第十周课下补做
课程知识点总结
-
在数据结构和算法中,排序是很重要的操作,要让一个类可以进行排序,有两种方法:
Comparable:“可比较的”,(欲参与比较的对象对应的元素类需实现Comparable接口)
使用这种策略来比较时,两个对象(这里两个对象是指一个类的两个不同实例)本身必须是“可比较的”,比较的标准由对象所在的类来定义,这种可比较的能力是对象本身固有的,因此不需要第三方参与就可以完成比较。要使得两个对象本身是可比较的,那么对象所在的类必须实现Comparable接口才可以,调用Collection.sort(List)。其compareTo()方法只要一个参数,因为这里只有“你”“我”的关系,没有第三方。
比如,两个人要比较身高,分辨高矮是人类固有的能力,两个人只要站到一起就能分出谁高谁矮。Comparator:“比较器”
使用这种策略来比较时,如何进行比较和两个对象本身无关,而是由第三者(即比较器)来完成的。第三方比较器类需要另外专门设计:只要实现Comparator接口,任何一个类(对象)都可能成为一个“比较器”,但比较器并不是比较自己的实例,而是比较其它类的两个不同对象,比较器在这里充当“仲裁者”的角色,这也就是为什么compare()方法需要两个参数,调用Collection.sort(List, Compatator)。
比如,两个人要比较谁智商更高,靠他们自身无法进行,这时要借助一个比较器(比如,智商测试题)。
-
泛型类声明:
class 名称<泛型列表> -
创建链表
LinkedList<String> mylist=new LinkedList<String>(); -
向链表增加节点
list.add(E obj); -
从链表中删除节点
list.remove(index) -
升序排序
public static sort(List<E>list) -
折半查找list是否含有和参数key一样的元素
int binarySearch(List<T>,Tkey,compareTo<T>c) -
数据结构的三个组成部分:
- 逻辑结构: 数据元素之间逻辑关系的描述
- 存储结构: 数据元素在计算机中的存储及其逻辑关系的表现称为数据的存储结构或物理结构。
- 数据操作: 对数据要进行的运算
-
元素之间的相互联系(关系)称为逻辑结构。数据元素之间的逻辑结构有四种基本类型:
- 集合:结构中的数据元素除了“同属于一个集合”外,没有其它关系。
- 线性结构(1:1):结构中的数据元素之间存在一对一的关系。
- 树型结构(1:M):结构中的数据元素之间存在一对多的关系。
- 图状结构或网状结构(M:N):结构中的数据元素之间存在多对多的关系。
习题补做
排序
- 代码链接
- 实验结果截图

单链表
- 代码链接
- 实验结果截图

第十五章教材代码分析
-
- 初步接触、了解泛型。知道泛型类声明和创建对象时要用具体类型来替换“<>”中的泛型
Cone<Circle> coneOne; coneOne = new Cone<Circle>(new- 泛型中的泛型变量bottom只能调用Object类中的方法
-
- 遍历链表方法:迭代器遍历和
get(int index)方法 Iterator<String> iter=list.iterator():创建迭代器iteriter.hasNext():判断链表中下一个结点是否还存在结点iter.next():判断列表中下一个结点是否是空结点,如果不是,获取下一个结点long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis():以毫秒为单位计算遍历完链表后的时间
- 遍历链表方法:迭代器遍历和
-
- 代码通过
LinkedList mylist=new LinkedList()创建链表对象,使用add(Object obj)方法依次添加结点
- 代码通过
LinkedList mylist = new LinkedList();//创建链表对象
mylist.add("你")`; //链表中的第一个节点
mylist.add("好")`; //链表中的第二个节点
- Example15_4
- 代码实现了链表中的排序和查找,通过
Comparable接口,实现int compareTo(Object b)来规定对象的大小关系。
- 代码实现了链表中的排序和查找,通过
public int compareTo(Object b) { //两个Student对象相等当且仅当二者的height值相等
Student st=(Student)b;
return (this.height-st.height);
}
- `Collections.sort(list)`:提供用于排序和查找的方法
-
- 代码实现
Collections类的对链表数据随机排列以及旋转链表数据的方法 list.add(new Integer(i)):添加结点Collections.shuffle(list):重新随机排列Collections.rotate(list, 1):旋转链表,向右旋转一次
- 代码实现
-
- 代码实现数据结构中的堆栈,遍历采用“后进先出”
- 创建堆栈对象:Stack
- 压栈操作:
public E push(E item);
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();//建立一个堆栈对象
stack.push(new Integer(1));//压栈,第一项为1
stack.push(new Integer(1));//压栈,第二项为1
- 弹栈操作:`public E pop()`;
- 判断堆栈是否还有数据:`public boolean empty()`;
- 获取堆栈顶端的数据,但不删除该数据:`public int search(Object data)`;
Integer F1 = stack.pop();//取出栈顶对象
int f1 = F1.intValue();//得到对象的int值
Integer F2 = stack.pop();//取出栈顶对象
int f2 = F2.intValue();//得到对象的int值
- Example15_7
- 代码体现散列映射的意义,利用GUI程序查询英语单词,用WordPolice类使用Scanner解析word.txt中的单词,然后将英文单词/汉语对应键/值存储到散列映射中供用户查询。 - Example15_8
- 代码实现用树集存放数据等信息
- 创建树集对象:
TreeSet<Student> mytree = new TreeSet<Student>() - 利用add方法为树集添加结点
mytree.add(st2);
mytree.add(st3);
mytree.add(st4);
- Example15_9
- 代码使用树映射进行排序,利用TreeMap
TreeMap<StudentKey, Student> treemap = new TreeMap<StudentKey, Student>() - 使用
public V put(K key,V value)方法添加结点
treemap.put(key[k], student[k]);//向树映射中添加键/值对 - 重写compareTo方法,定义排序方法
public int compareTo(Object b) {
StudentKey st = (StudentKey) b;
if ((this.d - st.d) == 0)
return -1;
else
return (int) ((this.d - st.d) * 1000);
}
- 调用Student类添加学生信息
String str[] = {"赵一", "钱二", "孙三", "李四"};
double math[] = {89, 45, 78, 76};
double english[] = {67, 66, 90, 56};
Student student[] = new Student[4];
- Example15_10
- 代码实现自动装箱和自动拆箱
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); //创建链表
list.add(i); //自动装箱,实际添加到list中的是new Integer(i)。
int m = list.get(k); //自动拆箱,获取Integer对象中的int型数据
第十五章课后编程题
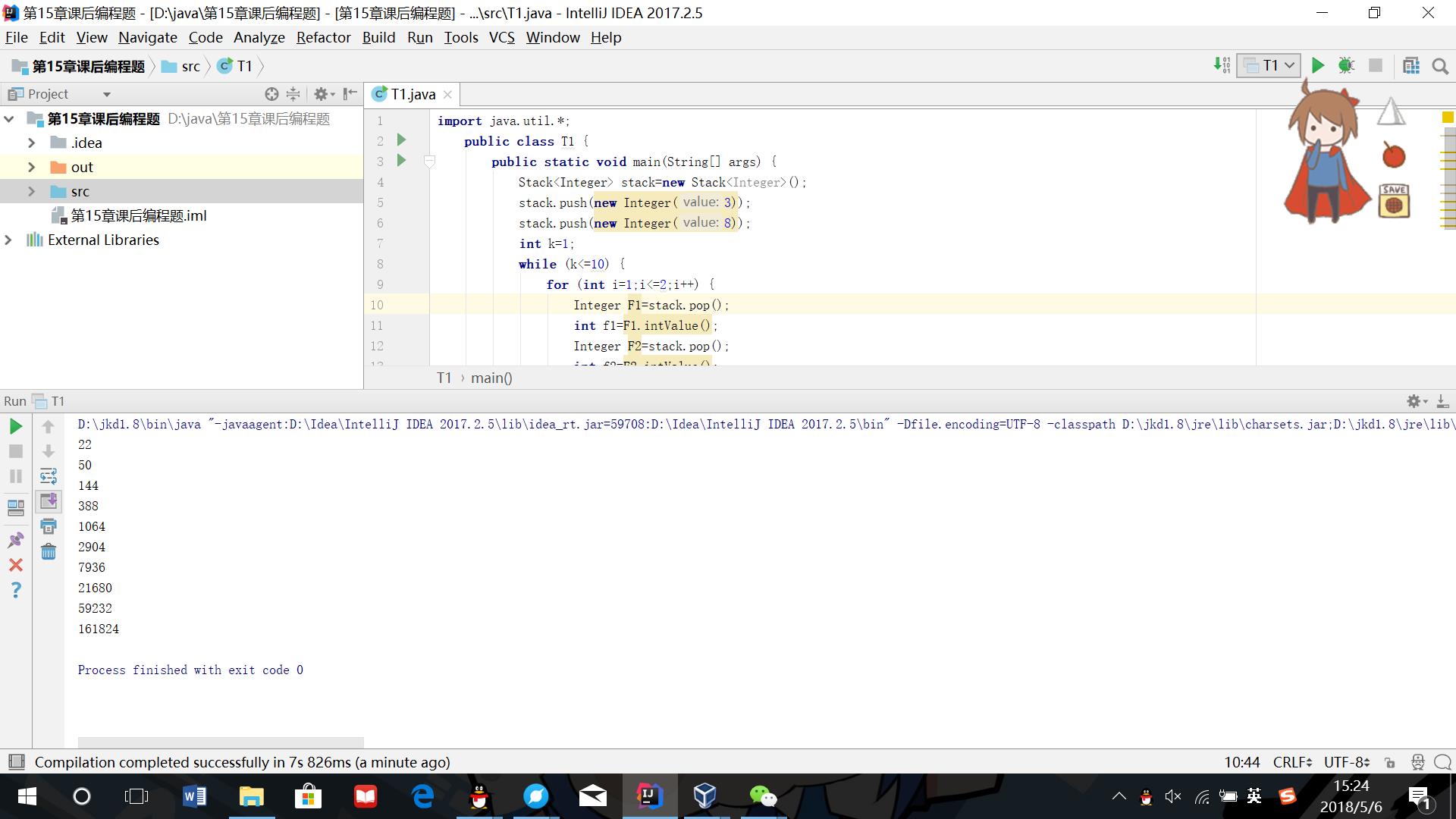
(1)使用堆栈结构输出an的若干项,其中an=2an-1+2an-2,a1=3,a2=8
- 代码:
import java.util.*;
public class T1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack<Integer>();
stack.push(new Integer(3));
stack.push(new Integer(8));
int k=1;
while (k<=10) {
for (int i=1;i<=2;i++) {
Integer F1=stack.pop();
int f1=F1.intValue();
Integer F2=stack.pop();
int f2=F2.intValue();
Integer temp= 2 * f1 + 2 * f2;
System.out.println(""+temp.toString());
stack.push(temp);
stack.push(F2);
k++;
}
}
}
}
- 运行结果截图:
(2)将链表中的学生英语成绩单存放到一个树集中,使得按成绩自动排序,并输出排序结果
- 代码:
import java.util.*;
class CollegeStu implements Comparable {
int english=0;
String name;
CollegeStu(int english,String name) {
this.name=name;
this.english=english;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object b) {
CollegeStu stu=(CollegeStu)b;
return (this.english-stu.english);
}
}
public class T2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<CollegeStu> list=new LinkedList<CollegeStu>();
int score []={ 90, 88, 80};
String name []={"张三","李四","王五"};
for (int i=0;i<score.length;i++) {
list.add(new CollegeStu(score[i],name[i]));
}
Iterator<CollegeStu> iter=list.iterator();
TreeSet<CollegeStu> mytree=new TreeSet<CollegeStu>();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
CollegeStu stu=iter.next();
mytree.add(stu);
}
Iterator<CollegeStu> te=mytree.iterator();
while (te.hasNext()) {
CollegeStu stu=te.next();
System.out.println(""+stu.name+" "+stu.english);
}
}
}
- 运行结果截图:

(3)有10个U盘,有两个重要的属性:价格和容量,编写一个应用程序,使用TreeMap<K,V>类,分别按照价格和容量排序输出10个U盘的详细信息。
- 代码:
import java.util.*;
class UDiscKey implements Comparable {
double key=0;
UDiscKey(double d) {
key=d;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object b) {
UDiscKey disc=(UDiscKey)b;
if((this.key-disc.key)==0) {
return -1;
}
else {
return (int) ((this.key - disc.key) * 1000);
}
}
}
class UDisc{
int amount;
double price;
UDisc(int m,double e) {
amount=m;
price=e;
}
}
public class T3 {
public static void main(String args[ ]) {
TreeMap<UDiscKey,UDisc> treemap= new TreeMap<UDiscKey,UDisc>();
int amount[]={8,16,32,64};
double price[]={40,50,64,128};
UDisc UDisc[]=new UDisc[4];
for(int k=0;k<UDisc.length;k++) {
UDisc[k]=new UDisc(amount[k],price[k]);
}
UDiscKey key[]=new UDiscKey[4] ;
for(int k=0;k<key.length;k++) {
key[k]=new UDiscKey(UDisc[k].amount);
}
for(int k=0;k<UDisc.length;k++) {
treemap.put(key[k],UDisc[k]);
}
int number=treemap.size();
Collection<UDisc> collection=treemap.values();
Iterator<UDisc> iter=collection.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
UDisc disc=iter.next();
System.out.println(""+disc.amount+"G "+disc.price+"元");
}
treemap.clear();
for(int k=0;k<key.length;k++) {
key[k]=new UDiscKey(UDisc[k].price);
}
for(int k=0;k<UDisc.length;k++) {
treemap.put(key[k],UDisc[k]);
}
number=treemap.size();
collection=treemap.values();
iter=collection.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()) {
UDisc disc=iter.next();
System.out.println(""+disc.amount+"G "+disc.price+"元");
}
}
}
- 运行结果截图:
