Qt与FFmpeg联合开发指南——编码:代码流程演示
Posted 思踌之路
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Qt与FFmpeg联合开发指南——编码:代码流程演示相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前两讲演示了基本的解码流程和简单功能封装,今天我们开始学习编码。编码就是封装音视频流的过程,在整个编码教程中,我会首先在一个函数中演示完成的编码流程,再解释其中存在的问题。下一讲我们会将编码功能进行封装并解释针对不同的输出环境代码上需要注意的地方。最后我们还会把之前做好的解码器添加进开发环境,实现PC屏幕和摄像头录制然后再通过播放器播放。
首先说明一下本章的目标:
- 通过Qt进行视频采集
- 通过Qt进行音频采集
- 对音视频编码成mp4文件并能够通过vlc播放
一、通过Qt进行视频采集
Qt提供了对桌面录屏的支持,我们可以很轻松的完成开发
// 首先获取到完整桌面的窗口句柄已经宽高信息 WId wid = QApplication::desktop()->winId(); int width = QApplication::desktop()->width(); int height = QApplication::desktop()->height(); // 截屏获得图片 static QScreen *screen = NULL; if (!screen) { screen = QGuiApplication::primaryScreen(); } QPixmap pix = screen->grabWindow(wid); const uchar *rgb = pix.toImage().bits();
这里有一点需要特别注意,当我们把上面的代码封装进函数以后,我们无法直接通过返回值获取到rgb数据。这个地方曾经卡了我好几天,原因在于经过grabWindow(wid)函数获取到的QPixmap对象是属于函数的局部变量,在函数结束以后这个该变量包括bits()包含的数据都会被清理掉。所以如果我们想在函数外部继续使用图片数据就必须对QImage进行一次深拷贝。我提供两条思路,一是直接将QImage对象进行深拷贝,然后使用它的bits()数据。但是这样的话如果我们只在外部析构bits()中的数据其实对内存的清理工作并不完整。另一个方法是我们直接对bits()里的数据进行拷贝,但是由于QImage对图片的保存数据并非是连续的寻址空间所以我们需要做一次转换。为了方便起见我们先按照第一种思路设计。
const uchar* VideoAcquisition::getRGB() { static QScreen *screen = NULL; if (!screen) { screen = QGuiApplication::primaryScreen(); } WId wid = QApplication::desktop()->winId(); int width = QApplication::desktop()->width(); int height = QApplication::desktop()->height(); QPixmap pix = screen->grabWindow(wid); QImage *image = new QImage(pix.toImage().copy(0, 0, width, height)); return image->bits(); }
二、通过Qt进行音频采集
与视频采集的图片不同,音频数据对应的是一段时间的录音。虽然Qt也提供了统一的音频录制接口,不过我们首先需要对录音设备进行初始化。主要是设置录音的参数和控制每次从音频缓存中读取的数据大小。这里我们以CD音质为标准,即采样率:44100Hz,通道数:2,采样位数:16bit,编码格式:audio/pcm。
首先初始化一个录音设备:QIODevice
QAudioFormat fmt; fmt.setSampleRate(44100); fmt.setChannelCount(2); fmt.setSampleSize(16); // 采样大小 = 采样位数 * 8 fmt.setSampleType(QAudioFormat::UnSignedInt); fmt.setByteOrder(QAudioFormat::LittleEndian); fmt.setCodec("audio/pcm"); QAudioInput *audioInput = new QAudioInput(fmt); QIODevice *device = audioInput->start();
假设我们每次从音频缓存中读取1024个采样点的数据,已知采样的其它条件为双通道和每个采样点两位。则我们用于保存数据的数组大小为:char *pcm = new char[1024 * 2 * 2]
const char* AudioAcquisition::getPCM() { int readOnceSize = 1024; // 每次从音频设备中读取的数据大小 int offset = 0; // 当前已经读到的数据大小,作为pcm的偏移量 int pcmSize = 1024 * 2 * 2; char *pcm = new char[pcmSize]; while (audioInput) { int remains = pcmSize - offset; // 剩余空间 int ready = audioInput->bytesReady(); // 音频采集设备目前已经准备好的数据大小 if (ready < readOnceSize) { // 当前音频设备中的数据不足 QThread::msleep(1); continue; } if (remains < readOnceSize) { // 当帧存储(pcmSize)的剩余空间(remainSize)小于单次读取数据预设(readSizeOnce)时 device->read(pcm + offset, remains); // 从设备中读取剩余空间大小的数据 // 读满一帧数据退出 break; } int len = device->read(pcm + offset, readOnceSize); offset += len; } return pcm; }
完成了音视频采集工作以后,接下来是本章的重点——编码——也就是调用FFmpeg库的过程。
三、对音视频编码成mp4文件
(1)初始化FFmpeg
av_register_all();
avcodec_register_all();
avformat_network_init();
(2)设置三个参数分别用于保存错误代码、错误信息和输出文件路径
int errnum = 0; char errbuf[1024] = { 0 }; char *filename = "D:/test.mp4"; // 视频采集对象 VideoAcquisition *va = new VideoAcquisition(); // 音频采集对象 AudioAcquisition *aa = new AudioAcquisition();
(3)创建输出的包装器
AVFormatContext *pFormatCtx = NULL; errnum = avformat_alloc_output_context2(&pFormatCtx, NULL, NULL, filename); if (errnum < 0) { av_strerror(errnum, errbuf, sizeof(errbuf)); }
(4)创建这对h264的编码器和编码器上下文,并向编码器上下文中配置参数
// h264视频编码器 const AVCodec *vcodec = avcodec_find_encoder(AVCodecID::AV_CODEC_ID_H264); if (!vcodec) { cout << "avcodec_find_encoder failed!" << endl; } // 创建编码器上下文 AVCodecContext *pVideoCodecCtx = avcodec_alloc_context3(vcodec); if (!pVideoCodecCtx) { cout << "avcodec_alloc_context3 failed!" << endl; } // 比特率、宽度、高度 pVideoCodecCtx->bit_rate = 4000000; pVideoCodecCtx->width = va->getWidth(); // 视频宽度 pVideoCodecCtx->height = va->getHeight(); // 视频高度 // 时间基数、帧率 pVideoCodecCtx->time_base = { 1, 25 }; pVideoCodecCtx->framerate = { 25, 1 }; // 关键帧间隔 pVideoCodecCtx->gop_size = 10; // 不使用b帧 pVideoCodecCtx->max_b_frames = 0; // 帧、编码格式 pVideoCodecCtx->pix_fmt = AVPixelFormat::AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P; pVideoCodecCtx->codec_id = AVCodecID::AV_CODEC_ID_H264; // 预设:快速 av_opt_set(pVideoCodecCtx->priv_data, "preset", "superfast", 0); // 全局头 pVideoCodecCtx->flags |= AV_CODEC_FLAG_GLOBAL_HEADER;
(5)开启编码器
errnum = avcodec_open2(pVideoCodecCtx, vcodec, NULL); if (errnum < 0) { cout << "avcodec_open2 failed!" << endl; }
(6)为封装器创建视频流
// 为封装器创建视频流 AVStream *pVideoStream = avformat_new_stream(pFormatCtx, NULL); if (!pVideoStream) { cout << "avformat_new_stream video stream failed!" << endl; } pVideoStream->codec->codec_tag = 0; pVideoStream->codecpar->codec_tag = 0; // 配置视频流的编码参数 avcodec_parameters_from_context(pVideoStream->codecpar, pVideoCodecCtx);
(7)创建从RGB格式到YUV420格式的转码器
SwsContext *pSwsCtx = sws_getContext( va->getWidth(), va->getHeight(), AVPixelFormat::AV_PIX_FMT_BGRA, // 输入 va->getWidth(), va->getHeight(), AVPixelFormat::AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P, // 输出 SWS_BICUBIC, // 算法 0, 0, 0); if (!pSwsCtx) { cout << "sws_getContext failed" << endl; }
(8)初始化一个视频帧的对象并分配空间
// 编码阶段的视频帧结构 AVFrame *vframe = av_frame_alloc(); vframe->format = AVPixelFormat::AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P; vframe->width = va->getWidth(); vframe->height = va->getHeight(); vframe->pts = 0; // 为视频帧分配空间 errnum = av_frame_get_buffer(vframe, 32); if (errnum < 0) { cout << "av_frame_get_buffer failed" << endl; }
以上8个步骤是对视频部分的代码演示,下面是音频部分。基本的操作过程和视频一致。
(9)创建aac的音频编码器和编码器上下文
// 创建音频编码器,指定类型为AAC const AVCodec *acodec = avcodec_find_encoder(AVCodecID::AV_CODEC_ID_AAC); if (!acodec) { cout << "avcodec_find_encoder failed!" << endl; } // 根据编码器创建编码器上下文 AVCodecContext *pAudioCodecCtx = avcodec_alloc_context3(acodec); if (!pAudioCodecCtx) { cout << "avcodec_alloc_context3 failed!" << endl; } // 比特率、采样率、采样类型、音频通道、文件格式 pAudioCodecCtx->bit_rate = 64000; pAudioCodecCtx->sample_rate = 44100; pAudioCodecCtx->sample_fmt = AVSampleFormat::AV_SAMPLE_FMT_FLTP; pAudioCodecCtx->channels = 2; pAudioCodecCtx->channel_layout = av_get_default_channel_layout(2); // 根据音频通道数自动选择输出类型(默认为立体声) pAudioCodecCtx->flags |= AV_CODEC_FLAG_GLOBAL_HEADER;
(10)开启编码器
// 打开编码器 errnum = avcodec_open2(pAudioCodecCtx, acodec, NULL); if (errnum < 0) { avcodec_free_context(&pAudioCodecCtx); cout << "avcodec_open2 failed" << endl; }
(11)向封装器添加音频流
// 添加音频流 AVStream *pAudiostream = avformat_new_stream(pFormatCtx, NULL); if (!pAudioStream) { cout << "avformat_new_stream failed" << endl; return -1; } pAudioStream->codec->codec_tag = 0; pAudioStream->codecpar->codec_tag = 0; // 配置音频流的编码器参数 avcodec_parameters_from_context(pAudioStream->codecpar, pAudioCodecCtx);
(12)创建从FLTP到S16的音频重采样上下文
SwrContext *swrCtx = NULL; swrCtx = swr_alloc_set_opts(swrCtx, av_get_default_channel_layout(2), AVSampleFormat::AV_SAMPLE_FMT_FLTP, 44100, // 输出 av_get_default_channel_layout(2), AVSampleFormat::AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16, 44100, // 输入 0, 0); errnum = swr_init(swrCtx); if (errnum < 0) { cout << "swr_init failed" << endl; }
(13)初始化音频帧的结构
// 创建音频帧 AVFrame *aframe = av_frame_alloc(); aframe->format = AVSampleFormat::AV_SAMPLE_FMT_FLTP; aframe->channels = 2; aframe->channel_layout = av_get_default_channel_layout(2); aframe->nb_samples = 1024; // 为音频帧分配空间 errnum = av_frame_get_buffer(aframe, 0); if (errnum < 0) { cout << "av_frame_get_buffer failed" << endl; }
音频部分的代码演示完成。下面是开启输出流,并循环进行音视频采集编码。
(14)打开输出的IO
// 打开输出流IO errnum = avio_open(&pFormatCtx->pb, filename, AVIO_FLAG_WRITE); // 打开AVIO流 if (errnum < 0) { avio_close(pFormatCtx->pb); cout << "avio_open failed" << endl; }
(15)写头文件
// 写文件头 errnum = avformat_write_header(pFormatCtx, NULL); if (errnum < 0) { cout << "avformat_write_header failed" << endl; }
(16)编码并将数据写入文件,由于我们还没有设计出控制功能,暂且只编码200帧视频帧。按25帧/秒计算,应该生成长度为8秒视频文件。可由于缓存的缘故,最后往往会丢几帧数据。因此实际长度不足8秒。
int vpts = 0; int apts = 0; while (vpts < 200) { // 视频编码 const uchar *rgb = va->getRGB(); // 固定写法:配置1帧原始视频画面的数据结构通常为RGBA的形式 uint8_t *srcSlice[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS] = { 0 }; srcSlice[0] = (uint8_t *)rgb; int srcStride[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS] = { 0 }; srcStride[0] = va->getWidth() * 4; // 转换 int h = sws_scale(pSwsCtx, srcSlice, srcStride, 0, va->getHeight(), vframe->data, vframe->linesize); if (h < 0) { cout << "sws_scale failed" << endl; break; } // pts递增 vframe->pts = vpts++; errnum = avcodec_send_frame(pVideoCodecCtx, vframe); if (errnum < 0) { cout << "avcodec_send_frame failed" << endl; continue; } // 视频编码报文 AVPacket *vpkt = av_packet_alloc(); errnum = avcodec_receive_packet(pVideoCodecCtx, vpkt); if (errnum < 0 || vpkt->size <= 0) { av_packet_free(&vpkt); cout << "avcodec_receive_packet failed" << endl; continue; } // 转换pts av_packet_rescale_ts(vpkt, pVideoCodecCtx->time_base, pVideoStream->time_base); vpkt->stream_index = pVideoStream->index; // 向封装器中写入压缩报文,该函数会自动释放pkt空间,不需要调用者手动释放 errnum = av_interleaved_write_frame(pFormatCtx, vpkt); if (errnum < 0) { av_strerror(errnum, errbuf, sizeof(errbuf)); cout << errbuf << endl; cout << "av_interleaved_write_frame failed" << endl; continue; } // 析构图像数据:注意这里只析构了图片的数据,实际的QImage对象还在内存中 delete rgb; // 音频编码 // 固定写法:配置一帧音频的数据结构 const char *pcm = aa->getPCM(); if (!pcm) { continue; } const uint8_t *in[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS] = { 0 }; in[0] = (uint8_t *)pcm; // 音频重采样 int len = swr_convert(swrCtx, aframe->data, aframe->nb_samples, // 输出 in, aframe->nb_samples); // 输入 if (len < 0) { cout << "swr_convert failed" << endl; continue; } // 音频编码 errnum = avcodec_send_frame(pAudioCodecCtx, aframe); if (errnum < 0) { cout << "avcodec_send_frame failed" << endl; continue; } // 音频编码报文 AVPacket *apkt = av_packet_alloc(); errnum = avcodec_receive_packet(pAudioCodecCtx, apkt); if (errnum < 0) { av_packet_free(&apkt); cout << "avcodec_receive_packet failed" << endl; continue; } apkt->stream_index = pAudioStream->index; apkt->pts = apts; apkt->dts = apts; apts += av_rescale_q(aframe->nb_samples, { 1, pAudioCodecCtx->sample_rate }, pAudioCodecCtx->time_base); // 写音频帧 errnum = av_interleaved_write_frame(pFormatCtx, apkt); if (errnum < 0) { av_strerror(errnum, errbuf, sizeof(errbuf)); cout << errbuf << endl; cout << "av_interleaved_write_frame failed" << endl; continue; } delete pcm; }
(17)写入文件尾和关闭IO
// 写入文件尾 errnum = av_write_trailer(pFormatCtx); if (errnum != 0) { cout << "av_write_trailer failed" << endl; } errnum = avio_closep(&pFormatCtx->pb); // 关闭AVIO流 if (errnum != 0) { cout << "avio_close failed" << endl; }
(18)清理
if (pFormatCtx) { avformat_close_input(&pFormatCtx); // 关闭封装上下文 } // 关闭编码器和清理上下文的所有空间 if (pVideoCodecCtx) { avcodec_close(pVideoCodecCtx); avcodec_free_context(&pVideoCodecCtx); } if (pAudioCodecCtx) { avcodec_close(pAudioCodecCtx); avcodec_free_context(&pAudioCodecCtx); } // 音视频转换上下文 if (pSwsCtx) { sws_freeContext(pSwsCtx); pSwsCtx = NULL; } if (swrCtx) { swr_free(&swrCtx); } // 清理音视频帧 if (vframe) { av_frame_free(&vframe); } if (aframe) { av_frame_free(&aframe); }
四、遗留问题
运行代码我们可以在设置的盘符下找到生成的mp4文件。查看文件属性,我们可以看到音视频数据都与我们之前的设置完全一致。也可以被播放器正常播放。
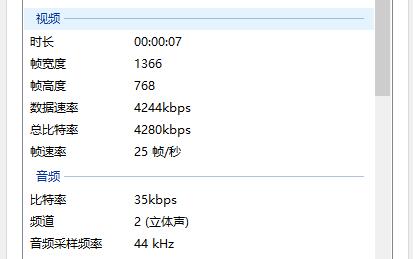
但是我们发现,音视频并不同步。另外就是视频采集的时候,QImage也没有被正确析构。我们将在下一章提供解决方案。
项目源码地址:
https://gitee.com/learnhow/ffmpeg_studio/blob/master/_64bit/src/screen_vcr_v12/demo.cpp
以上是关于Qt与FFmpeg联合开发指南——编码:代码流程演示的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章