors
}
function drawframe(points, t) {
var lineColors = getColors(points)
canvas.width = canvas.width
init(pen)
var percentPoints = drawBrokenLine(points, t, \'white\', true, \'yellow\')
var i = 0
while (percentPoints.length > 1) {
const currentColor = lineColors[++i]
percentPoints = drawBrokenLine(percentPoints, t, currentColor, true, currentColor)
}
const bezeirPoints = getBezierPoints(controlPoints, step, t)
drawBrokenLine(bezeirPoints, t, \'red\', false)
}
var timer
var state
var runFlag = true
function startBezier(t, recursive = false) {//iteration
// timer = setInterval(() => {
// if (t <= 1) {
// drawframe(controlPoints, t)
// t += step
// state = t
// } else {
// clearInterval(timer)
// drawframe(controlPoints, 1)
// recursive && startBezier(0)
// }
// }, 200)
timer = requestAnimationFrame(function frame() {
if (runFlag) {
if (t <= 1) {
drawframe(controlPoints, t)
t += step
state = t
requestAnimationFrame(frame)
} else {
cancelAnimationFrame(timer)
drawframe(controlPoints, 1)
recursive && startBezier(0)
}
} else {
cancelAnimationFrame(timer)
}
})
// const bezeirPoints = getBezierPoints(controlPoints, step, 0.5)
// drawBrokenLine(bezeirPoints, 1, \'red\')
}
btn1.onclick = function () {
startBezier(0)
}
btn2.onclick = function () {
controlPoints.splice(0, controlPoints.length)
canvas.width = canvas.width
// clearInterval(timer)
runFlag = true
init(pen)
}
var count = 0
btn3.onclick = function () {
if (++count % 2 === 1) {
btn3.value = \'继续\'
if (timer) {
//clearInterval(timer)
runFlag = false
}
} else {
btn3.value = \'暂停\'
console.log(state)
runFlag = true
startBezier(state)
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
真完了
欢迎大家加入QQ群471838073,一起大宝剑
以上是关于可视化n次贝塞尔曲线及过程动画演示--大宝剑的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章