二叉树的按行层序遍历及序列化和反序列化
Posted lshao
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了二叉树的按行层序遍历及序列化和反序列化相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.二叉树的序列化
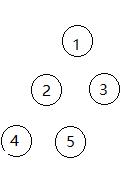
序列化:如图,按前序进行序列化可得到字符串1!2!3!4!-1!-1!5!-1!-1!3!-1!-1!,其中!表示一个值的结束,-1表示该节点为空。
反序列化:序列化的逆操作。
附代码
TreeNode* PreMakeTree(TreeNode* root,int value[]) { // ifsizeof(data)/sizeof(int) int e=value[k++]; if(e==-1) root=NULL; else{ root=(TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode)); root->val=e;; root->left=PreMakeTree(root->left,value); root->right=PreMakeTree(root->right,value); } return root; } void PreOrder(TreeNode* root) { if(root!=NULL) { printf("%d!",root->val); PreOrder(root->left); PreOrder(root->right); }else printf("-1!"); }
2.二叉树的分层遍历
1.维护last和nlast指针。
2.开始时last=root
3.队列每次入队更新nlast为当前入队结点
4.当current=last时,进行换行操作,同时更新为nlast
附代码
void LevelOrder1(TreeNode* root) { TreeNode* last; TreeNode* nlast; queue<TreeNode*> q; q.push(root); last=root; while(!q.empty()){ TreeNode* current=q.front(); q.pop(); printf("%d ",current->val); if(current->left!=NULL) { q.push(current->left); nlast=current->left; } if(current->right!=NULL) { q.push(current->right); nlast=current->right; } if(current==last) { printf("\\n"); last=nlast; } } }
以上是关于二叉树的按行层序遍历及序列化和反序列化的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章