数据验证框架 Apache BVal 简介
Posted sp42a
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据验证框架 Apache BVal 简介相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Apache BVal (源码)是实体数据验证 Java Bean Validation 的参考实现。Apache BVal 提供了 JSR 303 规范中所有内置 constraint 的实现,用于对 Bean 中的字段的值进行约束定义、描述和验证。若单单说 JSR 规范大渣可能还不清楚,但做过 POJO 的 Hibernate Validator 注解的朋友就知道是啥,——那为什么不使用主流的 Hibernate Validator 呢?因为这货净是个压缩包都已经 13mb 了(尽管可以有文档、源码其他在内),BVal 才只有 400 多 kb,而我只需要服务端验证而已,——天真的孩纸伤不起啊。俺的 ORM 也是 Mybatis 的,务求尽可能地轻量级。
Spring MVC 3.x 虽然自带了验证器 Validatior,可以在控制器中对表单提交的数据进行验证,但这个验证器是极其弱,因为你需要完全手工编码 if (null) else warn("不能空数据"),——太变态了(入下面的例子)——我们需要框架来减轻费时耗力的劳动,于是这类验证框架出现了。
import org.springframework.validation.Errors;
import org.springframework.validation.ValidationUtils;
import org.springframework.validation.Validator;
public class UserValidator implements Validator {
public boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return User.class.equals(clazz);
}
public void validate(Object obj, Errors errors) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ValidationUtils.rejectIfEmpty(errors, "username", null, "Username is empty.");
User user = (User) obj;
if (null == user.getPassword() || "".equals(user.getPassword()))
errors.rejectValue("password", null, "Password is empty.");
}
} 而我们理想的是这样的,在 POJO 身上声明验证条件的注解(Fields or Method 均可):
import javax.validation.constraints.Min;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;
public class User {
@NotNull(message = "用户名不能为空")
private String username;
private String password;
private int age;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
@NotNull(message = "密码不能为null")
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Min(value = 10, message = "年龄的最小值为10")
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
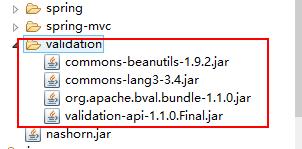
}好了,现在准备一下 BVal jar 包:
加入测试用例:
import static org.junit.Assert.assertNotNull;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.validation.ConstraintViolation;
import javax.validation.Validation;
import javax.validation.Validator;
import javax.validation.ValidatorFactory;
import org.apache.bval.jsr.ApacheValidationProvider;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.ajaxjs.business.model.News;
public class TestValidation {
@Test
public void testValid() {
News news = new News();
ValidatorFactory avf = Validation.byProvider(ApacheValidationProvider.class).configure().buildValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = avf.getValidator();
//news.setName("dsdsa");
Set<ConstraintViolation<News>> constraintViolations = validator.validate(news);
for (ConstraintViolation<News> constraintViolation : constraintViolations) {
System.out.println(constraintViolation.getMessage());
}
assertNotNull(constraintViolations);
}
}注解说明
@Vaild 是用于嵌套另外一个 pojo 的,如:
@NotNull
@Valid
private Person driver;那么,
Car car = new Car(null, "", 1);
Person driver = new Person();
car.setDriver(driver);
| Annotation | Supported data types | Use | Hibernate metadata impact |
|---|---|---|---|
@AssertFalse | Boolean, boolean | Checks that the annotated element is false | None |
@AssertTrue | Boolean, boolean | Checks that the annotated element is true | None |
@DecimalMax(value=, inclusive=) | BigDecimal, BigInteger, CharSequence, byte, short, int, long and the respective wrappers of the primitive types; Additionally supported by HV: any sub-type of Number | Checks whether the annotated value is less than the specified maximum, when inclusive=false. Otherwise whether the value is less than or equal to the specified maximum. The parameter value is the string representation of the max value according to the BigDecimal string representation. | None |
@DecimalMin(value=, inclusive=) | BigDecimal, BigInteger, CharSequence, byte, short, int, long and the respective wrappers of the primitive types; Additionally supported by HV: any sub-type of Number | Checks whether the annotated value is larger than the specified minimum, when inclusive=false. Otherwise whether the value is larger than or equal to the specified minimum. The parameter value is the string representation of the min value according to the BigDecimal string representation. | None |
@Digits(integer=, fraction=) | BigDecimal, BigInteger, CharSequence, byte, short, int, long and the respective wrappers of the primitive types; Additionally supported by HV: any sub-type of Number | Checks whether the annoted value is a number having up to integer digits and fraction fractional digits | Defines column precision and scale |
@Future | java.util.Date, supported by HV, if the Joda Time date/time API is on the class path: any implementations of ReadablePartial and ReadableInstant | Checks whether the annotated date is in the future | None |
@Max(value=) | BigDecimal, BigInteger, byte, short, int, long and the respective wrappers of the primitive types; Additionally supported by HV: any sub-type of CharSequence (the numeric value represented by the character sequence is evaluated), any sub-type of Number | Checks whether the annotated value is less than or equal to the specified maximum | Adds a check constraint on the column |
@Min(value=) | BigDecimal, BigInteger, byte, short, int, long and the respective wrappers of the primitive types; Additionally supported by HV: any sub-type of CharSequence (the numeric value represented by the char sequence is evaluated), any sub-type of Number | Checks whether the annotated value is higher than or equal to the specified minimum | Adds a check constraint on the column |
@NotNull | Any type | Checks that the annotated value is not null. | Column(s) are not nullable |
@Null | Any type | Checks that the annotated value is null | None |
@Past | java.util.Date, java.util.Calendar; Additionally date/time API is on the class path: any implementations of ReadablePartial and ReadableInstant | Checks whether the annotated date is in the past | None |
@Pattern(regex=, flag=) | CharSequence | Checks if the annotated string matches the regular expression regex considering the given flag match | None |
@Size(min=, max=) | CharSequence, Collection, Map and arrays | Checks if the annotated element's size is between min and max (inclusive) | Column length will be set to max |
@Valid | Any non-primitive type | Performs validation recursively on the associated object. If the object is a collection or an array, the elements are validated recursively. If the object is a map, the value elements are validated recursively. |
翻译是:
| Constraint | 详细信息 |
|---|---|
@Null | 被注释的元素必须为 null |
@NotNull | 被注释的元素必须不为 null |
@AssertTrue | 被注释的元素必须为 true |
@AssertFalse | 被注释的元素必须为 false |
@Min(value) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值 |
@Max(value) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值 |
@DecimalMin(value) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值 |
@DecimalMax(value) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值 |
@Size(max, min) | 被注释的元素的大小必须在指定的范围内 |
@Digits (integer, fraction) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须在可接受的范围内 |
@Past | 被注释的元素必须是一个过去的日期 |
@Future | 被注释的元素必须是一个将来的日期 |
@Pattern(value) | 被注释的元素必须符合指定的正则表达式 |
Apache BVal 提供额外的注解,在 org.apache.bval.constraints.* 下。
注入到 Spring
如果用 Apache BVal 结合 Spring 是怎么做的呢?首先在 MVC 的 xml 配置文件中加入以下:
<mvc:annotation-driven validator="validator"/>
<!-- 数据验证 Validator bean -->
<bean id="validator" class="org.springframework.validation.beanvalidation.LocalValidatorFactoryBean">
<property name="providerClass" value="org.apache.bval.jsr.ApacheValidationProvider" />
</bean>
<!-- // -->这是一种全局的配置方式,我们注入 Bval 的验证器,另外,还要让 MVC 打开注解驱动。加上了 <mvn:annotation-driven/> 之后 Spring 会自动检测 classpath 下的 JSR-303 提供者并自动启用对 JSR-303 的支持。然后就可以在 POJO 中添加注解,而且要在控制器中声明 bean 的验证,如下例的 @Valid T news,否则 Bval 不会起作用。
/**
* 新建
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String create(@Valid T news, BindingResult result,Model model) {
System.out.println("新建");
if (result.hasErrors()) {
LOGGER.info("create error!");
}else{
LOGGER.info("create ok!");
}
news.setService(getService());
try {
getService().create(news);
model.addAttribute("newlyId", news.getId());
} catch (ServiceException e) {
model.addAttribute("errMsg", e.toString());
}
return "common/entity/json_cud";
}一定要注意的是,控制器方法的参数顺序。Binding Result 必须在 Bean 后面。这是 Spring MVC 的约定。MVC 对控制器其他参数的顺序没什么规定,唯独这个 BindingResult 作了如此规定。目的是为了可以允许有多个 bean,于是也就有多个 BindingResult。
怎么处理错误就不详细说了,不同场景下要求不同。
自定义验证
可否自定义验证条件?我还没试,应该可以参考 Hibernate Validator 的做法。下面这篇文章说得很详细。
JSR 303 - Bean Validation 介绍及最佳实践
lk
调用 Apache BVal
07-18 补充如下:
可否脱离 Spring 运行?本身 BVal 就是一个独立的框架,因此答案不仅是可以的,而且非常简单。下面使用工厂和单例两种模式,返回一个校验器。
import javax.validation.Validation;
import javax.validation.Validator;
import javax.validation.ValidatorFactory;
import org.apache.bval.jsr.ApacheValidationProvider;
public enum MyValidatorFactory {
SINGLE_INSTANCE {
// BVal 与 JSR 接口结合,返回 ValidatorFactory 工厂
ValidatorFactory avf = Validation.byProvider(ApacheValidationProvider.class).configure().buildValidatorFactory();
@Override
public Validator getValidator() {
return avf.getValidator();
}
};
/**
* 返回一个校验器
* @return 校验器
*/
public abstract Validator getValidator();
}
这里一点技巧就是通过 Java 枚举来实现单例。
好了,拿一个 Bean 来测试下,分别有通过和报错两种情况的测试。
import java.util.Set;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import org.junit.*;
import javax.validation.ConstraintViolation;
import javax.validation.Validator;
import com.ajaxjs.framework.model.MyValidatorFactory;
import com.ajaxjs.framework.model.News;
public class TestValid {
@Test
public void testQuery() {
Validator v = MyValidatorFactory.SINGLE_INSTANCE.getValidator();
News news = new News();
news.setName("标题");
Set<ConstraintViolation<News>> result = v.validate(news);
assertTrue("应该通过校验", result.isEmpty());
News news2 = new News();
result = v.validate(news2);
assertTrue("应该不通过校验", !result.isEmpty());
System.out.println(result.size());
for(ConstraintViolation<News> r : result) {
System.out.println(r.getMessage());// 什么错?
System.out.println(r.getPropertyPath());// 哪个字段错?
}
}
}主要通过返回 ConstraintViolation 的 isEmpty() 方法来判断是否有错误。
另外可参考国人的开源实现:https://github.com/neoremind/fluent-validator
以上是关于数据验证框架 Apache BVal 简介的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章