Wannafly挑战赛16
Posted 人活着就是为了Chelly
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Wannafly挑战赛16相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
E(pbds)
题意:

1<=m,n<=5e5
分析:
首先指向关系形成了一个基环外向树森林
实际上我们可以完全不用真正的去移动每个球,而只需要在计数的时候考虑考虑就行了
对于树上的情况,我们假设在时间为now的时候在距离根为dis的点上放了个球,我们记录下now+dis
对于询问树上的情况,即查找在时间为i的时候有多少个球会到达x点,那么我们只需要考虑以x为根的子树里(now+dis==i+d[x])的个数即可,很显然这可以用dfs序+数据结构来搞
这个数据结构需要支持单点修改、询问区间内某一数字出现了多少次
树状数组+主席树?
我们换个角度,因为数字都不大,我们不妨对于每个数字都开一个set,查找就是在对应数字里的set里查找[l,r]中的数字有多少个,这个用pbds里的set就行了
还有一个case,如果询问在环上咋办?
我们可以记录每个球来到环上的时间,对于每个环直接用带模数组维护即可

1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 #include<ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp> 3 #define mp make_pair 4 using namespace std; 5 using namespace __gnu_pbds; 6 const int inf=1000000000; 7 typedef tree<pair<int,int>,null_type,less<pair<int,int> >,rb_tree_tag,tree_order_statistics_node_update> rbtree; 8 const int maxn=5e5; 9 int f[maxn+5],fa[maxn+5],c[maxn+5],len[maxn+5]; 10 int L[maxn+5],R[maxn+5],dep[maxn+5],root[maxn+5],id[maxn+5]; 11 int n,m,ans,dfn,color; 12 vector<int> g[maxn+5]; 13 rbtree rbt[2*maxn+5]; 14 multiset<pair<int,int> > s; 15 map<int,int> a[maxn+5]; 16 int find(int k) 17 { 18 if(f[k]==k) return k; 19 return f[k]=find(f[k]); 20 } 21 void addedge(int u,int v) 22 { 23 g[u].push_back(v); 24 } 25 void dfs(int k) 26 { 27 L[k]=++dfn; 28 for(auto u:g[k]) 29 { 30 if(c[u]) continue; 31 dep[u]=dep[k]+1; 32 root[u]=root[k]; 33 dfs(u); 34 } 35 R[k]=dfn; 36 } 37 int main() 38 { 39 scanf("%d",&n); 40 for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) f[i]=i; 41 for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) scanf("%d",&fa[i]),addedge(fa[i],i); 42 for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) 43 { 44 int u=find(i),v=find(fa[i]); 45 if(u!=v) 46 { 47 f[u]=v; 48 continue; 49 } 50 u=fa[i]; 51 ++color; 52 int tmp=0; 53 while(true) 54 { 55 ++len[color]; 56 c[u]=color; 57 id[u]=tmp++; 58 u=fa[u]; 59 if(u==fa[i]) break; 60 } 61 } 62 for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) 63 if(c[i]) root[i]=i,dfs(i); 64 scanf("%d",&m); 65 for(int i=1;i<=m;++i) 66 { 67 int x; 68 scanf("%d",&x); 69 x^=ans; 70 if(c[x]) 71 { 72 s.insert(mp(i,x)); 73 while(!s.empty()) 74 { 75 pair<int,int> u=*s.begin(); 76 if(u.first>i) break; 77 int color=c[u.second]; 78 ++a[color][(u.first-id[u.second]+len[color])%len[color]]; 79 s.erase(s.begin()); 80 } 81 int color=c[x]; 82 ans=a[color][(i-id[x]+len[color])%len[color]]; 83 printf("%d ",ans); 84 } 85 else 86 { 87 rbt[i+dep[x]].insert(mp(L[x],i)); 88 ans=rbt[i+dep[x]].order_of_key(mp(R[x],inf))-rbt[i+dep[x]].order_of_key(mp(L[x],-inf)); 89 printf("%d ",ans); 90 s.insert(mp(i+dep[x],root[x])); 91 } 92 } 93 return 0; 94 }
F(数据结构)
题意:

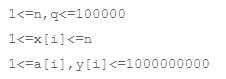
分析:
首先不考虑修改,对于一个给定的数组a,我们如何快速求出需要执行多少次操作才能把它全部变成0?
我们可以发现以下的性质:
1、有些位置对最终答案满贡献,其它位置对最终答案0贡献
2、极大值对最终答案是满贡献的
3、我们从初始的所有极大值开始每次隔1个数,直到遇到边界或者极小值,那么数到的数都会在过程中成为极大值
4、若一个极小值对答案有贡献,那么它到两边的极大值的距离都为偶数
于是我们就可以O(n)解决了
但是现在有修改操作,我们来考虑如何在之前信息的基础上维护一些东西
求答案的本质是找到那些极大值极小值,然后从极大值开始间隔1个数,我们可以用两个树状数组来维护奇数位/偶数位上的前缀和
然后我们用一个set去存下所有的极大值、极小值
对于一个修改(x,y)
我们找到一个set里的极小区间[l,r],使得l和r的极大极小性质一定不会被破坏
然后把这段区间对答案的贡献减掉
然后修改a[x]->y
再把这段区间对答案的贡献加上去
时间复杂度O(nlogn)

1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 typedef set<int>::iterator iter; 4 typedef long long ll; 5 const int maxn=1e5; 6 ll c[2][maxn+5]; 7 ll a[maxn+5]; 8 int n; 9 ll ans=0; 10 set<int> s; 11 int lowbit(int x) 12 { 13 return x&(-x); 14 } 15 void add(ll *c,int k,ll x) 16 { 17 for(;k<=n/2+1;k+=lowbit(k)) c[k]+=x; 18 } 19 void add(int k,ll x) 20 { 21 if(k&1) add(c[1],(k+1)>>1,x);else add(c[0],(k+1)>>1,x); 22 } 23 ll query(ll *c,int k) 24 { 25 ll ans=0; 26 for(;k;k-=lowbit(k)) ans+=c[k]; 27 return ans; 28 } 29 ll query(ll *c,int l,int r) 30 { 31 if(l>r) return 0; 32 return query(c,r)-query(c,l-1); 33 } 34 int type(int id) 35 { 36 if(a[id-1]<a[id]&&a[id]>=a[id+1]) return 1; 37 if(a[id-1]>=a[id]&&a[id]<a[id+1]) return -1; 38 return 0; 39 } 40 ll cal(int l,int r) 41 { 42 if(r-l<3) return 0; 43 if(a[l]<a[r]) 44 { 45 int R=(r+1)/2-1; 46 int L; 47 if((l&1)==(r&1)) L=(l+1)/2+1;else L=(l+2)/2; 48 return query(c[r&1],L,R); 49 } 50 else 51 { 52 int L=(l+1)/2+1; 53 int R; 54 if((l&1)==(r&1)) R=(r+1)/2-1;else R=r/2; 55 return query(c[l&1],L,R); 56 } 57 } 58 ll cal(iter l,iter r) 59 { 60 ll ans=0; 61 for(iter i=l;i!=r;++i) 62 { 63 iter tmp=i; 64 ++tmp; 65 ans+=cal(*i,*tmp); 66 } 67 ++r; 68 for(iter i=l;i!=r;++i) 69 if(type(*i)==1) ans+=a[*i]; 70 else 71 if(type(*i)==-1) 72 { 73 iter tmp1=i,tmp2=i; 74 --tmp1,++tmp2; 75 if((*tmp2-*i)%2==0&&(*i-*tmp1)%2==0) ans+=a[*i]; 76 } 77 else 78 { 79 iter tmp=i; 80 if(*i==1) ++tmp;else --tmp; 81 if((*tmp-*i)%2==0) ans+=a[*i]; 82 } 83 return ans; 84 } 85 int main() 86 { 87 scanf("%d",&n); 88 for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) scanf("%lld",&a[i]),add(i,a[i]); 89 s.insert(1),s.insert(n); 90 for(int i=2;i<n;++i) 91 if(type(i)!=0) s.insert(i); 92 iter tmp=s.end(); 93 ans=cal(s.begin(),--tmp); 94 int q; 95 scanf("%d",&q); 96 for(int i=1;i<=q;++i) 97 { 98 int x;ll y; 99 scanf("%d%lld",&x,&y); 100 int l=x-1,r=x+1; 101 if(r>n-1) r=n-1; 102 if(l<2) l=2; 103 iter L=s.lower_bound(l); 104 --L; 105 iter R=s.upper_bound(r); 106 ans-=cal(L,R); 107 int left=*L,right=*R; 108 add(x,y-a[x]); 109 a[x]=y; 110 if(type(x)!=0) s.insert(x); 111 else if(s.count(x)&&x>=2&&x<=n-1) s.erase(x); 112 if(x+1<n) 113 if(type(x+1)==0&&s.count(x+1)) s.erase(x+1); 114 else if(type(x+1)!=0) s.insert(x+1); 115 if(x-1>1) 116 if(type(x-1)==0&&s.count(x-1)) s.erase(x-1); 117 else if(type(x-1)!=0) s.insert(x-1); 118 L=s.lower_bound(left); 119 R=s.lower_bound(right); 120 ans+=cal(L,R); 121 printf("%lld ",ans); 122 } 123 return 0; 124 }
以上是关于Wannafly挑战赛16的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
