十文件和目录——文件属性和权限
Posted 游戏进行中
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了十文件和目录——文件属性和权限相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
10.1 文件
10.1.1 文件属性
文件属性都存放在 stat 结构体中
1 #include <asm/stat.h> 2 struct stat { 3 unsigned long st_dev; /* 磁盘分区上的设备编号,主要用于驱动开发 */ 4 unsigned long st_ino; /* 文件 i-node 号 */ 5 unsigned int st_mode; /* 文件类型和权限。如 O_WRONLY */ 6 unsigned int st_nlink; /* 链接数量 */ 7 unsigned int st_uid; /* 文件所有者的用户 ID */ 8 unsigned int st_gid; /* 文件所有组的组 ID */ 9 unsigned long st_rdev; /* 如果是真实设备的话,为真实设备号 */ 10 unsigned long __pad1; 11 long st_size; /* 文件大小,单位为 bytes */ 12 int st_blksize; /* I/O 操作中的块的大小,即磁盘块的大小 */ 13 int __pad2; 14 long st_blocks; /* 分配的 512 字节磁盘块的数量 */ 15 long st_atime; /* 最后一次次访问时间 */ 16 unsigned long st_atime_nsec; 17 long st_mtime; /* 最后一次的修改时间 */ 18 unsigned long st_mtime_nsec; 19 long st_ctime; /* 最后一次的文件状态改变时间 */ 20 unsigned long st_ctime_nsec; 21 unsigned int __unused4; 22 unsigned int __unused5; 23 };
10.1.2 文件属性操作函数
获取文件属性:
1 #include <sys/stat.h> 2 #include <unistd.h> 3 int stat(const char * file_name,struct stat *buf); //取得文件状态 4 int fstat(int fd, struct stat *buf); //由文件描述符取得文件状态 5 int lstat (const char * file_name, struct stat * buf); //由文件描述符取得文件状态
- 函数说明
- stat()用来将参数file_name所指的文件状态,复制到参数buf所指的结构中。
- fstat()用来将参数fildes所指的文件状态,复制到参数buf所指的结构中(struct stat)。
- Fstat()与stat()作用完全相同,不同处在于传入的参数为已打开的文件描述词。
- lstat()与stat()作用完全相同,都是取得参数 file_name 所指的文件状态,其差别在于,当文件为符号连接时,lstat 会返回该符号链接的有关信息,而不是由该符号链接引用的文件信息。
- 函数功能:
- 返回一个与 pathname 或 fd 指定的文件属性信息,存储在结构体 buf 中
- 函数参数:
- @pathname:文件路径的名字
- @buf: struct stat 结构体指针
- 返回值
- 执行成功则返回 0,失败返回 -1,错误代码存于errno
- 错误代码
- ENOENT 参数file_name指定的文件不存在
- ENOTDIR 路径中的目录存在但却非真正的目录
- ELOOP 欲打开的文件有过多符号连接问题,上限为16符号连接
- EFAULT 参数buf为无效指针,指向无法存在的内存空间
- EACCESS 存取文件时被拒绝
- ENOMEM 核心内存不足
- ENAMETOOLONG 参数file_name的路径名称太长
10.1.3 文件类型
- Linux中的七种文件和七种宏
- 普通文件(regular file) S_ISREG()
- 目录文件(directory file) S_ISDIR()
- 块特殊文件(block special file) S_ISBLK()
- 字符特殊文件(character special file) S_ISCHR()
- FIFO(named pipe) S_ISFIFO()
- 套接字(socket) S_ISSOCK()
- 符号链接(symbolic link) S_ISLNK()
10.1.4 例子
分析指定文件类型
file_type.c
1 #include <sys/types.h> 2 #include <sys/stat.h> 3 #include <fcntl.h> 4 #include <unistd.h> 5 #include <string.h> 6 #include <errno.h> 7 #include <stdlib.h> 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 10 int main(int argc, const char *argv[]) 11 { 12 if(argc < 2) { 13 fprintf(stderr, "usage: %s files\\n", argv[0]); 14 exit(1); 15 } 16 17 int i; 18 struct stat buff; 19 20 for(i = 1; i < argc; i++) { 21 memset(&buff, 0, sizeof(buff)); 22 23 if(lstat(argv[i], &buff) < 0) { 24 perror("lstat error"); 25 continue; 26 } 27 28 printf("%-20s", argv[i]); 29 30 //判断文件是何种类型 31 if(S_ISREG(buff.st_mode)) { 32 printf("regular file"); 33 } else if(S_ISDIR(buff.st_mode)) { 34 printf("directory"); 35 } else if(S_ISBLK(buff.st_mode)) { 36 printf("block file"); 37 } else if(S_ISCHR(buff.st_mode)) { 38 printf("character file"); 39 } else if(S_ISFIFO(buff.st_mode)) { 40 printf("named pipe"); 41 } else if(S_ISSOCK(buff.st_mode)) { 42 printf("socket"); 43 } else if(S_ISLNK(buff.st_mode)) { 44 printf("symbolic link"); 45 } else { 46 printf("unknown file type"); 47 } 48 49 printf("\\n"); 50 } 51 52 return 0; 53 }
编译执行:
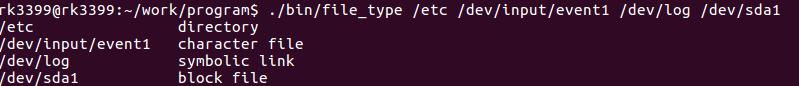
10.2 文件权限
10.2.1 权限介绍
- 9种访问权限
- 用户权限
- S_IRUSR,S_IWUSR,S_IXUSR
- 组权限
- S_IRGRP,S_IWGRP,S_IXGRP
- 其他权限
- S_IROTH,S_IWOTH,S_IXOTH
- 用户权限
- 文件权限通过按位或方式构造
10.2.2 例子
file_perm.c
1 #include <sys/types.h> 2 #include <sys/stat.h> 3 #include <fcntl.h> 4 #include <unistd.h> 5 #include <string.h> 6 #include <errno.h> 7 #include <stdlib.h> 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 10 int main(int argc, const char *argv[]) 11 { 12 if(argc < 2) { 13 fprintf(stderr, "usage: %s files\\n", argv[0]); 14 exit(1); 15 } 16 17 struct stat buff; 18 int i; 19 20 for(i = 1; i < argc; i++) { 21 memset(&buff, 0, sizeof(buff)); 22 if(lstat(argv[0], &buff) < 0) { 23 perror("lstat error"); 24 continue; 25 } 26 27 28 //获得文件的权限信息 29 mode_t mode = buff.st_mode; 30 printf("%-20s", argv[i]); 31 32 // user permission 33 if(S_IRUSR & mode) { 34 printf("r"); 35 } else { 36 printf("-"); 37 } 38 39 if(S_IWUSR & mode) { 40 printf("w"); 41 } else { 42 printf("-"); 43 } 44 45 if(S_IXUSR & mode) { 46 printf("x"); 47 } else { 48 printf("-"); 49 } 50 51 //group permission 52 if(S_IRGRP & mode) { 53 printf("r"); 54 } else { 55 printf("-"); 56 } 57 58 if(S_IWGRP & mode) { 59 printf("w"); 60 } else { 61 printf("-"); 62 } 63 64 if(S_IXGRP & mode) { 65 printf("x"); 66 } else { 67 printf("-"); 68 } 69 70 //other permission 71 if(S_IROTH & mode) { 72 printf("r"); 73 } else { 74 printf("-"); 75 } 76 77 if(S_IWOTH & mode) { 78 printf("w"); 79 } else { 80 printf("-"); 81 } 82 83 if(S_IXOTH & mode) { 84 printf("x"); 85 } else { 86 printf("-"); 87 } 88 89 90 printf("\\n"); 91 } 92 93 return 0; 94 }
编译执行


以上是关于十文件和目录——文件属性和权限的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章