音视频处理之FFmpeg封装格式20180510
Posted yuweifeng
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了音视频处理之FFmpeg封装格式20180510相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、FFMPEG的封装格式转换器(无编解码)
1.封装格式转换
所谓的封装格式转换,就是在AVI,FLV,MKV,MP4这些格式之间转换(对应.avi,.flv,.mkv,.mp4文件)。
需要注意的是,本程序并不进行视音频的编码和解码工作。而是直接将视音频压缩码流从一种封装格式文件中获取出来然后打包成另外一种封装格式的文件。
本程序的工作原理如下图1所示:
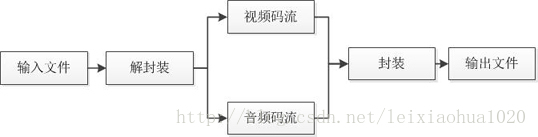
由图可见,本程序并不进行视频和音频的编解码工作,因此本程序和普通的转码软件相比,有以下两个特点:
处理速度极快。视音频编解码算法十分复杂,占据了转码的绝大部分时间。因为不需要进行视音频的编码和解码,所以节约了大量的时间。
视音频质量无损。因为不需要进行视音频的编码和解码,所以不会有视音频的压缩损伤。
2.基于FFmpeg的Remuxer的流程图
下面附上基于FFmpeg的Remuxer的流程图。图2中使用浅红色标出了关键的数据结构,浅蓝色标出了输出视频数据的函数。
可见成个程序包含了对两个文件的处理:读取输入文件(位于左边)和写入输出文件(位于右边)。中间使用了一个avcodec_copy_context()拷贝输入的AVCodecContext到输出的AVCodecContext。
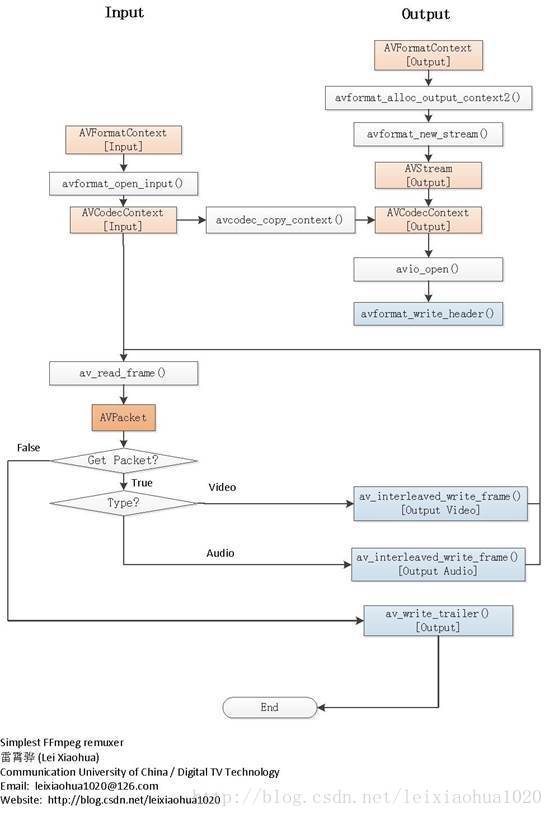
简单介绍一下流程中关键函数的意义:
输入文件操作:
avformat_open_input():打开输入文件,初始化输入视频码流的AVFormatContext。
av_read_frame():从输入文件中读取一个AVPacket。
输出文件操作:
avformat_alloc_output_context2():初始化输出视频码流的AVFormatContext。
avformat_new_stream():创建输出码流的AVStream。
avcodec_copy_context():拷贝输入视频码流的AVCodecContex的数值t到输出视频的AVCodecContext。
avio_open():打开输出文件。
avformat_write_header():写文件头(对于某些没有文件头的封装格式,不需要此函数。比如说MPEG2TS)。
av_interleaved_write_frame():将AVPacket(存储视频压缩码流数据)写入文件。
av_write_trailer():写文件尾(对于某些没有文件头的封装格式,不需要此函数。比如说MPEG2TS)。
二、FFmpegRemuxer代码
基于FFmpeg的封装格式转换器,取了个名字称为FFmpegRemuxer
主要是FFmpegRemuxer.cpp文件,代码如下(基本上每一行都有注释):

1 /***************************************************************************** 2 * Copyright (C) 2017-2020 Hanson Yu All rights reserved. 3 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 4 * File Module : FFmpegRemuxer.cpp 5 * Description : FFmpegRemuxer Demo 6 7 输出结果: 8 Input #0, flv, from \'cuc_ieschool1.flv\': 9 Metadata: 10 metadatacreator : iku 11 hasKeyframes : true 12 hasVideo : true 13 hasAudio : true 14 hasMetadata : true 15 canSeekToEnd : false 16 datasize : 932906 17 videosize : 787866 18 audiosize : 140052 19 lasttimestamp : 34 20 lastkeyframetimestamp: 30 21 lastkeyframelocation: 886498 22 encoder : Lavf55.19.104 23 Duration: 00:00:34.20, start: 0.042000, bitrate: 394 kb/s 24 Stream #0:0: Video: h264 (High), yuv420p, 512x288 [SAR 1:1 DAR 16:9], 15.17 fps, 15 tbr, 1k tbn, 30 tbc 25 Stream #0:1: Audio: mp3, 44100 Hz, stereo, s16p, 128 kb/s 26 Output #0, mp4, to \'cuc_ieschool1.mp4\': 27 Stream #0:0: Video: h264, yuv420p, 512x288 [SAR 1:1 DAR 16:9], q=2-31, 90k tbn, 30 tbc 28 Stream #0:1: Audio: mp3, 44100 Hz, stereo, s16p, 128 kb/s 29 Write 0 frames to output file 30 Write 1 frames to output file 31 Write 2 frames to output file 32 Write 3 frames to output file 33 . 34 . 35 . 36 37 * Created : 2017.09.21. 38 * Author : Yu Weifeng 39 * Function List : 40 * Last Modified : 41 * History : 42 * Modify Date Version Author Modification 43 * ----------------------------------------------- 44 * 2017/09/21 V1.0.0 Yu Weifeng Created 45 ******************************************************************************/ 46 #include <stdio.h> 47 48 49 /* 50 __STDC_LIMIT_MACROS and __STDC_CONSTANT_MACROS are a workaround to allow C++ programs to use stdint.h 51 macros specified in the C99 standard that aren\'t in the C++ standard. The macros, such as UINT8_MAX, INT64_MIN, 52 and INT32_C() may be defined already in C++ applications in other ways. To allow the user to decide 53 if they want the macros defined as C99 does, many implementations require that __STDC_LIMIT_MACROS 54 and __STDC_CONSTANT_MACROS be defined before stdint.h is included. 55 56 This isn\'t part of the C++ standard, but it has been adopted by more than one implementation. 57 */ 58 #define __STDC_CONSTANT_MACROS 59 60 61 #ifdef _WIN32//Windows 62 extern "C" 63 { 64 #include "libavformat/avformat.h" 65 }; 66 #else//Linux... 67 #ifdef __cplusplus 68 extern "C" 69 { 70 #endif 71 #include <libavformat/avformat.h> 72 #ifdef __cplusplus 73 }; 74 #endif 75 #endif 76 77 /***************************************************************************** 78 -Fuction : main 79 -Description : main 80 -Input : 81 -Output : 82 -Return : 83 * Modify Date Version Author Modification 84 * ----------------------------------------------- 85 * 2017/09/21 V1.0.0 Yu Weifeng Created 86 ******************************************************************************/ 87 int main(int argc, char* argv[]) 88 { 89 AVOutputFormat * ptOutputFormat = NULL;//The output container format.Muxing only, must be set by the caller before avformat_write_header(). 90 AVFormatContext * ptInFormatContext = NULL;//输入文件的封装格式上下文,内部包含所有的视频信息 91 AVFormatContext * ptOutFormatContext = NULL;//输出文件的封装格式上下文,内部包含所有的视频信息 92 AVPacket tOutPacket ={0};//存储一帧压缩编码数据给输出文件 93 const char * strInFileName=NULL, * strOutFileName = NULL;//输入文件名和输出文件名 94 int iRet, i; 95 int iFrameCount = 0;//输出的帧个数 96 AVStream * ptInStream=NULL,* ptOutStream=NULL;//输入音视频流和输出音视频流 97 98 if(argc!=3)//argc包括argv[0]也就是程序名称 99 { 100 printf("Usage:%s InputFileURL OutputFileURL\\r\\n",argv[0]); 101 printf("For example:\\r\\n"); 102 printf("%s InputFile.flv OutputFile.mp4\\r\\n",argv[0]); 103 return -1; 104 } 105 strInFileName = argv[1];//Input file URL 106 strOutFileName = argv[2];//Output file URL 107 108 av_register_all();//注册FFmpeg所有组件 109 110 /*------------Input------------*/ 111 if ((iRet = avformat_open_input(&ptInFormatContext, strInFileName, 0, 0)) < 0) 112 {//打开输入视频文件 113 printf("Could not open input file\\r\\n"); 114 } 115 else 116 { 117 if ((iRet = avformat_find_stream_info(ptInFormatContext, 0)) < 0) 118 {//获取视频文件信息 119 printf("Failed to find input stream information\\r\\n"); 120 } 121 else 122 { 123 av_dump_format(ptInFormatContext, 0, strInFileName, 0);//手工调试的函数,内部是log,输出相关的格式信息到log里面 124 125 /*------------Output------------*/ 126 127 /*初始化一个用于输出的AVFormatContext结构体 128 *ctx:函数调用成功之后创建的AVFormatContext结构体。 129 *oformat:指定AVFormatContext中的AVOutputFormat,用于确定输出格式。如果指定为NULL, 130 可以设定后两个参数(format_name或者filename)由FFmpeg猜测输出格式。 131 PS:使用该参数需要自己手动获取AVOutputFormat,相对于使用后两个参数来说要麻烦一些。 132 *format_name:指定输出格式的名称。根据格式名称,FFmpeg会推测输出格式。输出格式可以是“flv”,“mkv”等等。 133 *filename:指定输出文件的名称。根据文件名称,FFmpeg会推测输出格式。文件名称可以是“xx.flv”,“yy.mkv”等等。 134 函数执行成功的话,其返回值大于等于0 135 */ 136 avformat_alloc_output_context2(&ptOutFormatContext, NULL, NULL, strOutFileName); 137 if (!ptOutFormatContext) 138 { 139 printf("Could not create output context\\r\\n"); 140 iRet = AVERROR_UNKNOWN; 141 } 142 else 143 { 144 ptOutputFormat = ptOutFormatContext->oformat; 145 for (i = 0; i < ptInFormatContext->nb_streams; i++) 146 { 147 //Create output AVStream according to input AVStream 148 ptInStream = ptInFormatContext->streams[i]; 149 ptOutStream = avformat_new_stream(ptOutFormatContext, ptInStream->codec->codec);//给ptOutFormatContext中的流数组streams中的 150 if (!ptOutStream) //一条流(数组中的元素)分配空间,也正是由于这里分配了空间,后续操作直接拷贝编码数据(pkt)就可以了。 151 { 152 printf("Failed allocating output stream\\r\\\\n"); 153 iRet = AVERROR_UNKNOWN; 154 break; 155 } 156 else 157 { 158 if (avcodec_copy_context(ptOutStream->codec, ptInStream->codec) < 0) //Copy the settings of AVCodecContext 159 { 160 printf("Failed to copy context from input to output stream codec context\\r\\n"); 161 iRet = AVERROR_UNKNOWN; 162 break; 163 } 164 else 165 { 166 ptOutStream->codec->codec_tag = 0; 167 if (ptOutFormatContext->oformat->flags & AVFMT_GLOBALHEADER) 168 ptOutStream->codec->flags |= CODEC_FLAG_GLOBAL_HEADER; 169 170 } 171 } 172 } 173 if(AVERROR_UNKNOWN == iRet) 174 { 175 } 176 else 177 { 178 av_dump_format(ptOutFormatContext, 0, strOutFileName, 1);//Output information------------------ 179 //Open output file 180 if (!(ptOutputFormat->flags & AVFMT_NOFILE)) 181 { /*打开FFmpeg的输入输出文件,使后续读写操作可以执行 182 *s:函数调用成功之后创建的AVIOContext结构体。 183 *url:输入输出协议的地址(文件也是一种“广义”的协议,对于文件来说就是文件的路径)。 184 *flags:打开地址的方式。可以选择只读,只写,或者读写。取值如下。 185 AVIO_FLAG_READ:只读。AVIO_FLAG_WRITE:只写。AVIO_FLAG_READ_WRITE:读写。*/ 186 iRet = avio_open(&ptOutFormatContext->pb, strOutFileName, AVIO_FLAG_WRITE); 187 if (iRet < 0) 188 { 189 printf("Could not open output file %s\\r\\n", strOutFileName); 190 } 191 else 192 { 193 //Write file header 194 if (avformat_write_header(ptOutFormatContext, NULL) < 0) //avformat_write_header()中最关键的地方就是调用了AVOutputFormat的write_header() 195 {//不同的AVOutputFormat有不同的write_header()的实现方法 196 printf("Error occurred when opening output file\\r\\n"); 197 } 198 else 199 { 200 while (1) 201 { 202 //Get an AVPacket 203 iRet = av_read_frame(ptInFormatContext, &tOutPacket);//从输入文件读取一帧压缩数据 204 if (iRet < 0) 205 break; 206 207 ptInStream = ptInFormatContext->streams[tOutPacket.stream_index]; 208 ptOutStream = ptOutFormatContext->streams[tOutPacket.stream_index]; 209 //Convert PTS/DTS 210 tOutPacket.pts = av_rescale_q_rnd(tOutPacket.pts, ptInStream->time_base, ptOutStream->time_base, (AVRounding)(AV_ROUND_NEAR_INF | AV_ROUND_PASS_MINMAX)); 211 tOutPacket.dts = av_rescale_q_rnd(tOutPacket.dts, ptInStream->time_base, ptOutStream->time_base, (AVRounding)(AV_ROUND_NEAR_INF | AV_ROUND_PASS_MINMAX)); 212 tOutPacket.duration = av_rescale_q(tOutPacket.duration, ptInStream->time_base, ptOutStream->time_base); 213 tOutPacket.pos = -1; 214 //Write 215 /*av_interleaved_write_frame包括interleave_packet()以及write_packet(),将还未输出的AVPacket输出出来 216 *write_packet()函数最关键的地方就是调用了AVOutputFormat中写入数据的方法。write_packet()实际上是一个函数指针, 217 指向特定的AVOutputFormat中的实现函数*/ 218 if (av_interleaved_write_frame(ptOutFormatContext, &tOutPacket) < 0) 219 { 220 printf("Error muxing packet\\r\\n"); 221 break; 222 } 223 printf("Write %8d frames to output file\\r\\n", iFrameCount); 224 av_free_packet(&tOutPacket);//释放空间 225 iFrameCount++; 226 } 227 //Write file trailer//av_write_trailer()中最关键的地方就是调用了AVOutputFormat的write_trailer() 228 av_write_trailer(ptOutFormatContext);//不同的AVOutputFormat有不同的write_trailer()的实现方法 229 } 230 if (ptOutFormatContext && !(ptOutputFormat->flags & AVFMT_NOFILE)) 231 avio_close(ptOutFormatContext->pb);//该函数用于关闭一个AVFormatContext->pb,一般情况下是和avio_open()成对使用的。 232 } 233 } 234 } 235 avformat_free_context(ptOutFormatContext);//释放空间 236 } 237 } 238 avformat_close_input(&ptInFormatContext);//该函数用于关闭一个AVFormatContext,一般情况下是和avformat_open_input()成对使用的。 239 } 240 return 0; 241 }
具体代码见github:
https://github.com/fengweiyu/FFmpegFormat/FFmpegRemuxer
三、FFmpeg的封装格式处理:视音频复用器(muxer)
1.封装格式处理
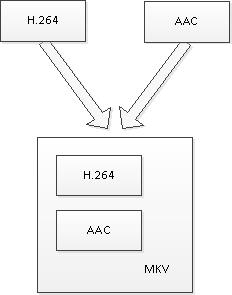
视音频复用器(Muxer)即是将视频压缩数据(例如H.264)和音频压缩数据(例如AAC)合并到一个封装格式数据(例如MKV)中去。
如图3所示。在这个过程中并不涉及到编码和解码。
2.基于FFmpeg的muxer的流程图
程序的流程如下图4所示。从流程图中可以看出,一共初始化了3个AVFormatContext,其中2个用于输入,1个用于输出。3个AVFormatContext初始化之后,通过avcodec_copy_context()函数可以将输入视频/音频的参数拷贝至输出视频/音频的AVCodecContext结构体。
然后分别调用视频输入流和音频输入流的av_read_frame(),从视频输入流中取出视频的AVPacket,音频输入流中取出音频的AVPacket,分别将取出的AVPacket写入到输出文件中即可。
其间用到了一个不太常见的函数av_compare_ts(),是比较时间戳用的。通过该函数可以决定该写入视频还是音频。
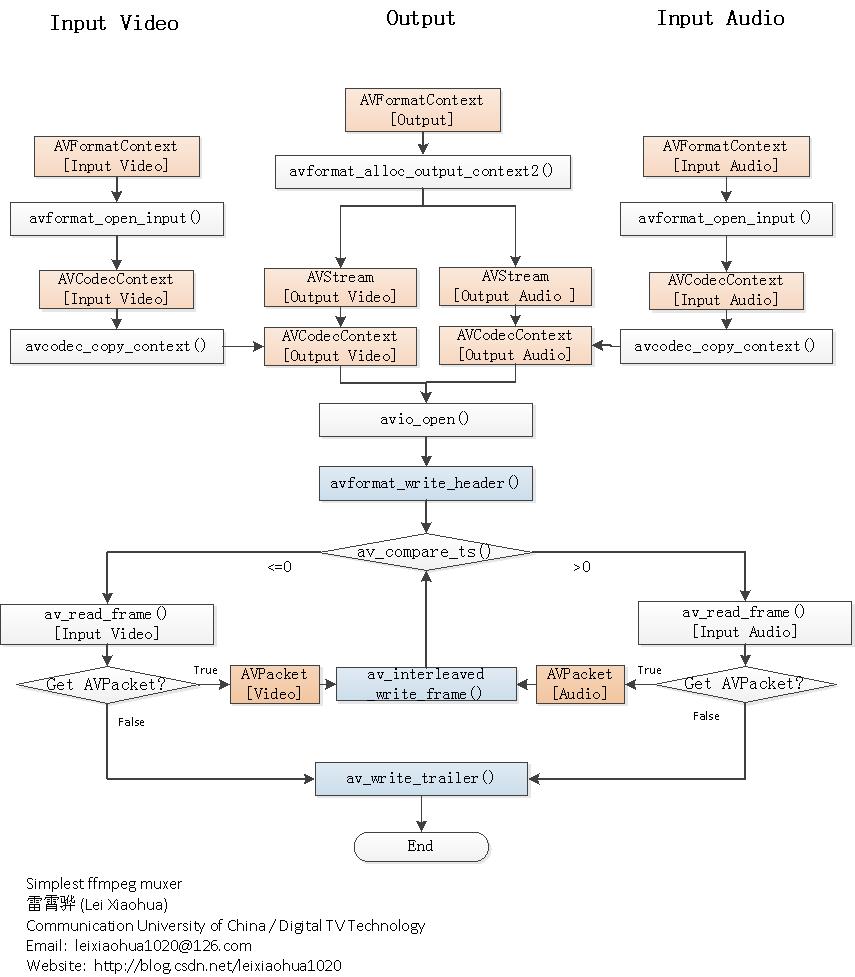
本文介绍的视音频复用器,输入的视频不一定是H.264裸流文件,音频也不一定是纯音频文件。可以选择两个封装过的视音频文件作为输入。程序会从视频输入文件中“挑”出视频流,音频输入文件中“挑”出音频流,再将“挑选”出来的视音频流复用起来。
PS1:对于某些封装格式(例如MP4/FLV/MKV等)中的H.264,需要用到名称为“h264_mp4toannexb”的bitstream filter。
PS2:对于某些封装格式(例如MP4/FLV/MKV等)中的AAC,需要用到名称为“aac_adtstoasc”的bitstream filter。
简单介绍一下流程中各个重要函数的意义:
avformat_open_input():打开输入文件。
avcodec_copy_context():赋值AVCodecContext的参数。
avformat_alloc_output_context2():初始化输出文件。
avio_open():打开输出文件。
avformat_write_header():写入文件头。
av_compare_ts():比较时间戳,决定写入视频还是写入音频。这个函数相对要少见一些。
av_read_frame():从输入文件读取一个AVPacket。
av_interleaved_write_frame():写入一个AVPacket到输出文件。
av_write_trailer():写入文件尾。
3.优化为可以从内存中读取音视频数据
打开文件的函数是avformat_open_input(),直接将文件路径或者流媒体URL的字符串传递给该函数就可以了。
但其是否支持从内存中读取数据呢?
分析ffmpeg的源代码,发现其竟然是可以从内存中读取数据的,代码很简单,如下所示:
ptInFormatContext = avformat_alloc_context();
pbIoBuf = (unsigned char *)av_malloc(IO_BUFFER_SIZE);
ptAVIO = avio_alloc_context(pbIoBuf, IO_BUFFER_SIZE, 0, NULL, FillIoBuffer, NULL, NULL);
ptInFormatContext->pb = ptAVIO;
ptInputFormat = av_find_input_format("h264");//得到ptInputFormat以便后面打开使用
if ((iRet = avformat_open_input(&ptInFormatContext, "", ptInputFormat, NULL)) < 0)
{
printf("Could not open input file\\r\\n");
}
else
{
}
关键要在avformat_open_input()之前初始化一个AVIOContext,而且将原本的AVFormatContext的指针pb(AVIOContext类型)指向这个自行初始化AVIOContext。
当自行指定了AVIOContext之后,avformat_open_input()里面的URL参数就不起作用了。示例代码开辟了一块空间iobuffer作为AVIOContext的缓存。
FillIoBuffer则是将数据读取至iobuffer的回调函数。FillIoBuffer()形式(参数,返回值)是固定的,是一个回调函数,如下所示(只是个例子,具体怎么读取数据可以自行设计)。
示例中回调函数将文件中的内容通过fread()读入内存。
int FillIoBuffer(void *opaque, unsigned char *o_pbBuf, int i_iMaxSize)
{
int iRet=-1;
if (!feof(g_fileH264))
{
iRet = fread(o_pbBuf, 1, i_iMaxSize, g_fileH264);
}
else
{
}
return iRet;
}
整体结构大致如下:
FILE *fp_open;
int fill_iobuffer(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size){
...
}
int main(){
...
fp_open=fopen("test.h264","rb+");
AVFormatContext *ic = NULL;
ic = avformat_alloc_context();
unsigned char * iobuffer=(unsigned char *)av_malloc(32768);
AVIOContext *avio =avio_alloc_context(iobuffer, 32768,0,NULL,fill_iobuffer,NULL,NULL);
ic->pb=avio;
err = avformat_open_input(&ic, "nothing", NULL, NULL);
...//解码
}
4.将音视频数据输出到内存
同时再说明一下,和从内存中读取数据类似,ffmpeg也可以将处理后的数据输出到内存。
回调函数如下示例,可以将输出到内存的数据写入到文件中。
//写文件的回调函数
int write_buffer(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size){
if(!feof(fp_write)){
int true_size=fwrite(buf,1,buf_size,fp_write);
return true_size;
}else{
return -1;
}
}
主函数如下所示:
FILE *fp_write;
int write_buffer(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size){
...
}
main(){
...
fp_write=fopen("src01.h264","wb+"); //输出文件
...
AVFormatContext* ofmt_ctx=NULL;
avformat_alloc_output_context2(&ofmt_ctx, NULL, "h264", NULL);
unsigned char* outbuffer=(unsigned char*)av_malloc(32768);
AVIOContext *avio_out =avio_alloc_context(outbuffer, 32768,0,NULL,NULL,write_buffer,NULL);
ofmt_ctx->pb=avio_out;
ofmt_ctx->flags=AVFMT_FLAG_CUSTOM_IO;
...
}
从上述可以很明显的看到,知道把写回调函数放到avio_alloc_context函数对应的位置就可以了。
四、FFmpegMuxer代码
基于FFmpeg的视音频复用器,取了个名字称为FFmpegMuxer
主要是FFmpegMuxer.cpp文件,代码如下(基本上每一行都有注释):

1 /***************************************************************************** 2 * Copyright (C) 2017-2020 Hanson Yu All rights reserved. 3 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 4 * File Module : FFmpegMuxer.cpp 5 * Description : FFmpegMuxer Demo 6 7 *先将H.264文件读入内存, 8 *再输出封装格式文件。 9 10 输出结果: 11 book@book-desktop:/work/project/FFmpegMuxer$ make clean;make 12 rm FFmpegMuxer 13 g++ FFmpegMuxer.cpp -I ./include -rdynamic ./lib/libavformat.so.57 ./lib/libavcodec.so.57 ./lib/libavutil.so.55 ./lib/libswresample.so.2 -o FFmpegMuxer 14 book@book-desktop:/work/project/FFmpegMuxer$ export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=./lib 15 book@book-desktop:/work/project/FFmpegMuxer$ ./FFmpegMuxer sintel.h264 sintel.mp4 16 Input #0, h264, from \'sintel.h264\': 17 Duration: N/A, bitrate: N/A 18 Stream #0:0: Video: h264 (High), yuv420p(progressive), 640x360, 25 fps, 25 tbr, 1200k tbn, 50 tbc 19 Output #0, mp4, to \'sintel.mp4\': 20 Stream #0:0: Unknown: none 21 [mp4 @ 0x9352d80] Using AVStream.codec.time_base as a timebase hint to the muxer is deprecated. Set AVStream.time_base instead. 22 [mp4 @ 0x9352d80] Using AVStream.codec to pass codec parameters to muxers is deprecated, use AVStream.codecpar instead. 23 Write iFrameIndex:1,stream_index:0,num:25,den:1 24 Write iFrameIndex:2,stream_index:0,num:25,den:1 25 Write iFrameIndex:3,stream_index:0,num:25,den:1 26 . 27 . 28 . 29 30 * Created : 2017.09.21. 31 * Author : Yu Weifeng 32 * Function List : 33 * Last Modified : 34 * History : 35 * Modify Date Version Author Modification 36 * ----------------------------------------------- 37 * 2017/09/21 V1.0.0 Yu Weifeng Created 38 ******************************************************************************/ 39 #include <stdio.h> 40 41 42 /* 43 __STDC_LIMIT_MACROS and __STDC_CONSTANT_MACROS are a workaround to allow C++ programs to use stdint.h 44 macros specified in the C99 standard that aren\'t in the C++ standard. The macros, such as UINT8_MAX, INT64_MIN, 45 and INT32_C() may be defined already in C++ applications in other ways. To allow the user to decide 46 if they want the macros defined as C99 does, many implementations require that __STDC_LIMIT_MACROS 47 and __STDC_CONSTANT_MACROS be defined before stdint.h is included. 48 49 This isn\'t part of the C++ standard, but it has been adopted by more than one implementation. 50 */ 51 #define __STDC_CONSTANT_MACROS 52 53 54 #ifdef _WIN32//Windows 55 extern "C" 56 { 57 #include "libavformat/avformat.h" 58 }; 59 #else//Linux... 60 #ifdef __cplusplus 61 extern "C" 62 { 63 #endif 64 #include <libavformat/avformat.h> 65 #ifdef __cplusplus 66 }; 67 #endif 68 #endif 69 70 #define IO_BUFFER_SIZE 32768 //缓存32k 71 72 static FILE * g_fileH264=NULL; 73 74 75 /***************************************************************************** 76 -Fuction : FillIoBuffer 77以上是关于音视频处理之FFmpeg封装格式20180510的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
